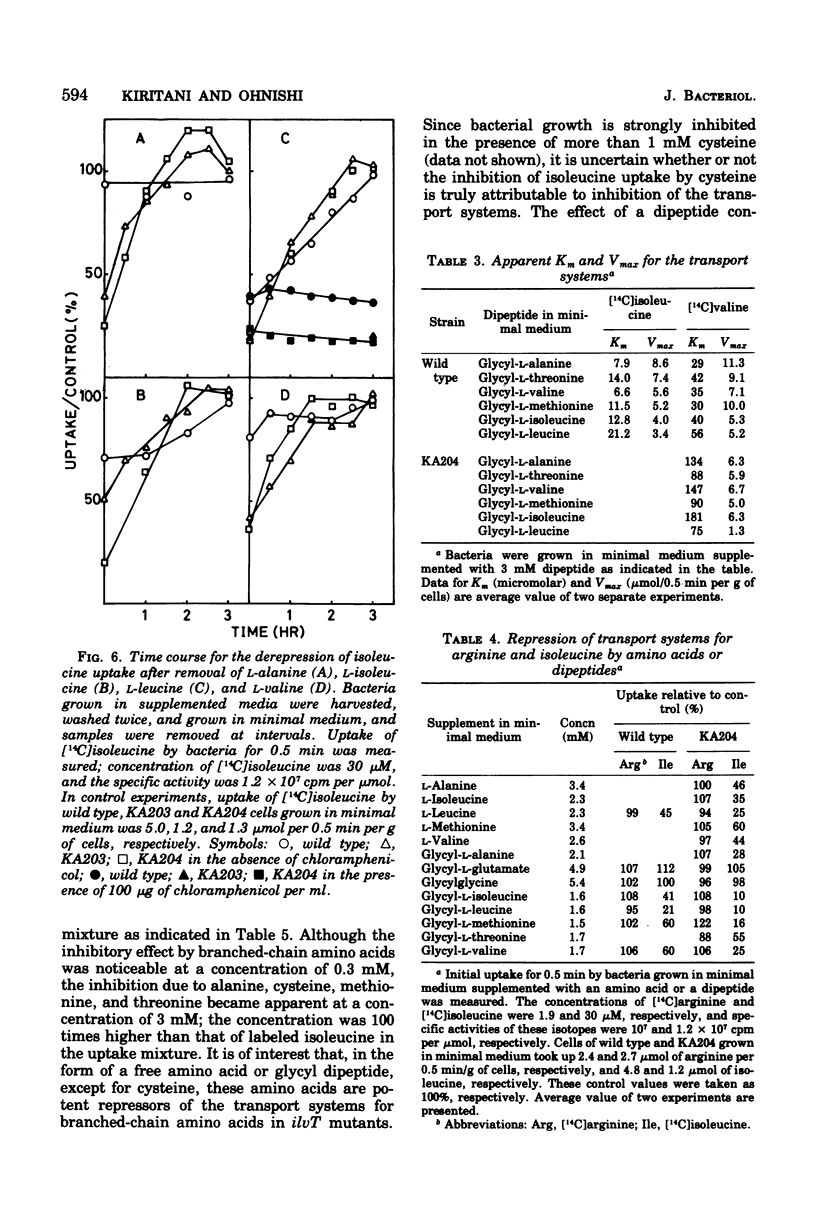
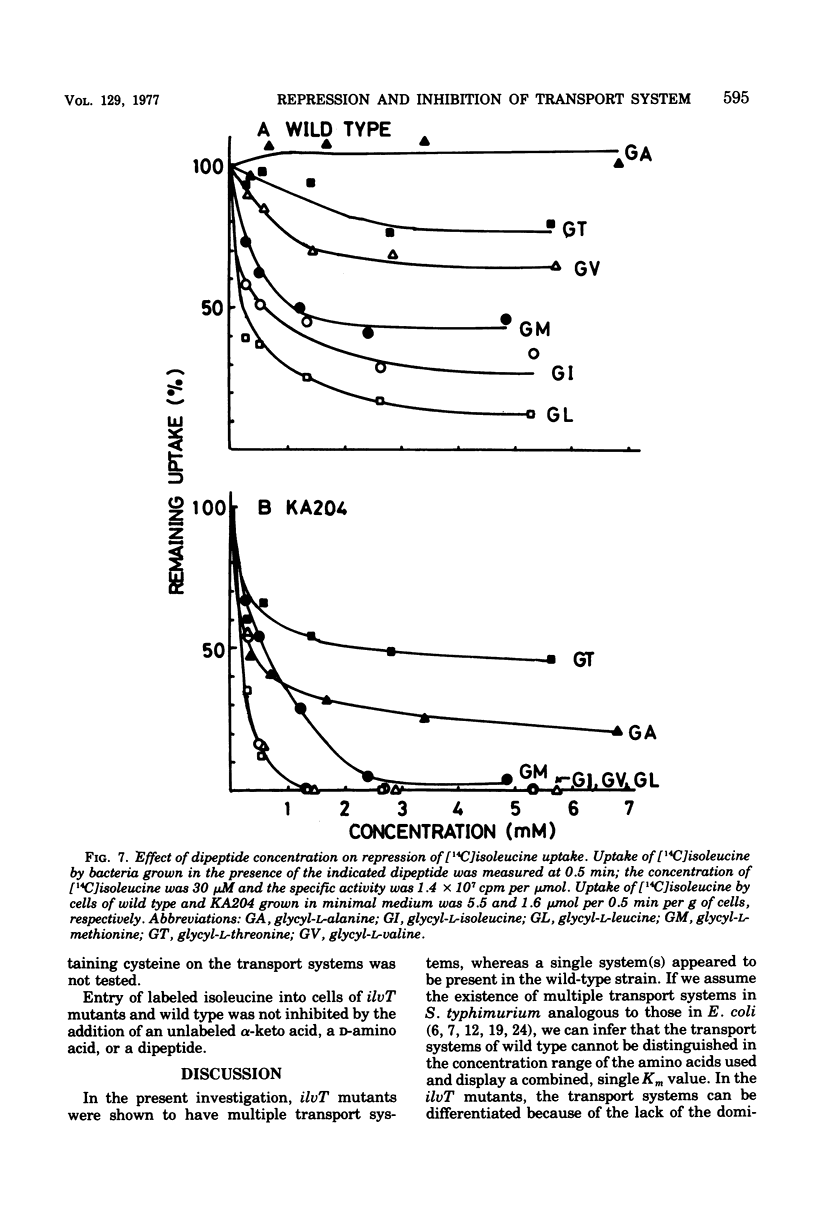
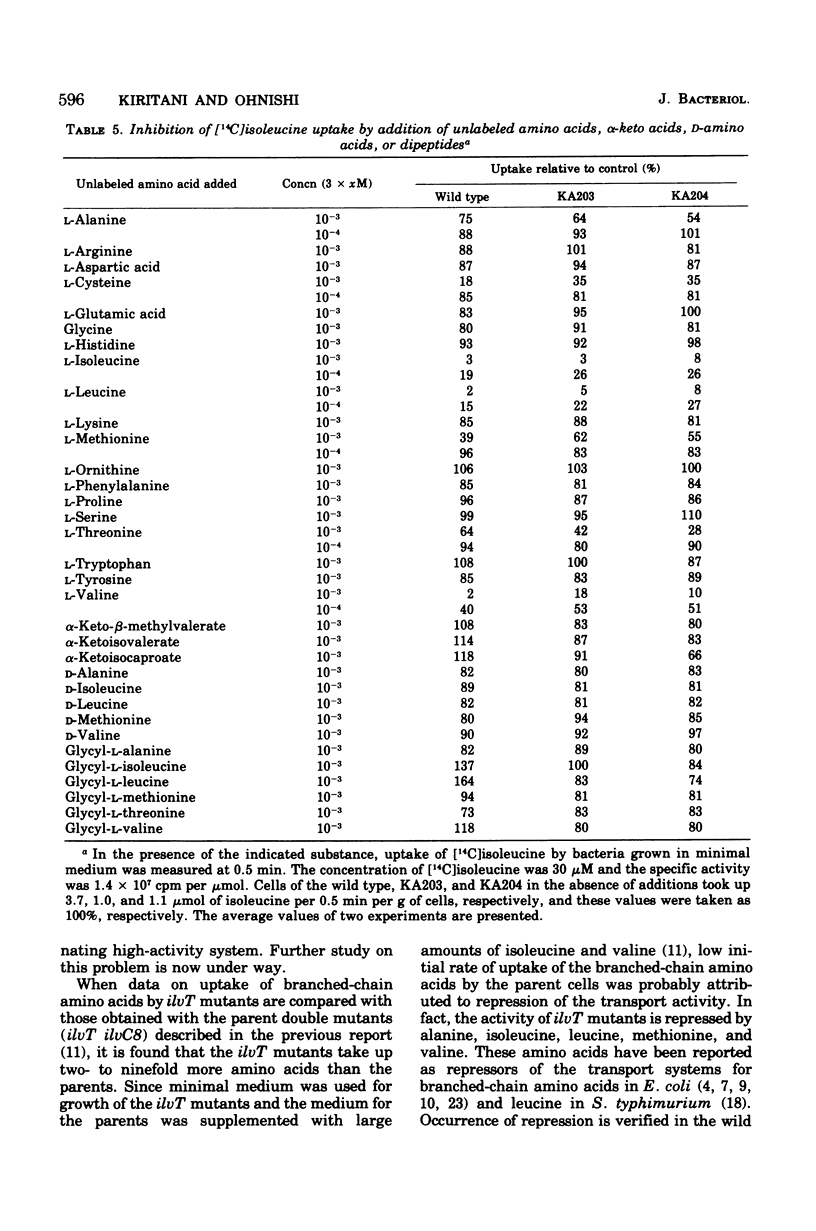
Abstract
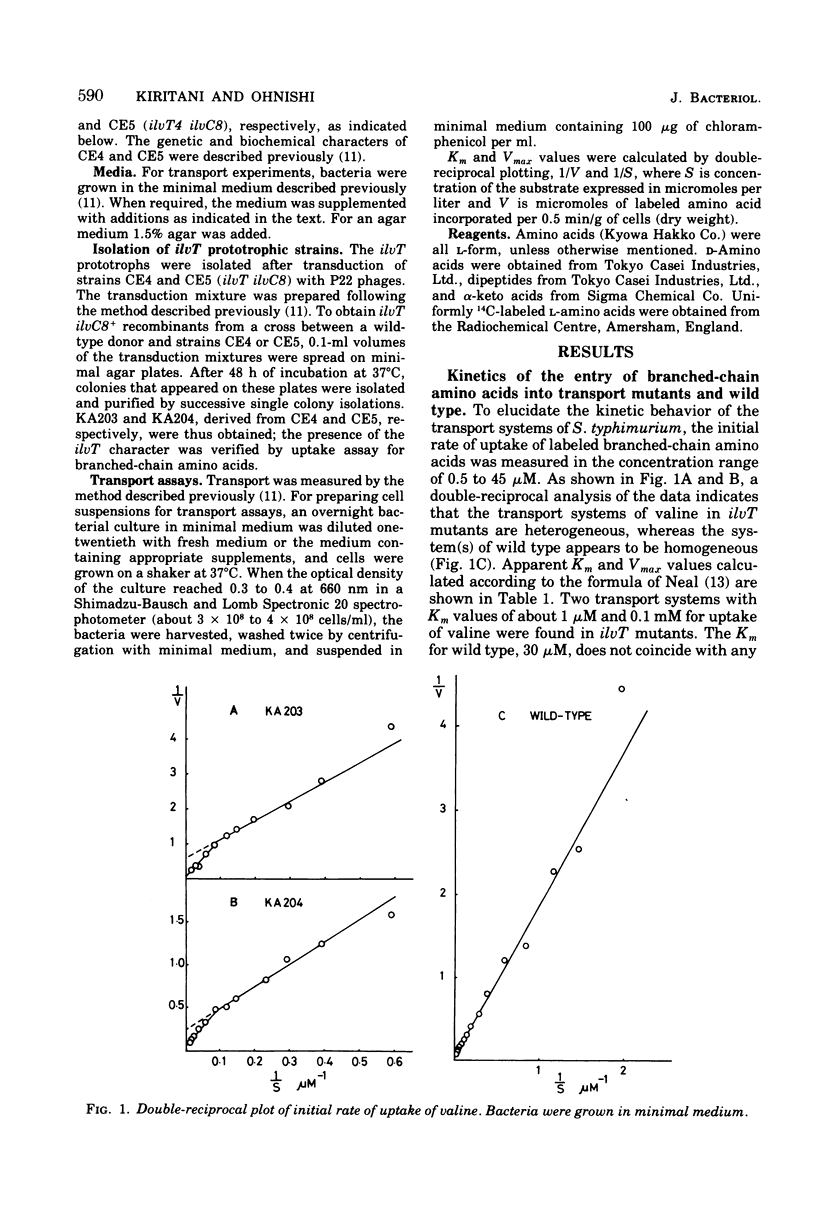
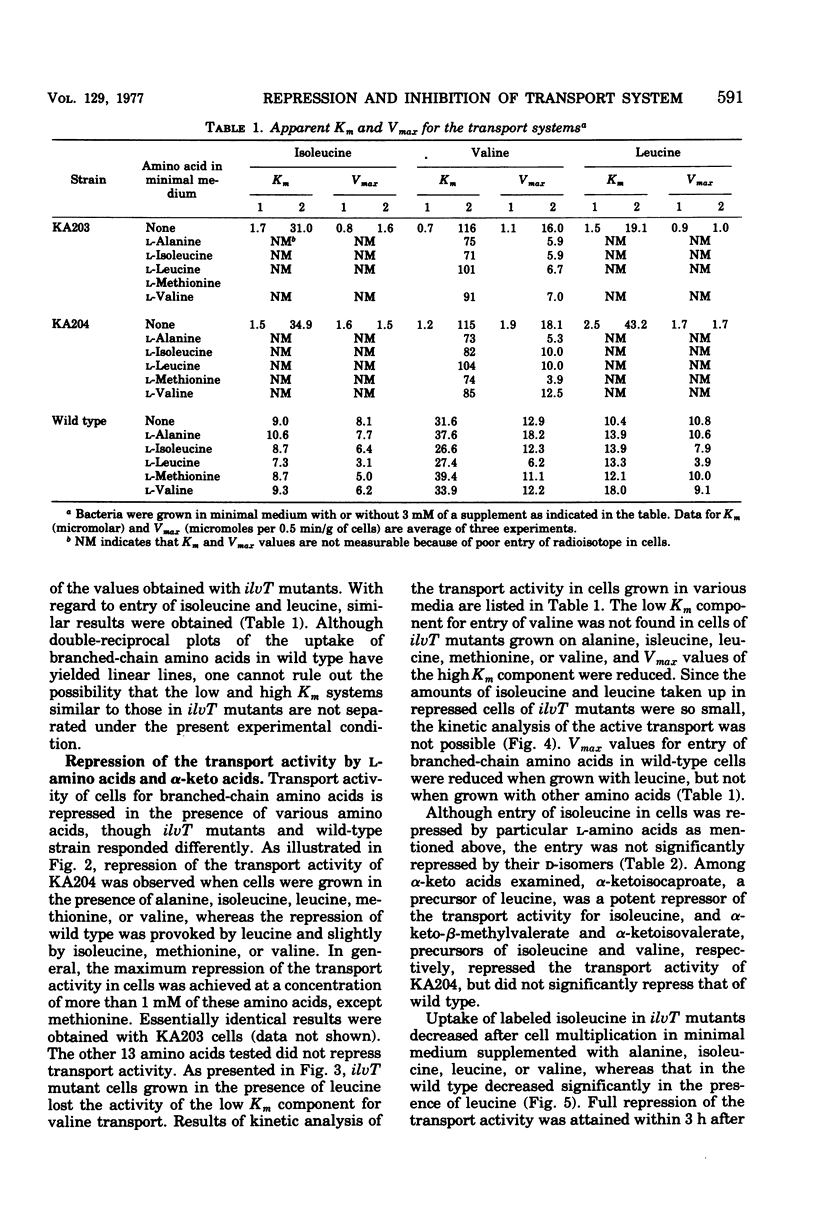
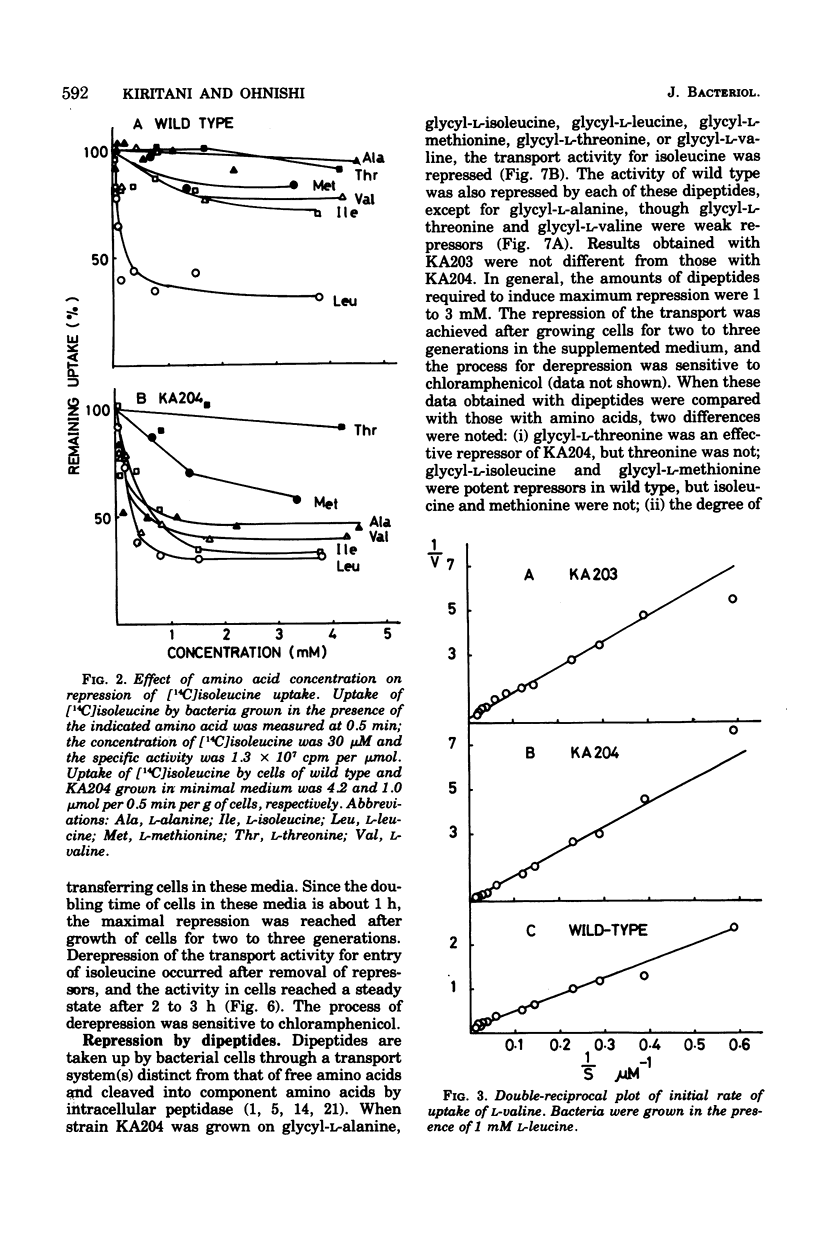
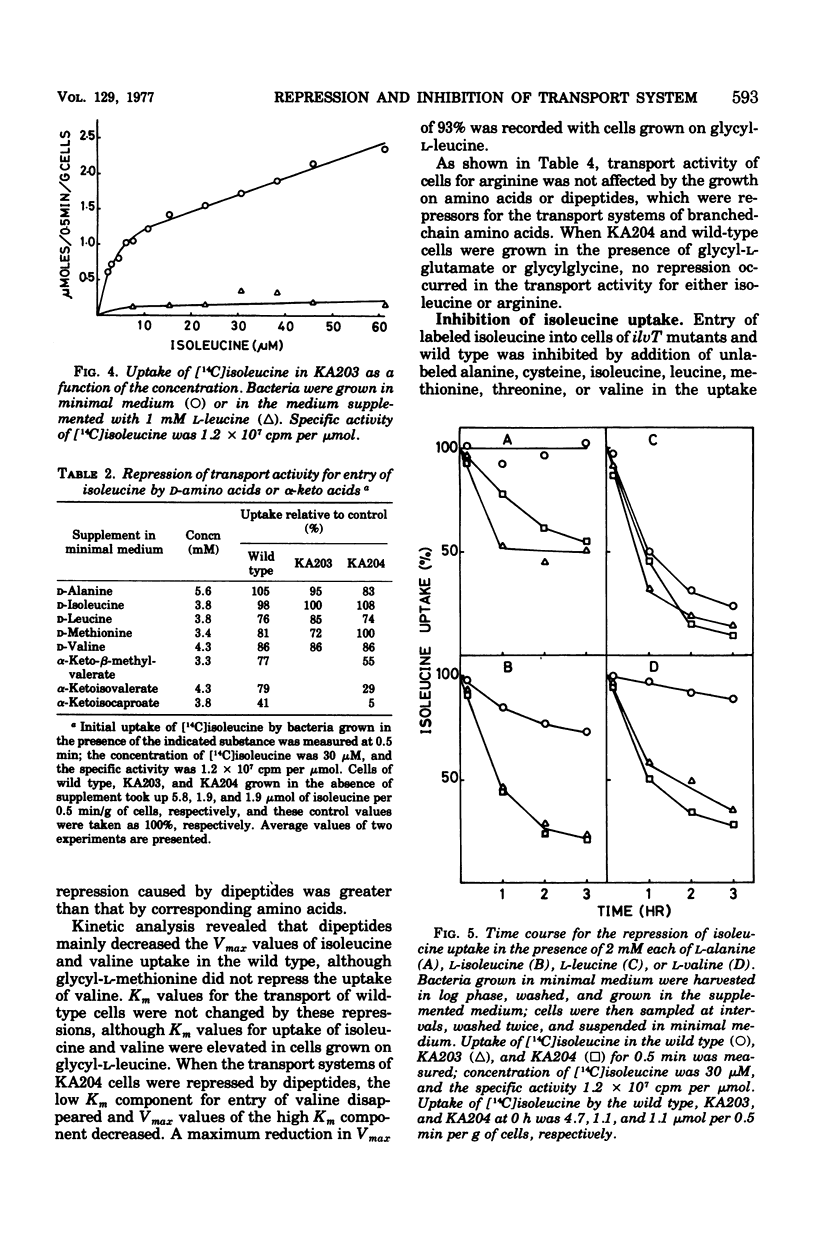
Kinetics of the transport systems common for entry of L-isoleucine, L-leucine, and L-valine in Salmonella typhimurium LT2 have been analyzed as a function of substrateconcentration in the range of 0.5 to 45 muM. The systems of transport mutants, KA203 (ilvT3) and KA204 (ilvT4), are composed of two components; apparent Km values for uptake of isoleucine, leucine, and valine by the low Km component are 2 muM, 2 to 3 muM, and 1 muM, respectively, and by the high Km component 30 muM, 20 to 40 muM, and 0.1 mM, respectively. The transport system(s) of the wild type has not been separated into components but rather displays single Km values of 9 muM for isoleucine, 10 muM for leucine, and 30 muM for valine. The transport activity of the wild type was repressed by L-leucine, alpha ketoisocaproate, glycyl-L-isoleucine, glycyl-L-leucine, and