Abstract
A study of the distribution of pyrrolidone carboxylyl peptidase (PCP) activity among cell fractions of Streptococcus cremoris HP revealed that this enzyme is associated with a particulate fraction, which mainly consists of membrane material. This location could only be established using a gentle nonmechanical method for the disruption of spheroplasts under the conditions of which intracellular marker enzymes are released. The effect of monovalent anions and treatments, which do not destroy covalent binding, suggests an association of the enzyme with surrounding structures determined by both hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions. The activity of PCP associated with cells harvested from different growth phases and in the solubilized state was studied as a function of the temperature in the absence and in the presence of the membrane-interfering agent n-butanol. A decrease in the apparent activation energy, inherent to the solubilized enzyme, is induced in situ at a lower transition temperature. Only with logarithmic-phase cells is this transition followed (mid-logarithmic cells) or accompanied (late logarithmic cells) by a secondary decrease in the energy of activation. n-Butanol appeared to decrease the lower transition temperature of the enzyme activity in situ, and additionally it exerted an effect on the manifestation of the secondary transition. Thecorganization of membrane components, mainly the lipids.
Full text
PDF

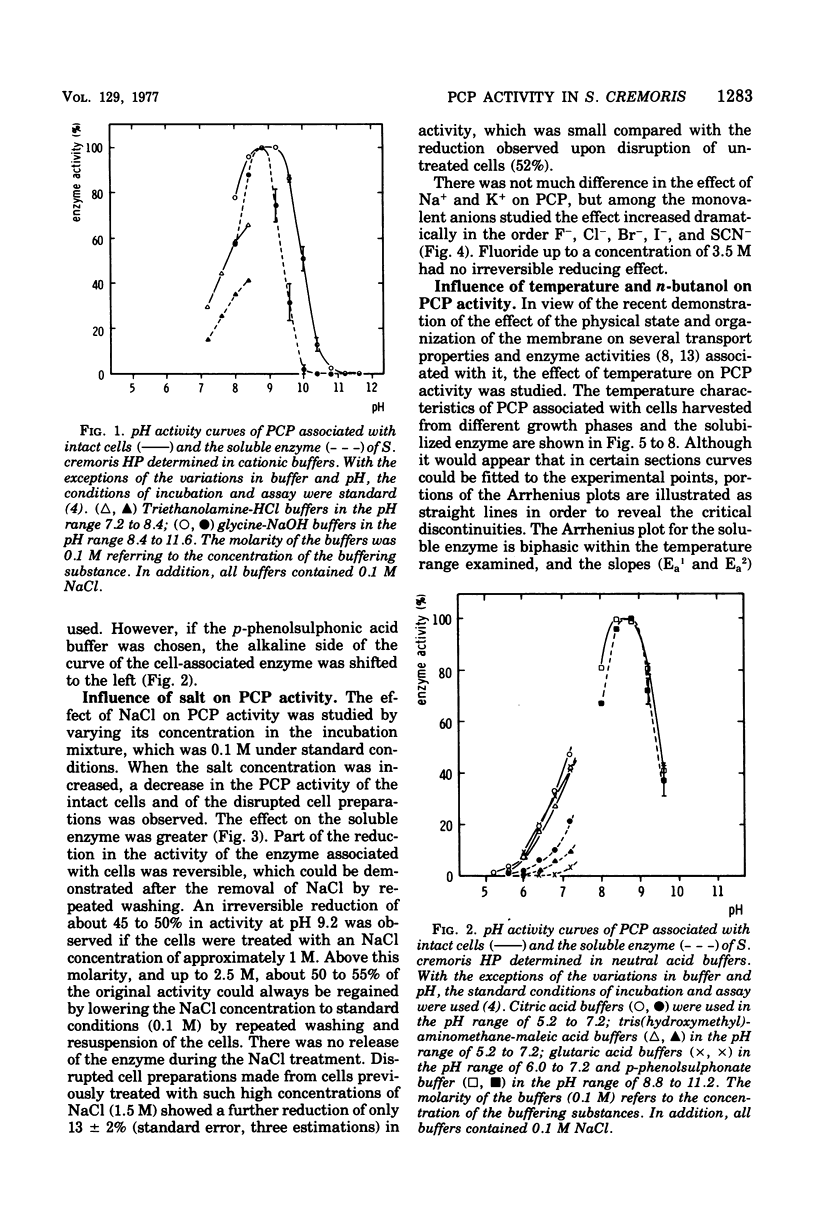
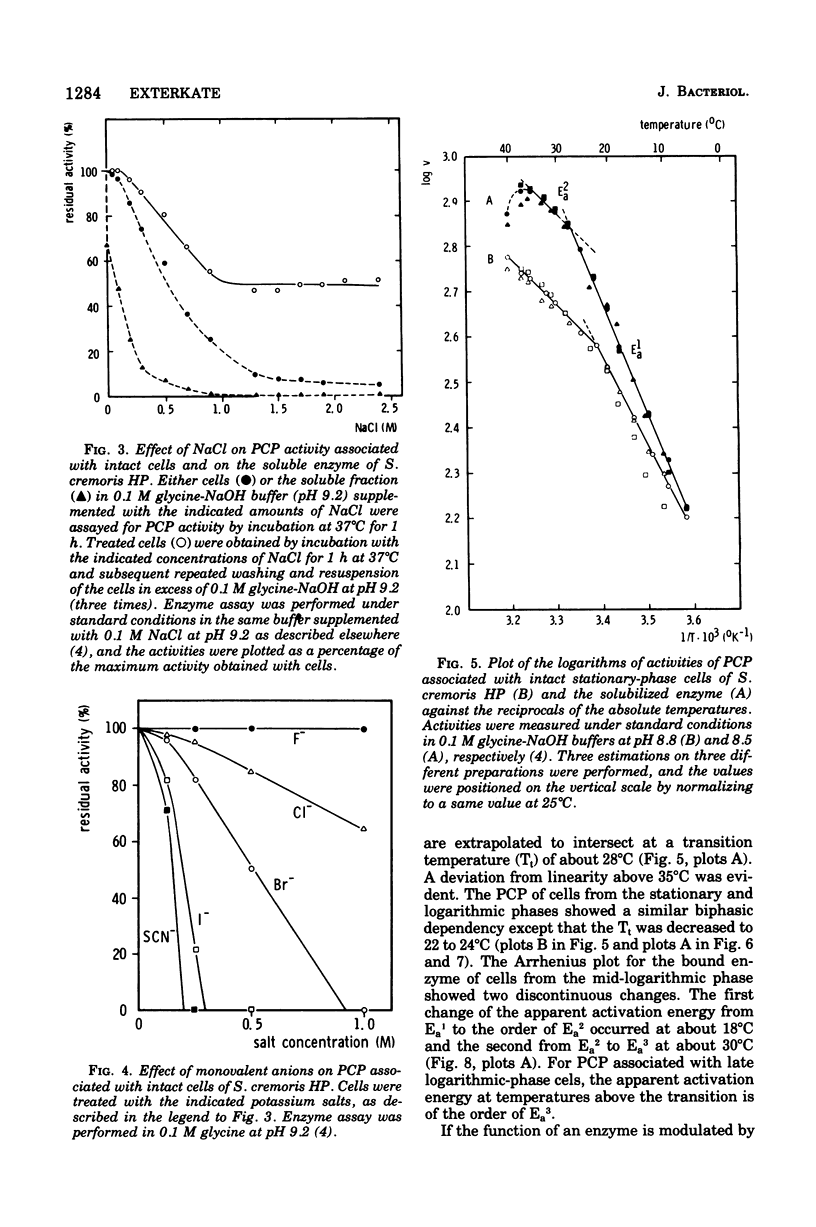
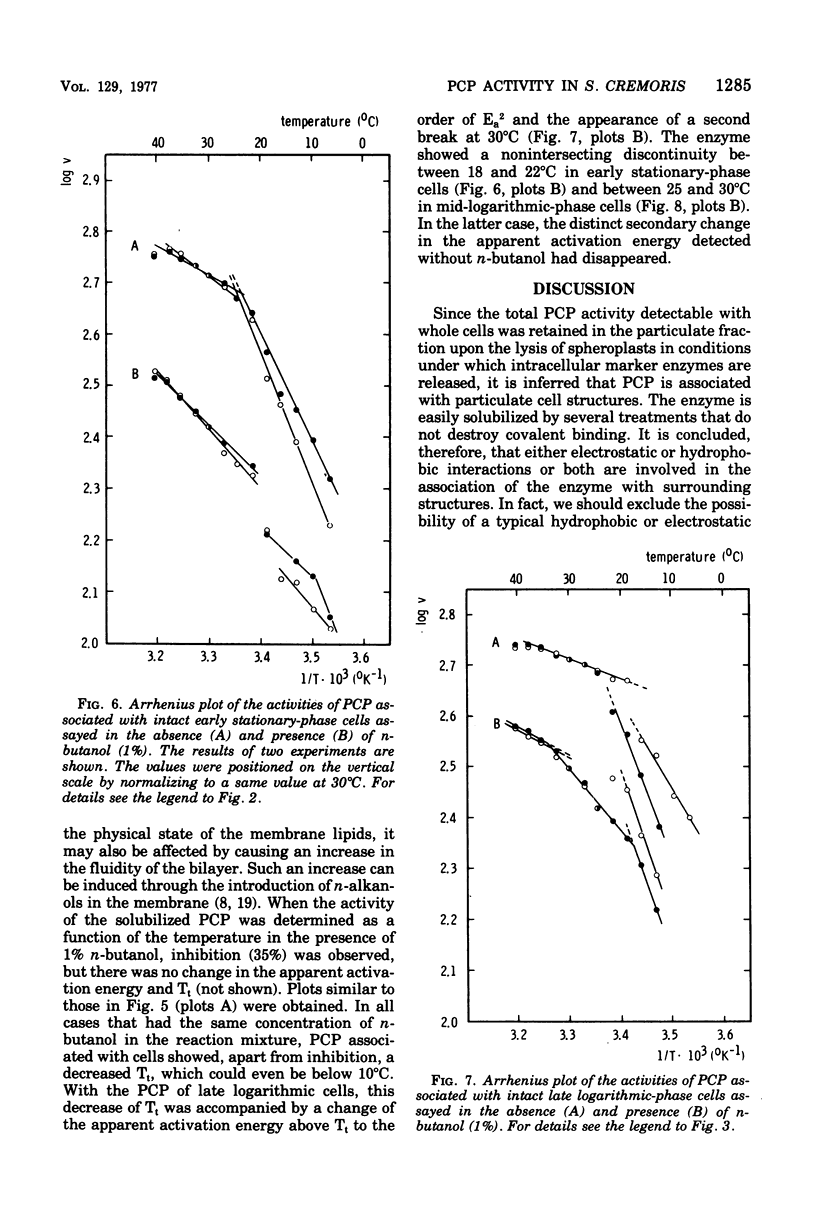
