Abstract
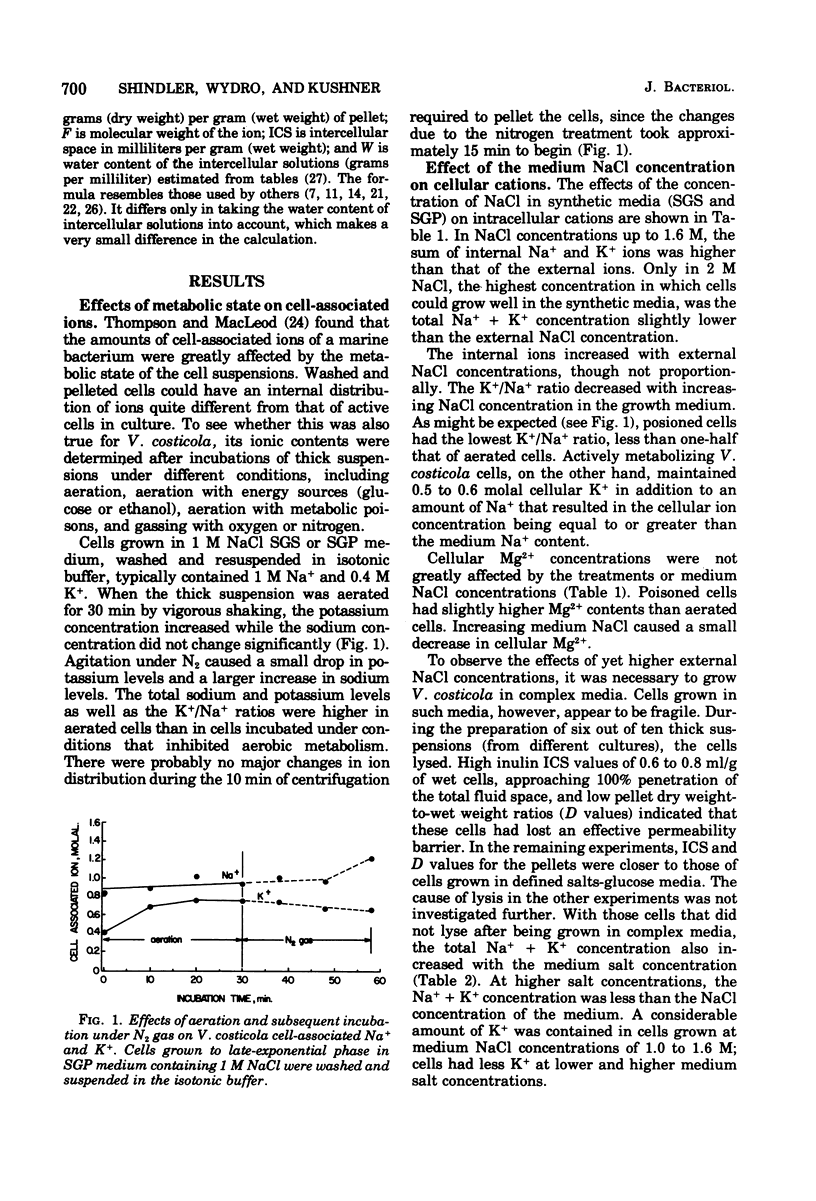
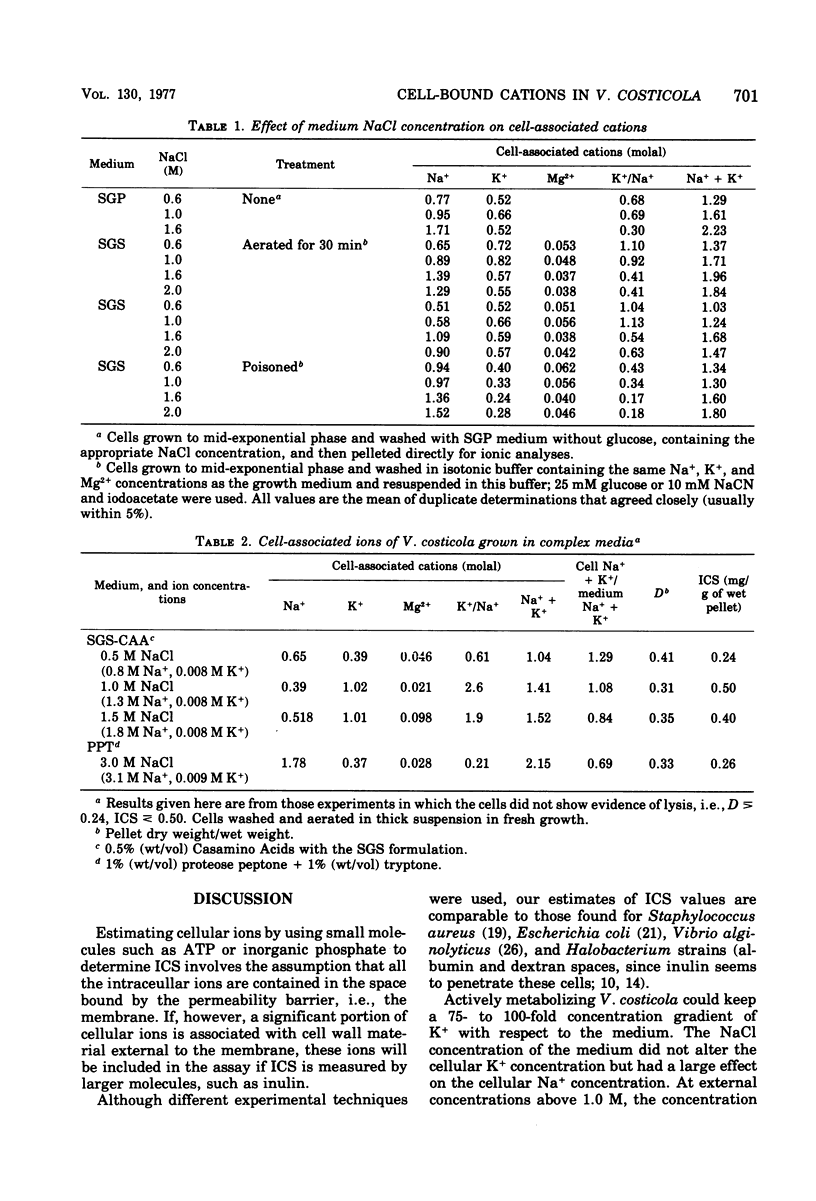
Over most of the range of salt concentrations in which the moderately halophilic bacterium Vibrio costicola could grow, the sum of the cell-associated Na+ + K+ ions was at least as high as in the external medium. This is in contrast to other moderate halophiles, which have substantially lower internal than external salt concentrations for most of their growth range. The relative amounts of Na+ and K+ in V. costicola varied with environmental conditions. The K+/Na+ ratio fell during anaerobic incubation or when cells were poisoned. As Na+ ions left the cells, K+ ions entered. However, movement of these ions was not tightly coupled, since K+ content of cells could increase without a corresponding decrease in Na+ content. The Mg2+ contents of cells varied little with environmental conditions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN A. D. ASPECTS OF BACTERIAL RESPONSE TO THE IONIC ENVIRONMENT. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:296–329. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.296-329.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Uptake and retention of metals by cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1502–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1502-1518.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D. Microbial water stress. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):803–846. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.803-846.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Penetrability of a marine pseudomonad by inulin, sucrose, and glycerol and its relation to the mechanism of lysis. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Feb;16(2):75–81. doi: 10.1139/m70-014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., INGRAM M. The freezing points of bacterial cells in relation to halophilism. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Feb;20(1):27–31. doi: 10.1099/00221287-20-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:506–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman G. Nature of the major inorganic ions concentrated during growth of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Oct;84(2):297–302. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-2-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth M. P., Kushner D. J. Nutrition and distribution of salt response in populations of moderately halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Apr;16(4):253–261. doi: 10.1139/m70-047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg M., Sachs L., Ginzburg B. Z. Ion metabolism in a Halobacterium. I. Influence of age of culture on intracellular concentrations. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Feb;55(2):187–207. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg M. The unusual membrane permeability of two halophilic unicellular organisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr;173(3):370–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gochnauer M. B., Kushner D. J. Potassium binding, growth, and survival of an extremely halophilic bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Jan;17(1):17–23. doi: 10.1139/m71-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Silverman M. P. The state of binding of intracellular K + in Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jul;18(7):993–995. doi: 10.1139/m72-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Transport of phosphate across the surface of Micrococcus pyogenes; nature of the cell inorganic phosphate. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Oct;9(2):273–287. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui M., Wada S. Intracellular concentrations of Na+, K+, and cl minus of a moderately halophilic bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Oct;19(10):1181–1186. doi: 10.1139/m73-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson A. T., Sprott G. D., McDonald I. J., Tessier H. Some properties of an unidentified halophile: growth characteristics, internal salt concentration, and morphology. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jun;22(6):780–786. doi: 10.1139/m76-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Measures J. C. Role of amino acids in osmoregulation of non-halophilic bacteria. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):398–400. doi: 10.1038/257398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., SOLOMON A. K. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. I. Intracellular Na and K concentrations and net cation movement. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Nov;45:355–369. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKACS F. P., MATULA T. I., MACLEOD R. A. NUTRITION AND METABOLISM OF MARINE BACTERIA. XIII. INTRACELLULAR CONCENTRATIONS OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM IONS IN A MARINE PSEUDOMONAD. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:510–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.510-518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Meers J. L. The influence of NaCl concentration of the medium on the potassium content of Aerobacter aerogenes and on the inter-relationships between potassium, magnesium and ribonucleic acid in the growing bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):319–325. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Functions of Na+ and K+ in the active transport of -aminoisobutyric acid in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):4066–4074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Na+ and K+ gradients and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7106–7111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemoto T., Tsuruoka T., Hayashi M. Role of Na + and K + in preventing lysis of a slightly halophilic Vibrio alginolyticus. Can J Microbiol. 1973 May;19(5):563–571. doi: 10.1139/m73-093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wydro R., Kogut M., Kushner D. J. Salt response of ribosomes of a moderately halophilic bacterium. FEBS Lett. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):210–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80453-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


