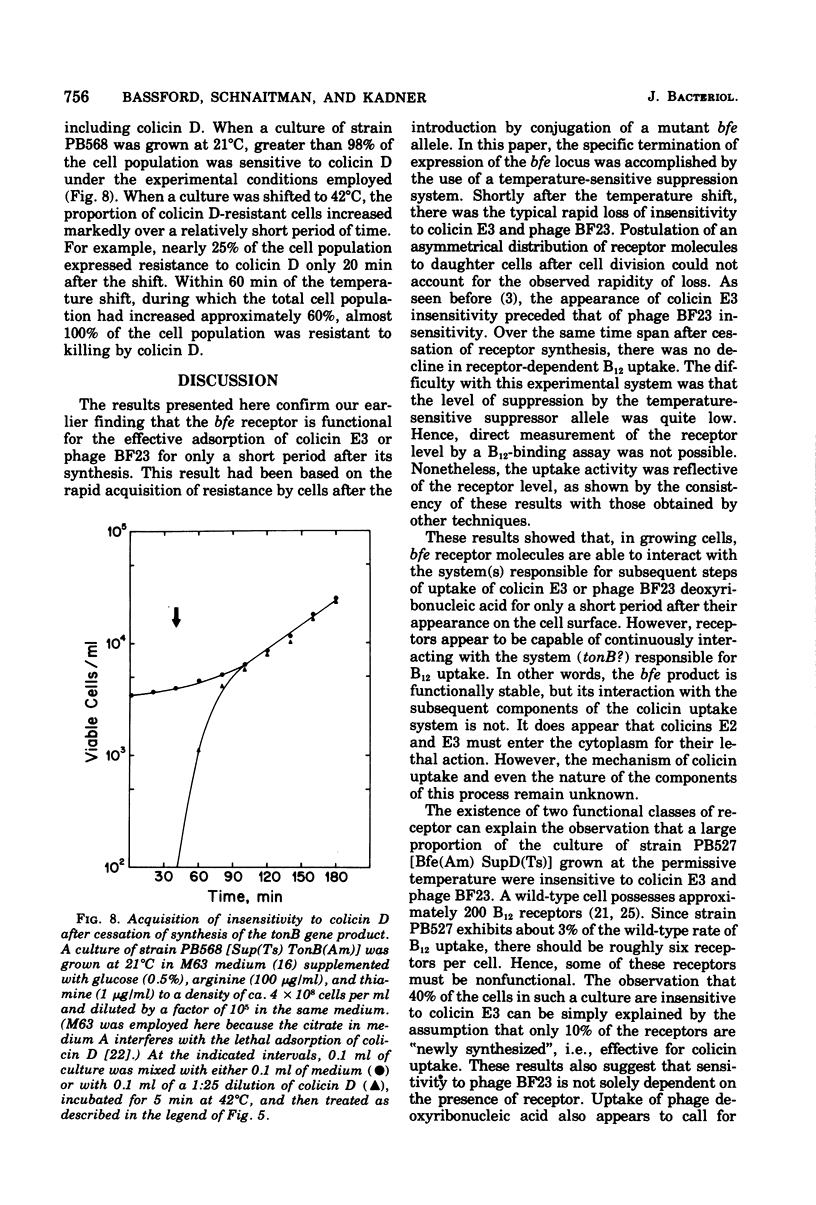
Abstract
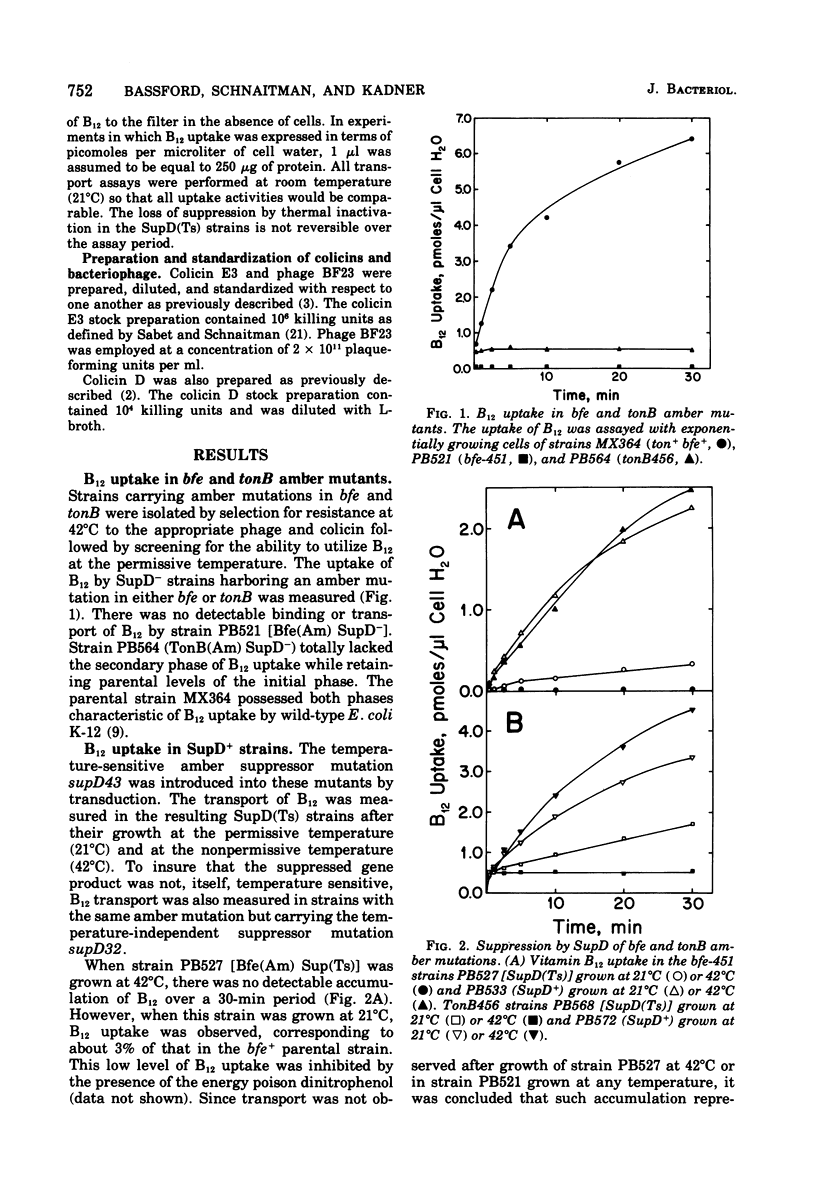
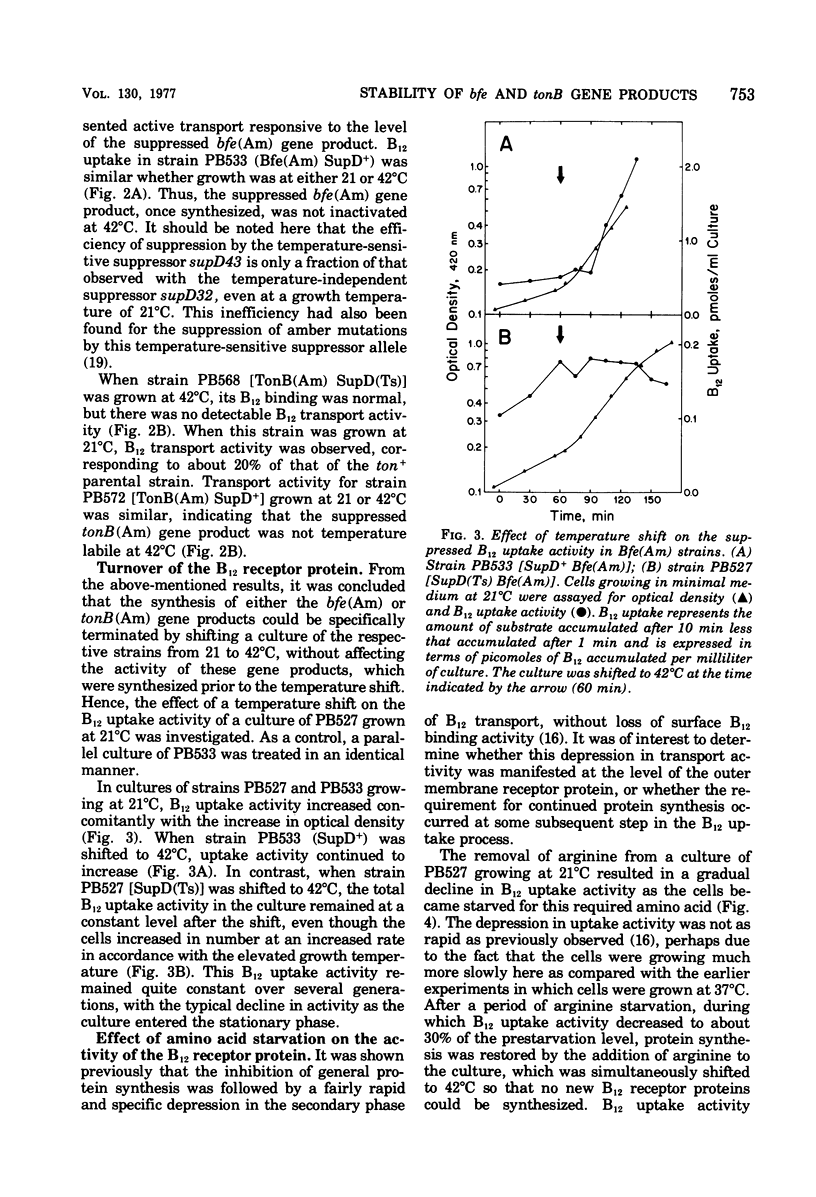
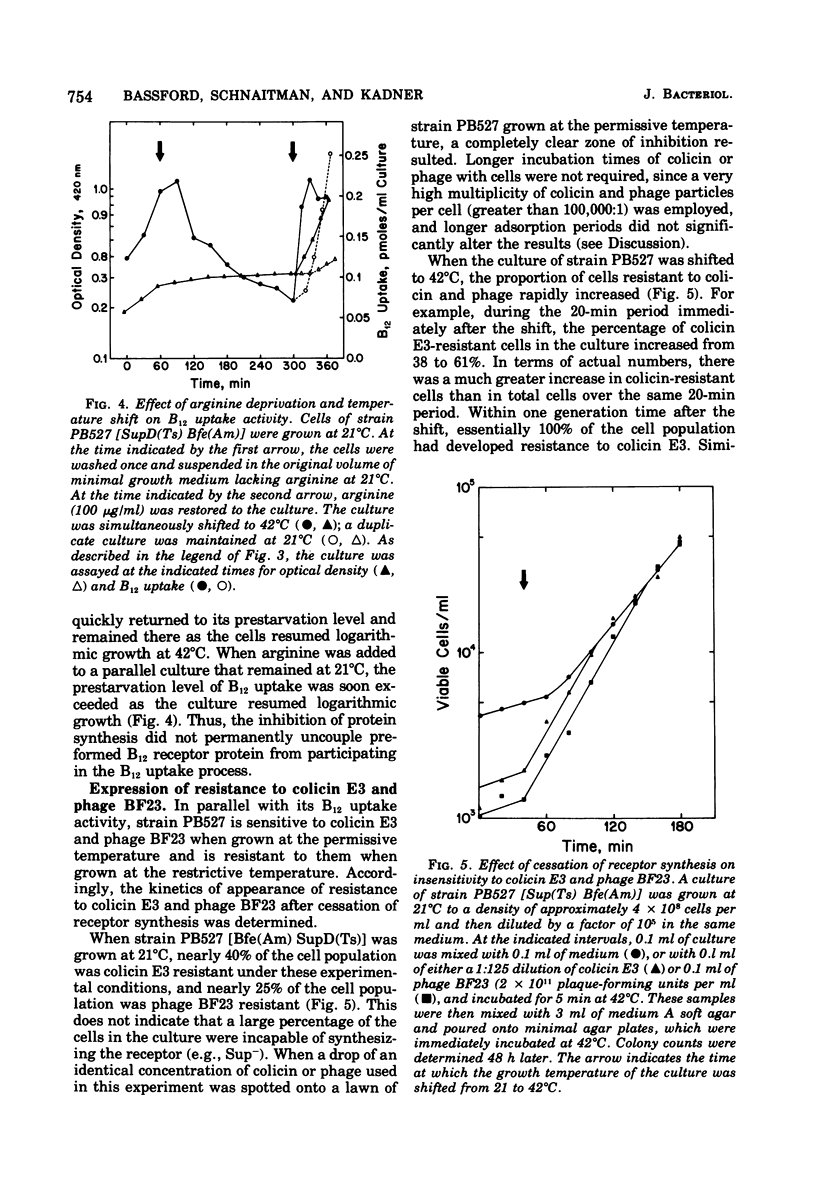
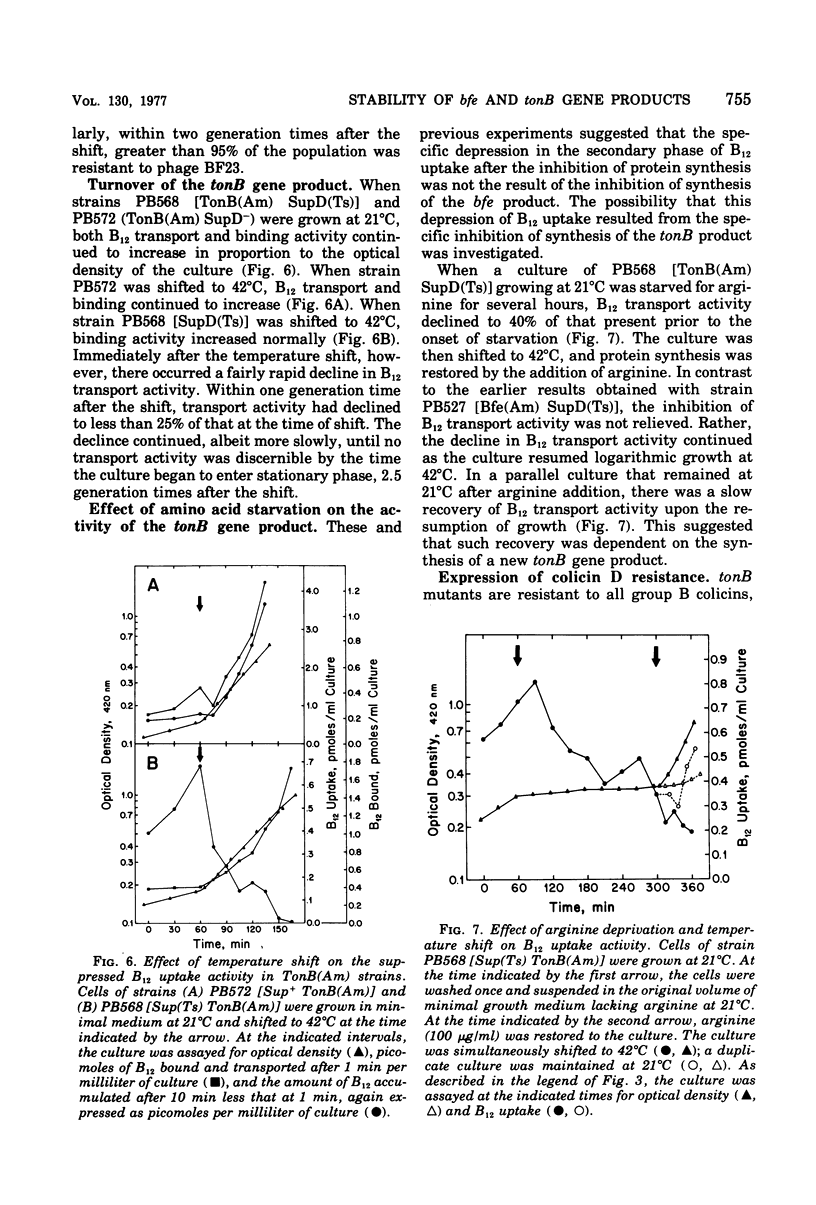
The expression of several functional properties of the products of the bfe and tonB genes in Escherichia coli was measured after the specific termination of the synthesis of the products of these genes. This was accomplished by the use of a temperature-sensitive amber suppressor mutation, which allowed control, by manipulation of the growth temperature, of the level of product formed from suppressible mutant alleles of the bfe or tonB gene. The bfe product is an outer membrane receptor protein for vitamin B12, the E-colicins, and bacteriophage BF23. The identity of the tonB product is unknown, but it is necessary for a subsequent step of uptake of vitamin B12, iron chelates, all of the group B colicins, and bacteriophages T1 and phi 80. Results from a different experimental system had shown that the termination of expression of the bfe locus was rapidly followed by loss of sensitivity to colicins E2 and E3 and, subsequently, to bacteriophage BF23. This was confirmed with this experimental system. Receptors that were no longer functional for colicin or phage uptake remained fully effective for B12 uptake, showing that receptors are stable on the cell surface. This supports previous contentions for the presence of different functional