glycyl-L-methionine. That for the transport mutants was repressed by L-alanine, L-isoleucine, L-methionine, L-valine, alpha-ketoisovalerate, alpha-keto-beta-methylvalerate, glycyl-L-alanine, glycyl-L-threonine, and glycyl-L-valine, in addition to the compounds described above. Repression of the mutant transport systems resulted in disappearance of the low Km component for valine uptake, together with a decrease in Vmax of the high Km component; the kinetic analysis with isoleucine and leucine as substrates was not possible because of poor uptake. The maximum reduction of the transport activity for isoleucine was obtained after growing cells for two to three generations in a medium supplemented with repressor, and for the depression, protein synthesis was essential after removal of the repressor. The transport activity for labeled isoleucine in the transport mutant and wild-type strains was inhibited by unlabeled L-alanine, L-cysteine, L-isoleucine, L-leucine, L-methionine, L-threonine, and L-valine. D-Amino acids neither repressed nor inhibited the transport activity of cells for entry of isoleucine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. J., Quay S. C., Oxender D. L. Mapping of two loci affecting the regulation of branched-chain amino acid transport in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):80–90. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.80-90.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anraku Y., Naraki T., Kanzaki S. Transport of sugars and amino acids in bacteria. VI. Changes induced by valine in the branched chain amino acid transport systems of Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1973 Jun;73(6):1149–1161. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anraku Y. Transport of sugars and amino acids in bacteria. 3. Studies on the restoration of active transport. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3128–3135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Felice M., Guardiola J., Lamberti A., Iaccarino M. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants altered in the transport systems for oligo- and dipeptides. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):751–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.751-756.