Abstract
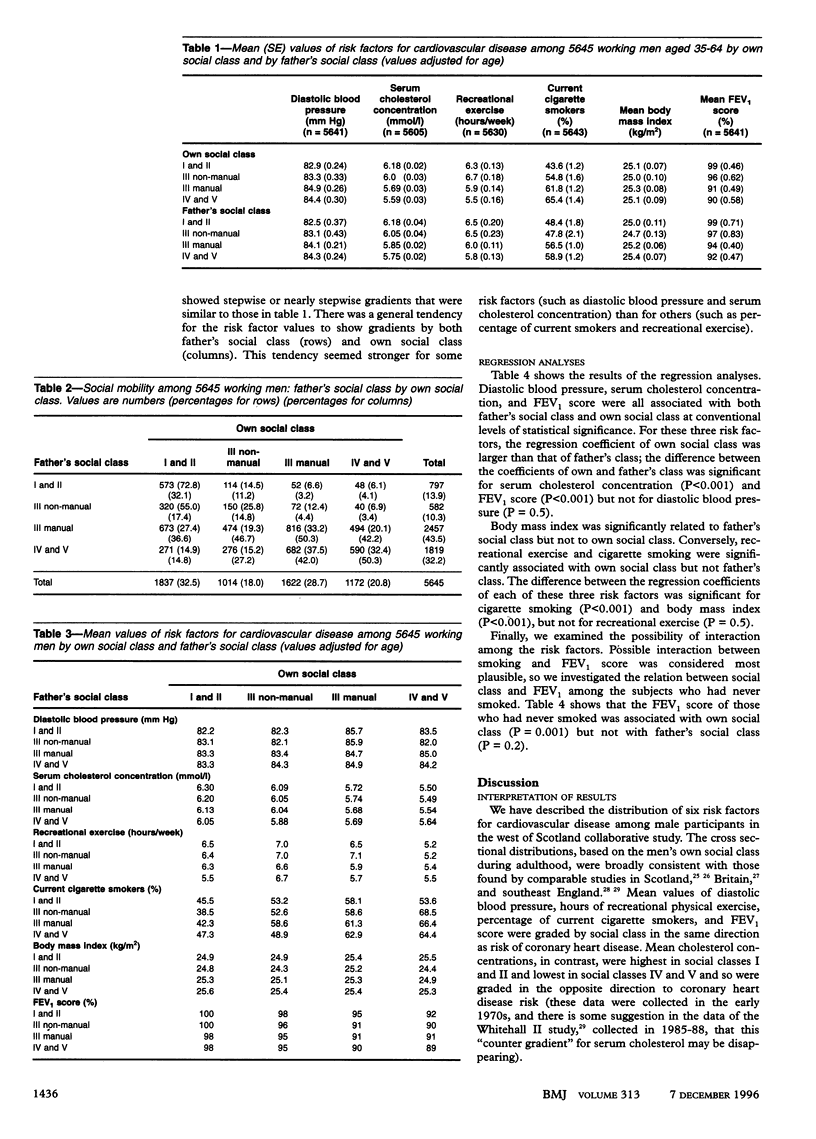
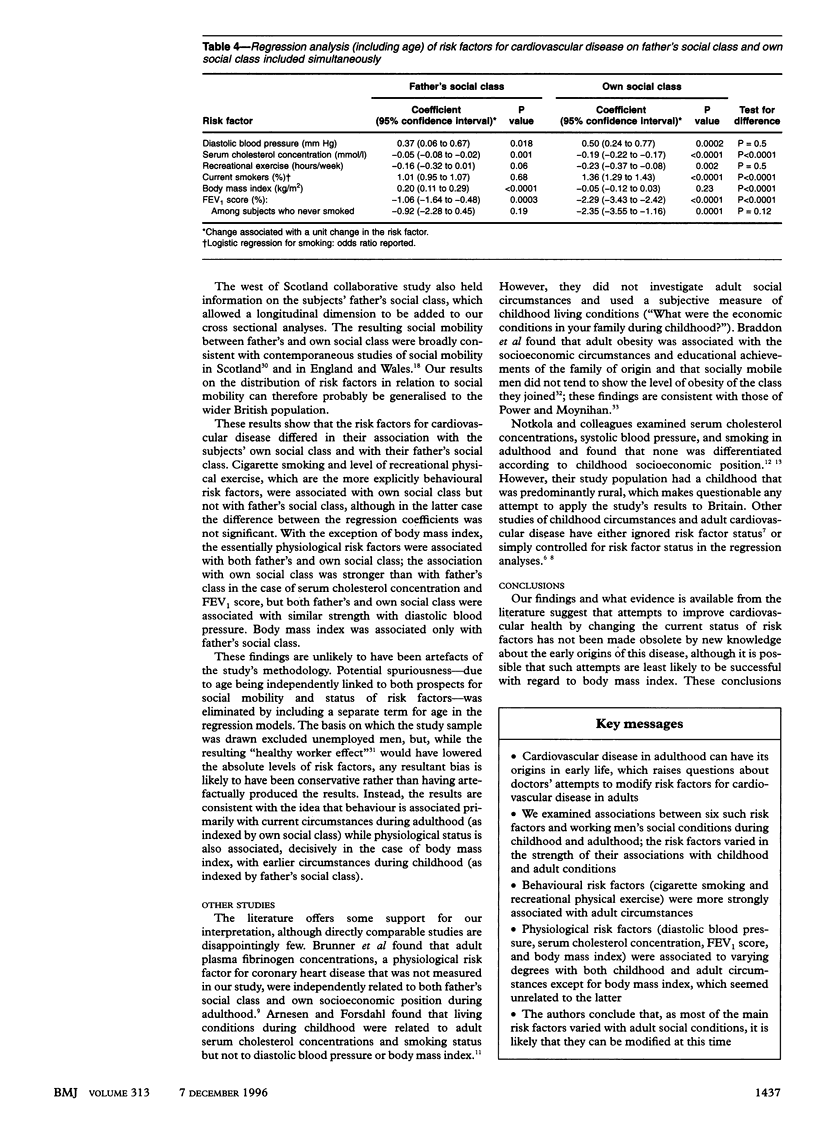
OBJECTIVE: To investigate strength of associations between risk factors for cardiovascular disease and socioeconomic position during childhood and adulthood. DESIGN: Cross sectional analysis of status of cardiovascular risk factors and past and present social circumstances. SUBJECTS: 5645 male participants in the west of Scotland collaborative study, a workplace screening study. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES: Strength of association between each risk factor for cardiovascular disease (diastolic blood pressure, serum cholesterol concentration, level of recreational physical exercise, cigarette smoking, body mass index, and FEV1 score (forced expiratory volume in one second as percentage of expected value) and social class during childhood (based on father's main occupation) and adulthood (based on own occupation at time of screening). RESULTS: All the measured risk factors were significantly associated with both father's and own social class (P < 0.05), apart from exercise and smoking (not significantly associated with father's social class) and body mass index (not significantly associated with own social class). For all risk factors except body mass index, the regression coefficient of own social class was larger than the regression coefficient of father's social class. The difference between the coefficients was significant for serum cholesterol concentration, cigarette smoking, body mass index, and FEV1 score (all P < 0.001). CONCLUSIONS: Subjects' status for behavioural risk factors (exercise and smoking) was associated primarily with current socioeconomic circumstances, while status for physiological risk factors (serum cholesterol, blood pressure, body mass index, and FEV1) was associated to varying extents with both past and present socioeconomic circumstances.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnesen E., Forsdahl A. The Tromsø heart study: coronary risk factors and their association with living conditions during childhood. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1985 Sep;39(3):210–214. doi: 10.1136/jech.39.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. J., Martyn C. N. The maternal and fetal origins of cardiovascular disease. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1992 Feb;46(1):8–11. doi: 10.1136/jech.46.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartley M., Power C., Blane D., Smith G. D., Shipley M. Birth weight and later socioeconomic disadvantage: evidence from the 1958 British cohort study. BMJ. 1994 Dec 3;309(6967):1475–1478. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6967.