states for colicin receptors. The functional properties of the tonB product, measured by B12 uptake or sensitivity to the group B colicin D, were unstable, declining extensively after cessation of its synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B., Taylor A. L. Recalibrated linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):116–167. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.116-167.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassford P. J., Jr, Bradbeer C., Kadner R. J., Schnaitman C. A. Transport of vitamin B12 in tonB mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):242–247. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.242-247.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassford P. J., Jr, Kadner R. J., Schnaitman C. A. Biosynthesis of the outer membrane receptor for vitamin B12, E colicins, and bacteriophage BF23 by Escherichia coli: kinetics of phenotypic expression after the introduction of bfe+ and bfe alleles. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):265–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.265-275.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbeer C., Woodrow M. L., Khalifah L. I. Transport of vitamin B12 in Escherichia coli: common receptor system for vitamin B12 and bacteriophage BF23 on the outer membrane of the cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1032–1039. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1032-1039.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbeer C., Woodrow M. L. Transport of vitamin B12 in Escherichia coli: energy dependence. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):99–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.99-104.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton R. S. Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli K12 mutants resistant to bacteriophage BF23 and the E-group colicins. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;113(2):154–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00333188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group B. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):96–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.96-101.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo P. M., Bradbeer C. Transport of vitamin B 12 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):745–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.745-750.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo P. M., Kadner R. J., Bradbeer C. Isolation of vitamin B 12 transport mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):751–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.751-757.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Masi D. R., White J. C., Schnaitman C. A., Bradbeer C. Transport of vitamin B12 in Escherichia coli: common receptor sites for vitamin B12 and the E colicins on the outer membrane of the cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):506–513. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.506-513.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. W., Braun V. Nature of the energy requirement for the irreversible adsorption of bacteriophages T1 and phi80 to Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):409–415. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.409-415.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantke K., Braun V. Membrane receptor dependent iron transport in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 1;49(3):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80771-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasper P., Whitney E., Silver S. Genetic locus determining resistance to phage BF23 and colicins E 1 , E 2 and E 3 in Escherichia coli. Genet Res. 1972 Jun;19(3):305–312. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadner R. J., Bassford P. J., Jr Relation of cell growth and colicin tolerance to vitamin B12 uptake in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):254–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.254-264.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadner R. J., Liggins G. L. Transport of vitamin B12 in Escherichia coli: genetic studies. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):514–521. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.514-521.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeschger M. P., Woods S. L. A temperature-sensitive suppressor enabling the manipulation of the level of individual proteins in intact cells. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Reeves P. Iron uptake in colicin B-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1052–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1052-1062.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabet S. F., Schnaitman C. A. Purification and properties of the colicin E3 receptor of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1797–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmis K., Hedges A. J. The killing of sensitive cells by colicin D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):200–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. C., Newton A. An additional step in the transport of iron defined by the tonB locus of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2147–2151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne R., Frick K., Neilands J. B. Siderophore protection against colicins M, B, V, and Ia in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.7-12.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. C., DiGirolamo P. M., Fu M. L., Preston Y. A., Bradbeer C. Transport of vitamin B 12 in Escherichia coli. Location and properties of the initial B 12 -binding site. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3978–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