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong C. E., Weiner J. H. Purification of a leucine-specific binding protein from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 27;38(6):1076–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guardiola J., De Felice M., Klopotowski T., Iaccarino M. Multiplicity of isoleucine, leucine, and valine transport systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):382–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.382-392.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guardiola J., De Felice M., Klopotowski T., Iaccarino M. Mutations affecting the different transport systems for isoleucine, leucine, and valine in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):393–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.393-405.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INUI Y., AKEDO H. AMINO ACID UPTAKE BY ESCHERICHIA COLI GROWN IN PRESENCE OF AMINO ACIDS. EVIDENCE FOR REPRESSIBILITY OF AMINO ACID UPTAKE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 25;94:143–152. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanzaki S., Anraku Y. Transport of sugars and amino acids in bacteria. IV. Regulation of valine transport activity by valine and cysteine. J Biochem. 1971 Aug;70(2):215–224. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiritani K. Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium defective in transport of branched-chain amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1093–1101. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1093-1101.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi F. J., Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. 8. The transport of amino acids by membranes prepared from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):7844–7857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal J. L. Analysis of Michaelis kinetics for two independent, saturable membrane transport functions. J Theor Biol. 1972 Apr;35(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(72)90196-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penrose W. R., Nichoalds G. E., Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Purification and properties of a leucine-binding protein from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5921–5928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Amino acid transport systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5914–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quay S. C., Kline E. L., Oxender D. L. Role of leucyl-tRNA synthetase in regulation of branched-chain amino-acid transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3921–3924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quay S. C., Oxender D. L., Tsuyumu S., Umbarger H. E. Separate regulation of transport and biosynthesis of leucine, isoleucine, and valine in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):994–1000. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.994-1000.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmanian M., Claus D. R., Oxender D. L. Multiplicity of leucine transport systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1258–1266. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1258-1266.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. C., Oxender D. L. Transport systems for alanine, serine, and glycine in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):12–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.12-18.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman A. J., Gilvarg C. Peptide transport and metabolism in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:397–408. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton B. A., Savageau M. A. Transport of biosynthetic intermediates: homoserine and threonine uptake in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1002–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1002-1009.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton B. A., Savageau M. A. Transport of biosynthetic intermediates: regulation of homoserine and threonine uptake in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):114–120. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.114-120.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. M. Leucine transport in Escherichia coli. The resolution of multiple transport systems and their coupling to metabolic energy. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4477–4485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