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braddon F. E., Rodgers B., Wadsworth M. E., Davies J. M. Onset of obesity in a 36 year birth cohort study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Aug 2;293(6542):299–303. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6542.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner E., Davey Smith G., Marmot M., Canner R., Beksinska M., O'Brien J. Childhood social circumstances and psychosocial and behavioural factors as determinants of plasma fibrinogen. Lancet. 1996 Apr 13;347(9007):1008–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr M. L., Sweetnam P. M. Family size and paternal unemployment in relation to myocardial infarction. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1980 Jun;34(2):93–95. doi: 10.1136/jech.34.2.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebi-Kryston K. L., Hawthorne V. M., Rose G., Shipley M. J., Gillis C. R., Hole D. J., Carmen W., Eshleman S., Higgins M. W. Breathlessness, chronic bronchitis and reduced pulmonary function as predictors of cardiovascular disease mortality among men in England, Scotland and the United States. Int J Epidemiol. 1989 Mar;18(1):84–88. doi: 10.1093/ije/18.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsdahl A. Living conditions in childhood and subsequent development of risk factors for arteriosclerotic heart disease. The cardiovascular survey in Finnmark 1974-75. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1978 Mar;32(1):34–37. doi: 10.1136/jech.32.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliksman M. D., Kawachi I., Hunter D., Colditz G. A., Manson J. E., Stampfer M. J., Speizer F. E., Willett W. C., Hennekens C. H. Childhood socioeconomic status and risk of cardiovascular disease in middle aged US women: a prospective study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1995 Feb;49(1):10–15. doi: 10.1136/jech.49.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne V. M., Fry J. S. Smoking and health: the association between smoking behaviour, total mortality, and cardiorespiratory disease in west central Scotland. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1978 Dec;32(4):260–266. doi: 10.1136/jech.32.4.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne V. M., Watt G. C., Hart C. L., Hole D. J., Smith G. D., Gillis C. R. Cardiorespiratory disease in men and women in urban Scotland: baseline characteristics of the Renfrew/Paisley (midspan) study population. Scott Med J. 1995 Aug;40(4):102–107. doi: 10.1177/003693309504000402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G. A., Salonen J. T. Socioeconomic conditions in childhood and ischaemic heart disease during middle age. BMJ. 1990 Nov 17;301(6761):1121–1123. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6761.