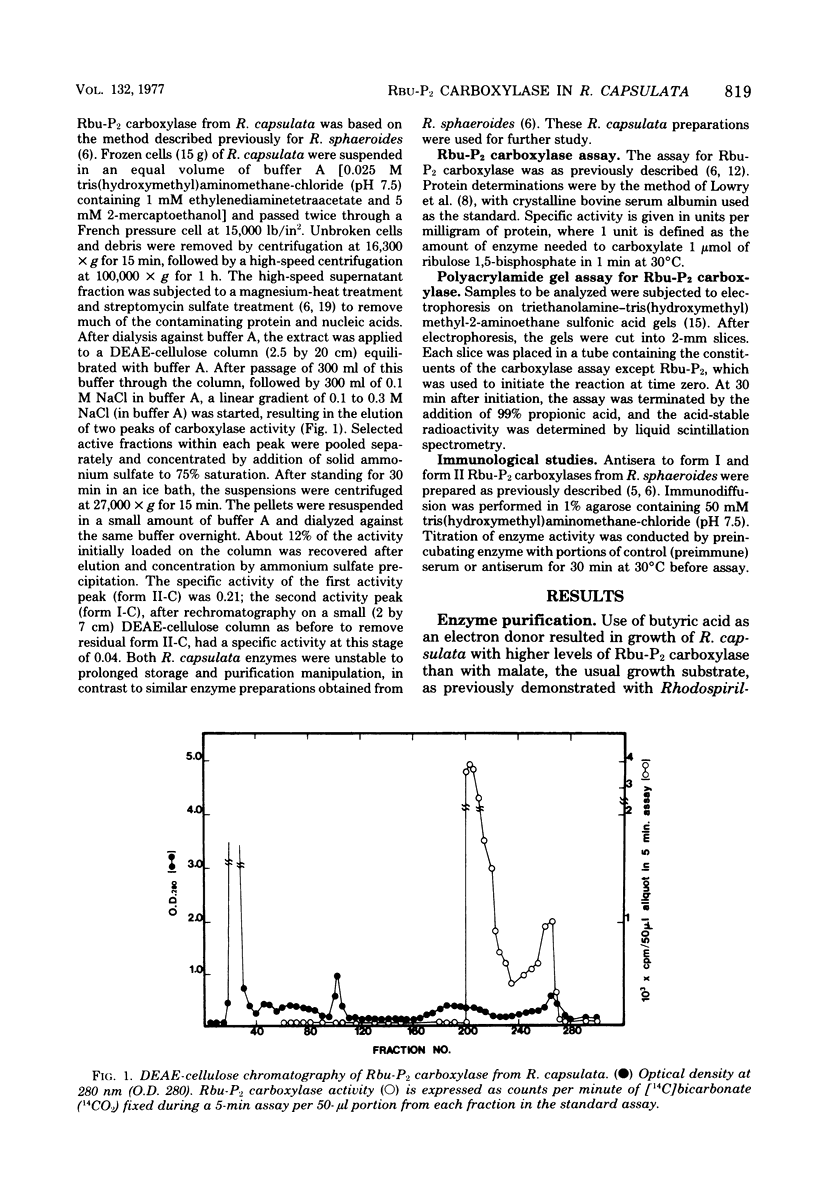
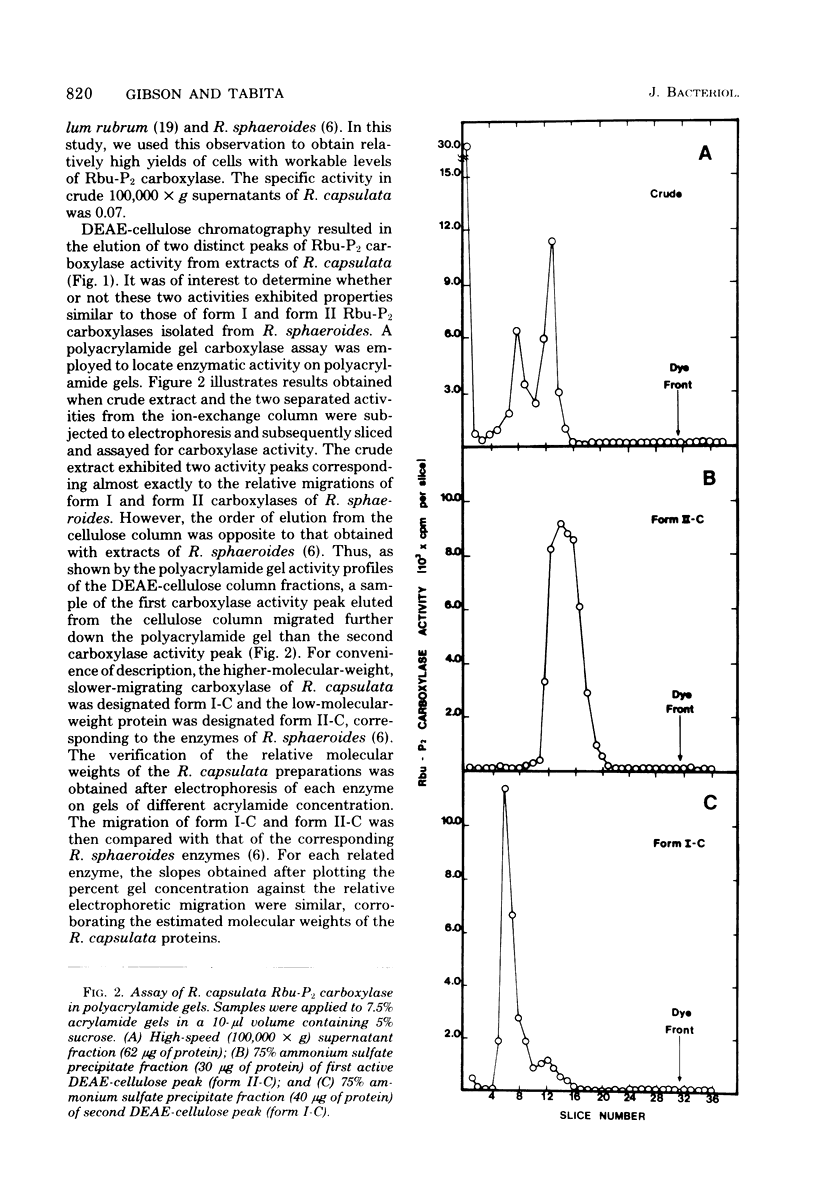
