Abstract
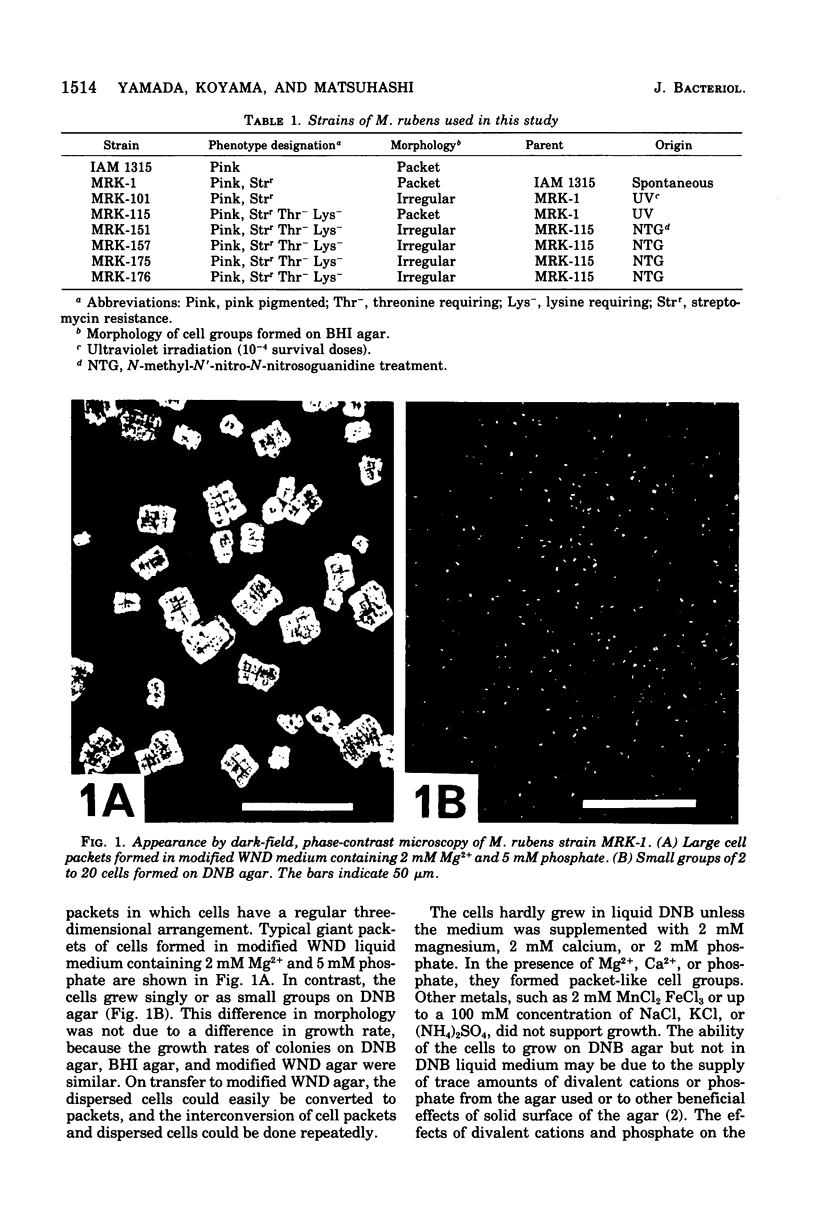
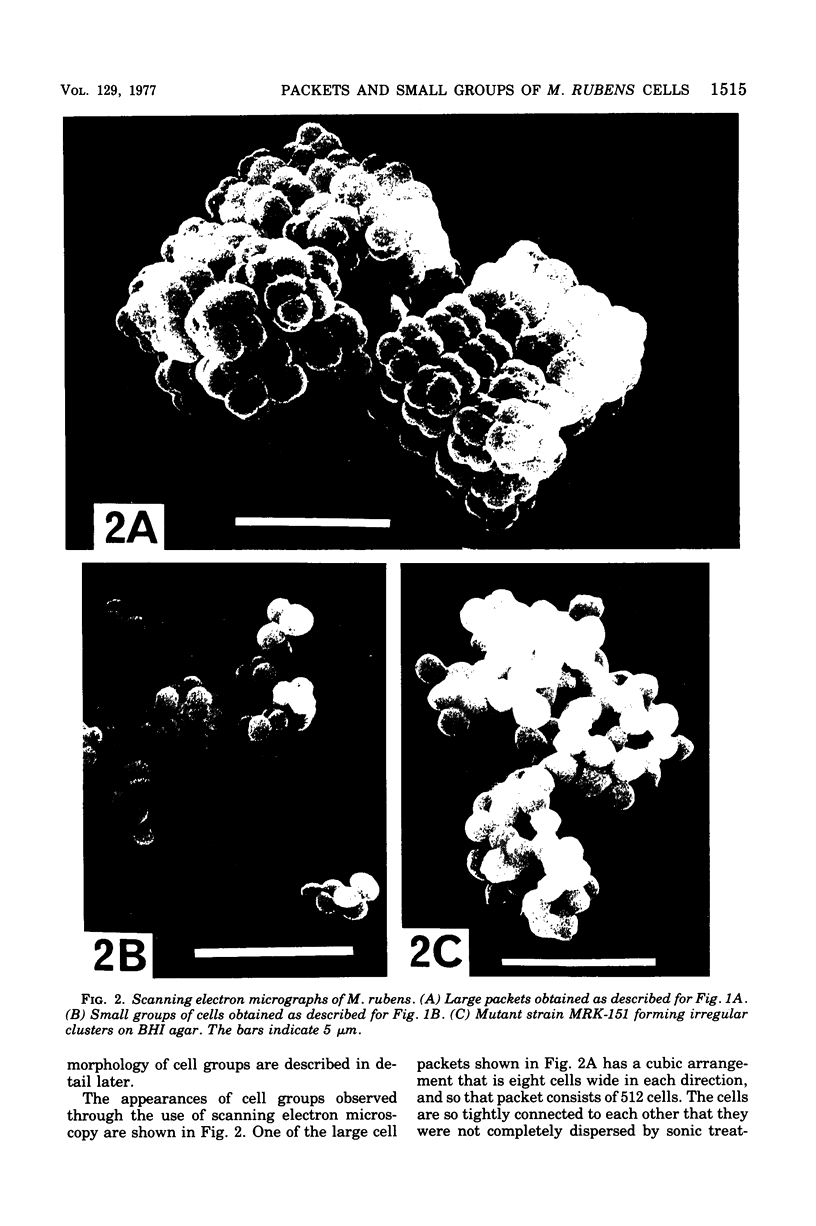
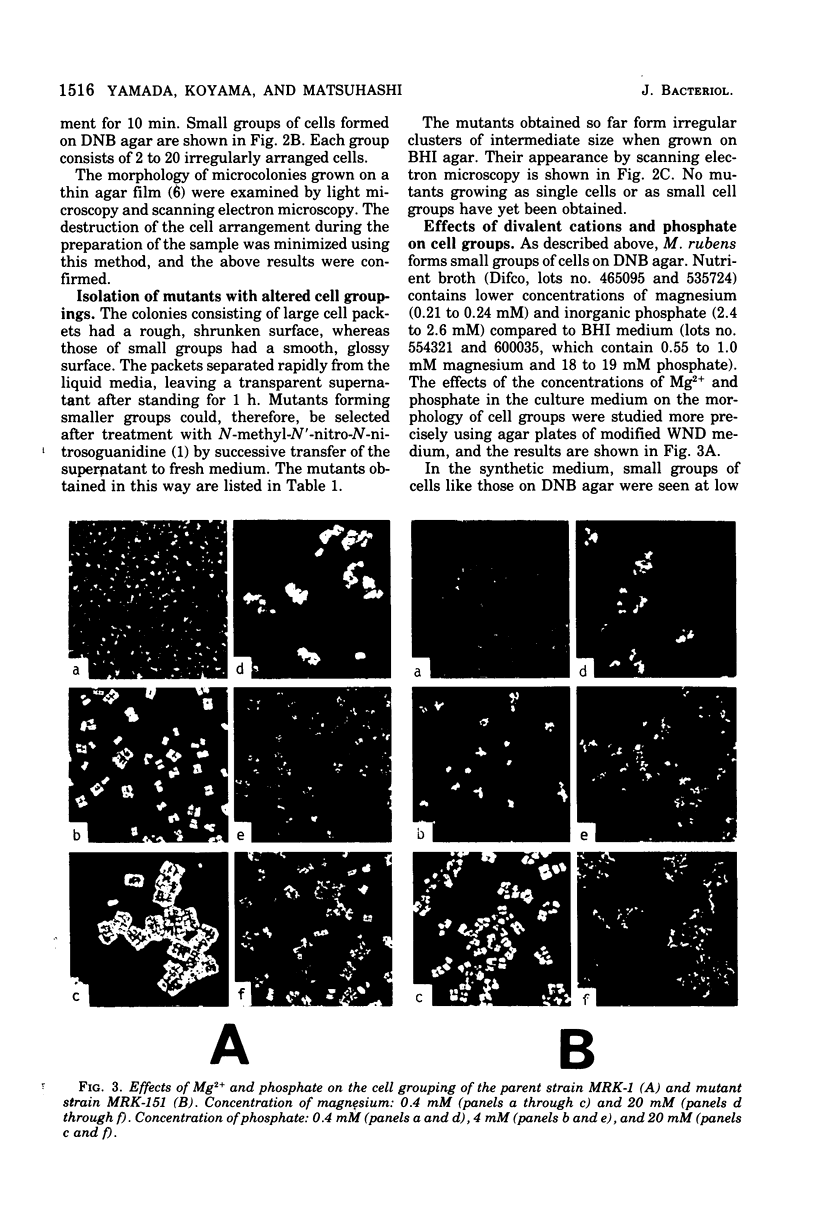
Micrococcus rubens, a gram-positive occus, usually forms large, cubic packets of more than 500 cells that are regularly arranged in three-dimensional cell groups. In medium with extremely low concentration of Mg2+ and phosphate, in which the cells can only grow on a agar surface, it formed small groups of 2 to 20 cells. Irregularly arraged cell groups of intermediated size were obtained in culture media containing intermediated concentrations of Mg2+ and phosphate. Mutants that formed irregular cell groups of intermediate size under normal culture conditions were also obtained.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- WOLIN H. L., NAYLOR H. B. Basic nutritional requirements of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):163–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.163-167.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Hirose A., Matsuhashi M. Association of lack of cell wall teichuronic acid with formation of cell packets of Micrococcus lysodeikticus (luteus) mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):678–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.678-686.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]