Abstract
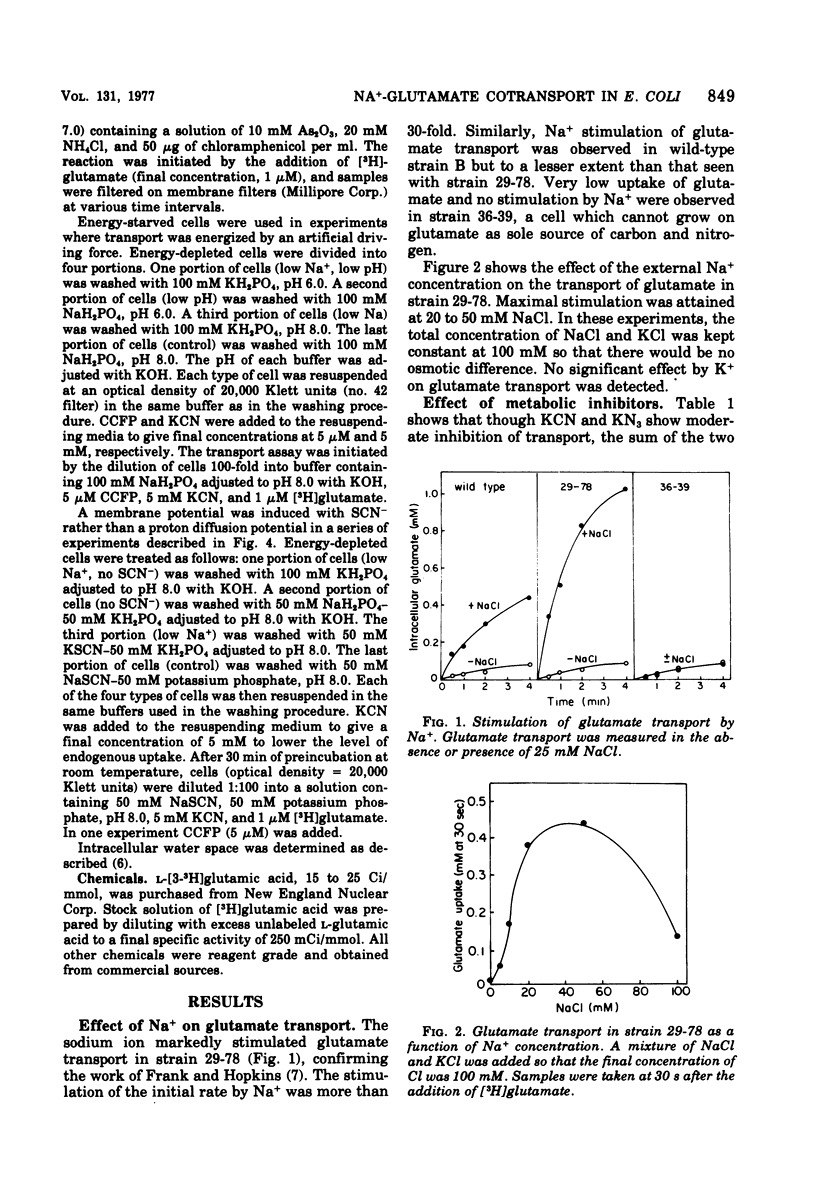
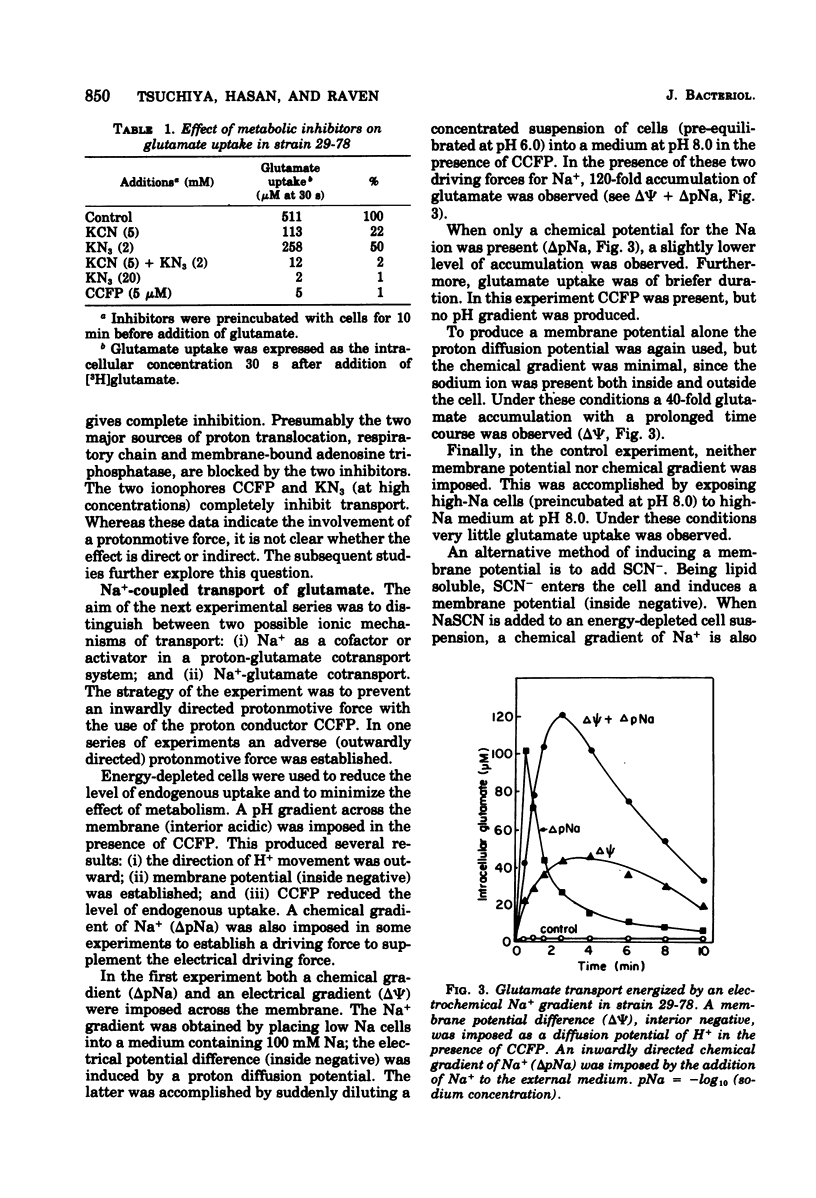
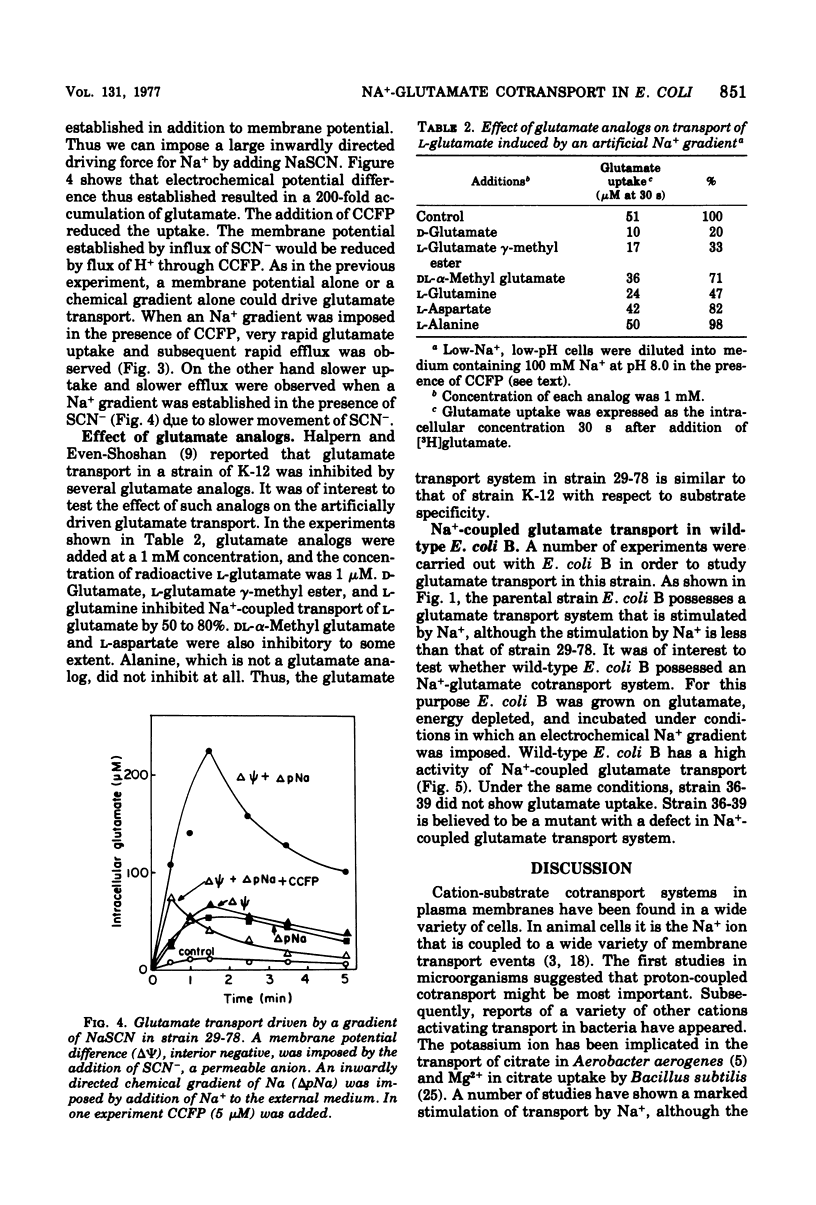
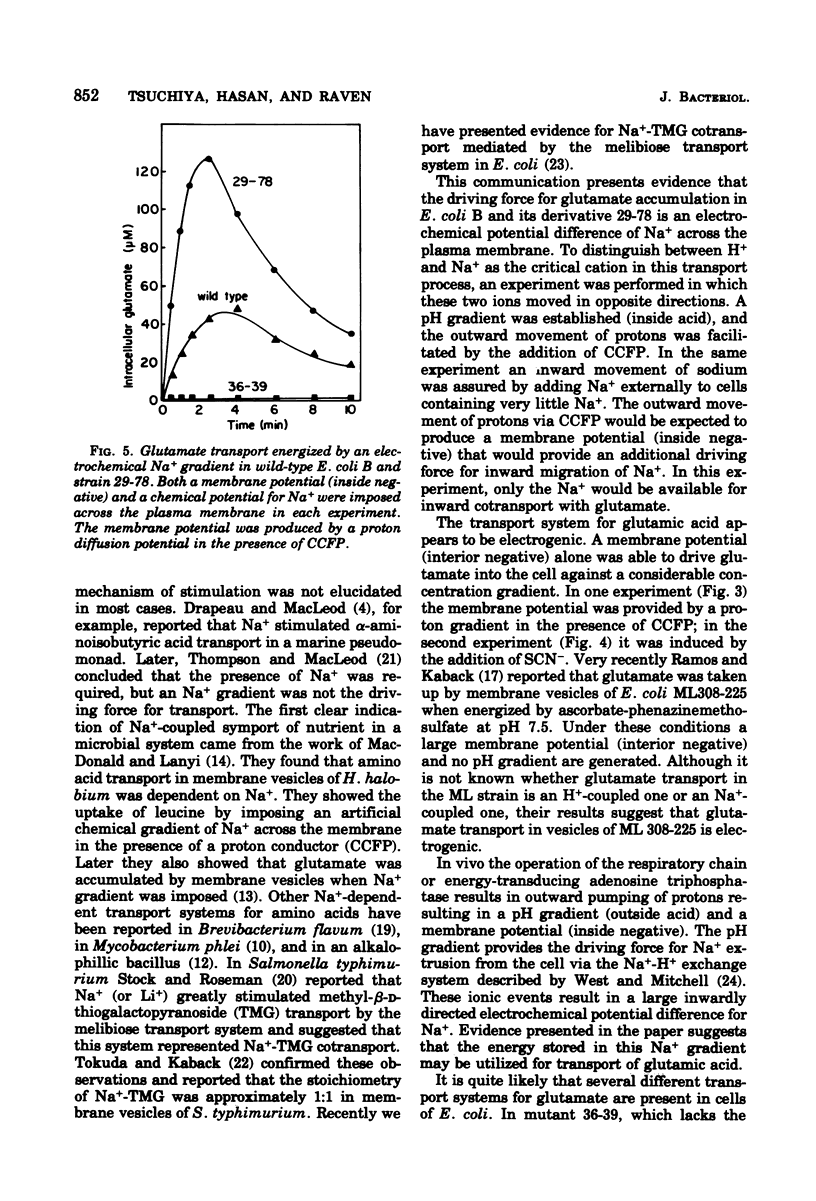
The role of Na+ in glutamate transport was studied in Escherichia coli B, strain 29-78, which possesses a very high activity of glutamate transport (L. Frank and I. Hopkins, J. Bacteriol., 1969). Energy-depleted cells were exposed to radioactive glutamate in the presence of a sodium gradient, a membrane potential, or both. One hundred- to 200-fold accumulation of the amino acid was attained in the presence of both electrical and chemical driving forces for the sodium ion. Somewhat lower accumulation values were obtained when either chemical or electrical driving forces were applied separately. A chemical driving force was produced by the addition of external Na+ to Na+-free cells. A membrane potential was established by a diffusion potential either of H+ in the presence of carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone or of SCN-. These results support the hypothesis of a Na+-glutamate cotransport. Na+-driven glutamate transport was also observed in wild-type E. coli B but not in a strain of K-12.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger E. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the active transport of proline and glutamine in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Concentration spécifique réversible des amino acides chez Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Nov;91(5):693–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane R. K. Na+ -dependent transport in the intestine and other animal tissues. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1000–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagon R. G., Wilkerson L. S. A potassium-dependent citric acid transport system in Aerobacter aerogenes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1944–1950. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flagg J. L., Wilson T. H. A protonmotive force as the source of energy for galactoside transport in energy depleted Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1977 Mar 8;31(3):233–255. doi: 10.1007/BF01869407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Hopkins I. Sodium-stimulated transport of glutamate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):329–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.329-336.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern Y. S., Barash H., Dover S., Druck K. Sodium and potassium requirements for active transport of glutamate by Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):53–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.53-58.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern Y. S., Even-Shoshan A. Properties of the glutamate transport system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1009–1016. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1009-1016.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Kosmakos F. C., Brodie A. F. Active transport of proline in membrane preparations from Mycobacterium phlei. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6965–6970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane S., Marcus M., Barash H., Halpern Y. S. Sodium-dependent glutamate transport in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli K-12. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama N., Kiyomiya A., Nosoh Y. Na+-dependent uptake of amino acids by an alkalophilic Bacillus. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 15;72(1):77–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80816-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Yearwood-Drayton V., MacDonald R. E. Light-induced glutamate transport in Halobacterium halobium envelope vesicles. I. Kinetics of the light-dependent and the sodium-gradient-dependent uptake. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1595–1603. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. E., Lanyi L. K. Light-induced leucine transport in Halobacterium halobium envelope vesicles: a chemiosmotic system. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2882–2889. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner K. M., Frank L. Sodium-stimulated glutamate transport in osmotically shocked cells and membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1093–1098. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1093-1098.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niven D. F., Hamilton W. A. Mechanisms of energy coupling to the transport of amino acids by Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):517–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The relationship between the electrochemical proton gradient and active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):854–859. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Coupled transport of sodium and organic solutes. Physiol Rev. 1970 Oct;50(4):637–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiio I., Miyajima R., Kashima N. Na+-dependent transport of threonine in Brevibacterium flavum. J Biochem. 1973 Jun;73(6):1185–1193. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Roseman S. A sodium-dependent sugar co-transport system in bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):132–138. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80168-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Na+ and K+ gradients and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7106–7111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Kaback H. R. Sodium-dependent methyl 1-thio-beta-D-galactopyranoside transport in membrane vesicles isolated from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochemistry. 1977 May 17;16(10):2130–2136. doi: 10.1021/bi00629a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Raven J., Wilson T. H. Co-transport of Na+ and methul-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside mediated by the melibiose transport system of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 May 9;76(1):26–31. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91663-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. Proton/sodium ion antiport in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):87–90. doi: 10.1042/bj1440087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willecke K., Gries E. M., Oehr P. Coupled transport of citrate and magnesium in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):807–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



