Abstract
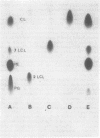
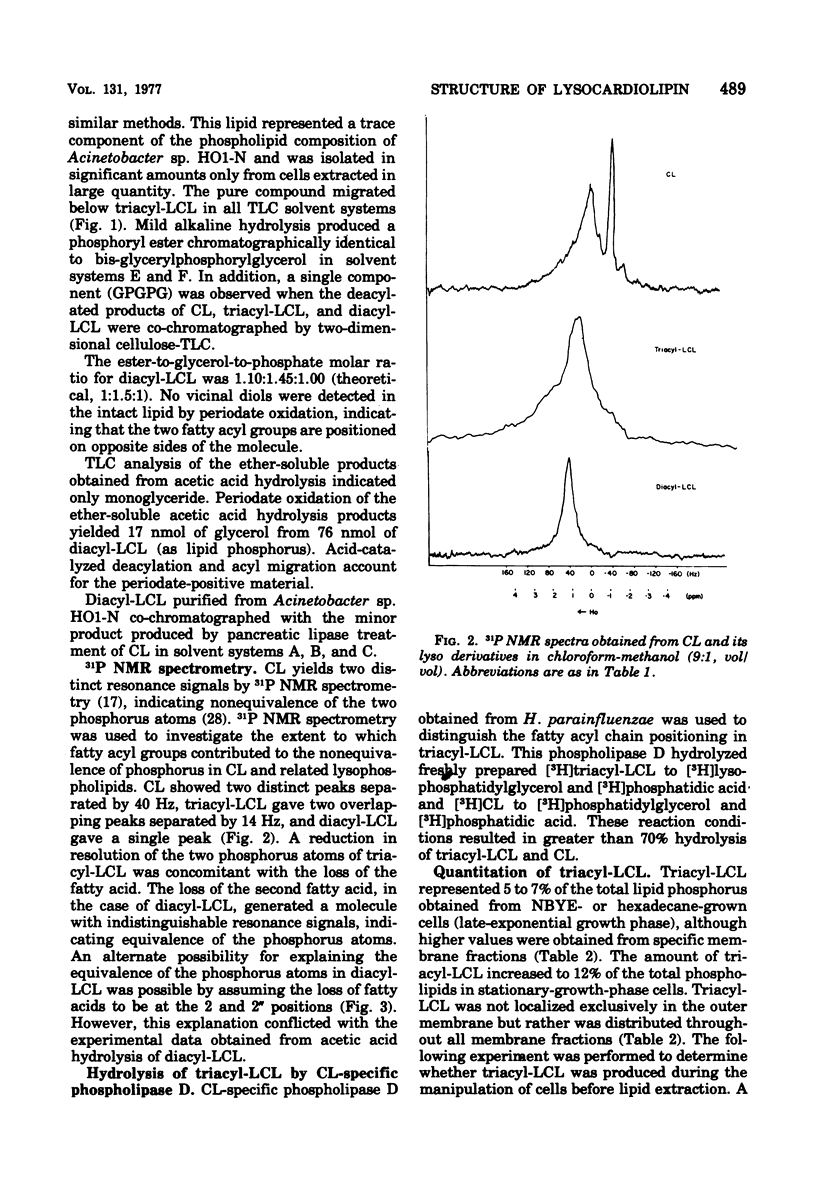
Triacyl-lysocardiolipin (triacyl-LCL) and diacyl-LCL were isolated from Acinetobacter sp. HO1-N, and their structures were determined by chemical, physical, and enzymatic procedures. Deacylation of triacyl-LCL and diacyl-LCL yielded bis-glycerylphosphorylglycerol. Periodate oxidation of both lysolipids was negative. Diglyceride and 2-monoglyceride resulted from the acetic acid hydrolysis of triacyl-LCL, whereas 2-monoglyceride was the sole product obtained from diacyl-LCL. Cardiolipin (CL)-specific phospholipase D treatment of triacyl-LCL yielded lysophosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidic acid. Pancreatic lipase treatment of CL yielded triacyl-LCL and diacyl-LCL. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry showed two resonance peaks separated by 40 HZ for CL, two overlapping peaks separated by 14 HZ for triacyl-LCL, and one peak for diacyl-LCL. The proportion of lysocardiolipin increased as a function of cell age, representing 2 to 3% of the total phospholipids in early- and mid-exponential growth, 5 to 7% in late-exponential growth, and 12% in the stationary growth phase.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright F. R., White D. A., Lennarz W. J. Studies on enzymes involved in the catabolism of phospholipids in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3968–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Lipids of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: structure and metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):833–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.833-843.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrachan L. The bond hydrolyzed by cardiolipin-specific phospholipase D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;296(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audet A., Cole R., Proulx P. Polyglycerophosphatide metabolism in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 24;380(3):414–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerve K. S., Daae L. N., Bremer J. The selective loss of lysophospholipids in some commonly used lipid-extraction procedures. Anal Biochem. 1974 Mar;58(1):238–245. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90463-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. S., Benns G., Proulx P. Formation of acyl phosphatidyl glycerol by Escherichia coli extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):355–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., LESTER R. L. A SIMPLE, SPECIFIC SPRAY FOR THE DETECTION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS ON THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAMS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:126–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A., Otten B. J., Wassenberg H. W., Veerkamp J. H. Comparison of the phospholipid composition of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus strains. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):824–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.824-829.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A., Veerkamp J. H. Biochemical changes in Bifidobacterium bifidum var. Pennsylvanicus after cell wall inhibition. I. Composition of lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;176(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnerty W. R., Makula R. A. Microbial lipid metabolism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1975 Oct;4(1):1–40. doi: 10.3109/10408417509105485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman B. A., Sissenstein R., McManus T. T., Woodward J. E., Lee I. M., Mudd J. B. Lipid composition and lipid metabolism of Spiroplasma citri. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):946–954. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.946-954.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., ISHERWOOD F. A. Separation of the phosphoric esters on the filter paper chromatogram. Nature. 1949 Dec 31;164(4183):1107-12, illust. doi: 10.1038/1641107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson T. O., Glonek T., Myers T. C. Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):623–628. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langworthy T. A., Mayberry W. R., Smith P. F. A sulfonolipid and novel glucosamidyl glycolipids from the extreme thermoacidophile Bacillus acidocaldarius. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 22;431(3):550–569. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACFARLANE M. G., WHEELDON L. W. Position of the fatty acids in cardiolipin. Nature. 1959 Jun 27;183:1808–1808. doi: 10.1038/1831808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makula R. A., Finnerty W. R. Microbial assimilation of hydrocarbons: identification of phospholipids. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):348–355. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.348-355.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makula R. A., Finnerty W. R. Phospholipid composition of Desulfovibrio species. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1279–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1279-1283.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makula R., Finnerty W. R. Microbial assimilation of hydrocarbons. I. Fatty acids derived from normal alkanes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2102–2107. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2102-2107.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKUYAMA H., NOJIMA S. STUDIES ON HYDROLYSIS OF CARDIOLIPIN BY SNAKE VENOM PHOSPHOLIPASE A. J Biochem. 1965 Apr;57:529–538. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., White D. C. Cardiolipin-specific phospholipase D activity in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):111–115. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.111-115.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P., Smith P. F., Mayberry W. R. Lipids of a sterol-nonrequiring Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):798–807. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.798-807.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P. The synthesis of polar lipids by mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):158–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell G. L., Jacobus J. The nonequivalence of the phosphorus atoms in cardiolipin. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4024–4026. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proulx P. R., van Deenen L. L. Acylation of lysophosphoglycerides by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 7;125(3):591–593. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER F., STEPHENS N. A simplified spectrophotometric determination of ester groups in lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:244–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. C., Finnerty W. R. Characterization of intracytoplasmic hydrocarbon inclusions from the hydrocarbon-oxidizing Acinetobacter species HO1-N. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):481–489. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.481-489.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senff L. M., Wegener W. S., Brooks G. F., Finnerty W. R., Makula R. A. Phospholipid composition and phospholipase A activity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):874–880. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.874-880.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., White D. C. Metabolism of the glycosyl diglycerides and phosphatidylglucose of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.126-132.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F. Comparative lipid biochemistry of mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):139–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Koostra W. L. Phospholipids and glycolipids of sterol-requiring Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1853–1862. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1853-1862.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torregrossa R. E., Makula R. A., Finnerty W. R. Outer membrane phospholipase A from Acinetobacter sp. HO1-N. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):493–498. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.493-498.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker A. N., White D. C. Detection of a rapidly metabolizing portion of the membrane cardiolipin in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1058–1064. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1058-1064.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C. Lipid composition of the electron transport membrane of Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1159–1170. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1159-1170.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haas G. H., Sarda L., Roger J. Positional specific hydrolysis of phospholipids by pancreatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 2;106(3):638–640. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]