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. W., Kaplan G. A., Cohen R. D., Kauhanen J., Wilson T. W., Smith N. L., Salonen J. T. Childhood and adult socioeconomic status as predictors of mortality in Finland. Lancet. 1994 Feb 26;343(8896):524–527. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91468-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmot M. G., Rose G., Shipley M., Hamilton P. J. Employment grade and coronary heart disease in British civil servants. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1978 Dec;32(4):244–249. doi: 10.1136/jech.32.4.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmot M. G., Smith G. D., Stansfeld S., Patel C., North F., Head J., White I., Brunner E., Feeney A. Health inequalities among British civil servants: the Whitehall II study. Lancet. 1991 Jun 8;337(8754):1387–1393. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93068-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkola V., Punsar S., Karvonen M. J., Haapakoski J. Socio-economic conditions in childhood and mortality and morbidity caused by coronary heart disease in adulthood in rural Finland. Soc Sci Med. 1985;21(5):517–523. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(85)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power C., Moynihan C. Social class and changes in weight-for-height between childhood and early adulthood. Int J Obes. 1988;12(5):445–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper A. G., Pocock S. J., Walker M., Cohen N. M., Wale C. J., Thomson A. G. British Regional Heart Study: cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged men in 24 towns. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jul 18;283(6285):179–186. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6285.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez J., Rodríguez B., de la Fuente L., Barrio G., Vicente J., Roca J., Royuela L. Opiates or cocaine: mortality from acute reactions in six major Spanish cities. State Information System on Drug Abuse (SEIT) Working Group. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1995 Feb;49(1):54–60. doi: 10.1136/jech.49.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth M. E., Cripps H. A., Midwinter R. E., Colley J. R. Blood pressure in a national birth cohort at the age of 36 related to social and familial factors, smoking, and body mass. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Nov 30;291(6508):1534–1538. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6508.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M., Shewry M. C., Smith W. C., Tunstall-Pedoe H. Social status and coronary heart disease: results from the Scottish Heart Health Study. Prev Med. 1992 Jan;21(1):136–148. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(92)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