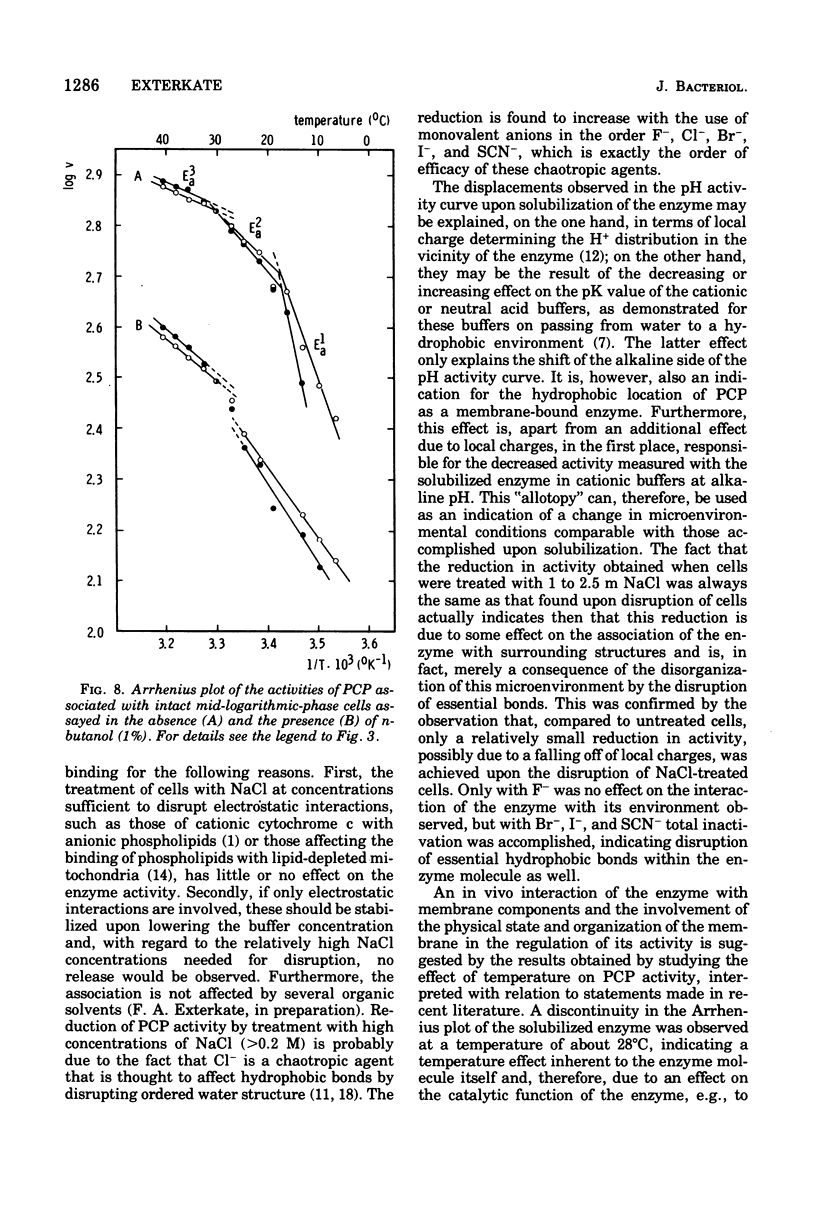


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAS M. L., CRANE F. L. PROTEOLIPIDS. I. FORMATION OF PHOSPHOLIPID-CYTOCHROME C COMPLEXES. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:696–700. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Armentrout R. W. Pyrrolidonyl peptidase. An enzyme for selective removal of pyrrolidonecarboxylic acid residues from polypeptides. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):516–521. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eletr S., Zakim D., Vessey D. A. A spin-label study of the role of phospholipids in the regulation of membrane-bound microsomal enzymes. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 5;78(2):351–362. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A. A modified colorimetric method for the determination of pyrrolidone carboxylyl peptidase activity in bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1973 May;53(1):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90440-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay D., Mathias A. P., Rabin B. R. The active site and mechanism of action of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. 5. The charge types at the active centre. Biochem J. 1962 Oct;85(1):139–144. doi: 10.1042/bj0850139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourcans B., Jain M. K. Role of phospholipids in transport and enzymic reactions. Adv Lipid Res. 1974;12(0):147–226. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024912-1.50011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinna L. S. Multiple thermal discontinuities in glucose-6-phosphatase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 22;403(2):388–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatefi Y., Hanstein W. G. Solubilization of particulate proteins and nonelectrolytes by chaotropic agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1129–1136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Papahadjopoulos D. Phospholipid requirements for (Na + + K + )-ATPase activity: head-group specificity and fatty acid fluidity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 1;282(1):277–292. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenaz G. Discussion paper: studies on the organization of proteins and lipids in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Jun 20;195:39–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrisett J. D., Pownall H. J., Plumlee R. T., Smith L. C., Zehner Z. E. Multiple thermotropic phase transitions in Escherichia coli membranes and membrane lipids. A comparison of results obtained by nitroxyl stearate paramagnetic resonance, pyrene excimer fluorescence, and enzyme activity measurements. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6969–6976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulczyk M., Szewczuk A. Pyrrolidonyl peptidase in bacteria: a new colorimetric test for differentiation of enterobacteriaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Apr;61(1):9–13. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Träuble H. Phase transitions in cells, membranes, and lipids of Escherichia coli. Detection by fluorescent probes, light scattering, and dilatometry. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2625–2634. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. H., Jain M. K., Koch A. L. Activation of the beta-galactoside transport system in Escherichia coli ML-308 by n-alkanols. Modification of lipid-protein interaction by a change in bilayer fluidity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczuk A., Kwiatkowska J. Pyrrolidonyl peptidase in animal, plant and human tissues. Occurrence and some properties of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jul;15(1):92–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczuk A., Mulczyk M. Pyrrolidonyl peptidase in bacteria. The enzyme from Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(1):63–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uliana J. A., Doolittle R. F. Pyrrolidonecarboxylyl peptidase: studies on the specificity of the enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 May;131(2):561–565. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90430-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilschut J. C., Scherphof G. L. The effect of partial degradation of mitochondrial phospholipids by phospholipase A on the temperature dependence of succinate-cytochrome c reductase and cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90296-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisnieski B. J., Parkes J. G., Huang Y. O., Fox C. F. Physical and physiological evidence for two phase transitions in cytoplasmic membranes of animal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