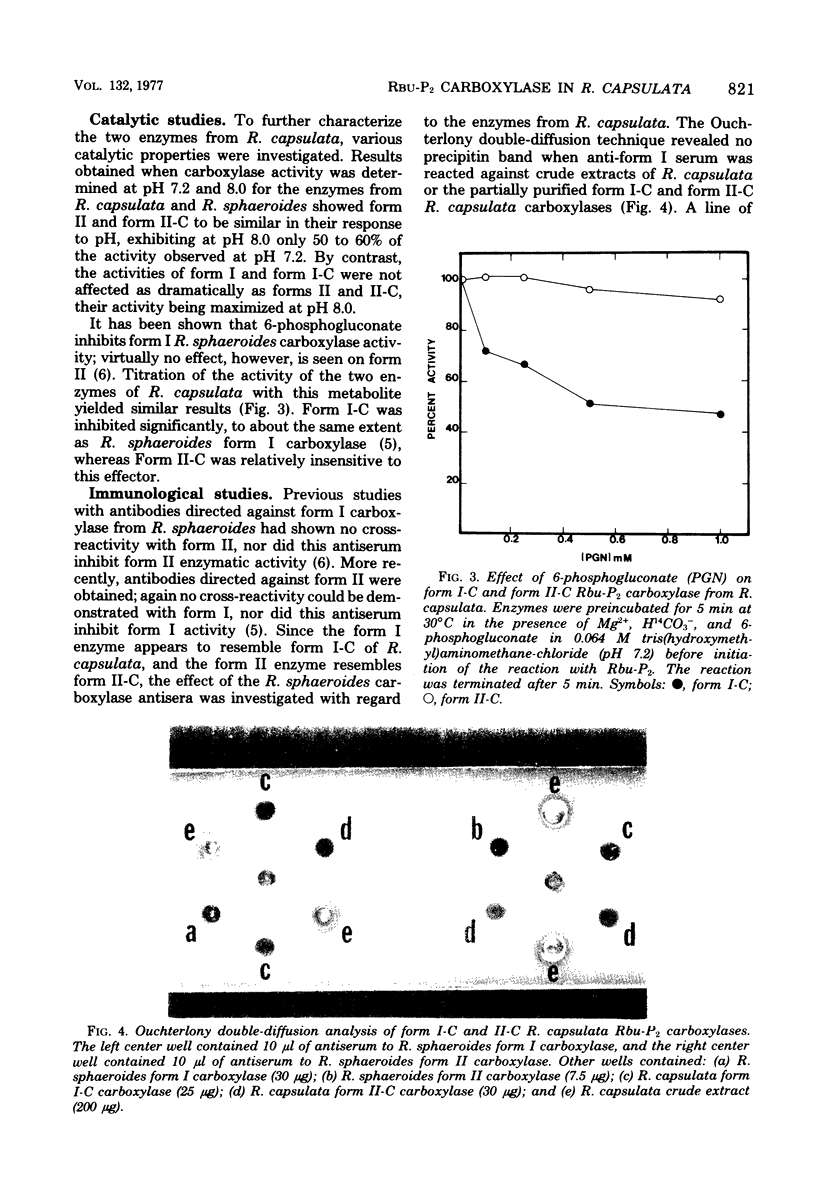
Abstract
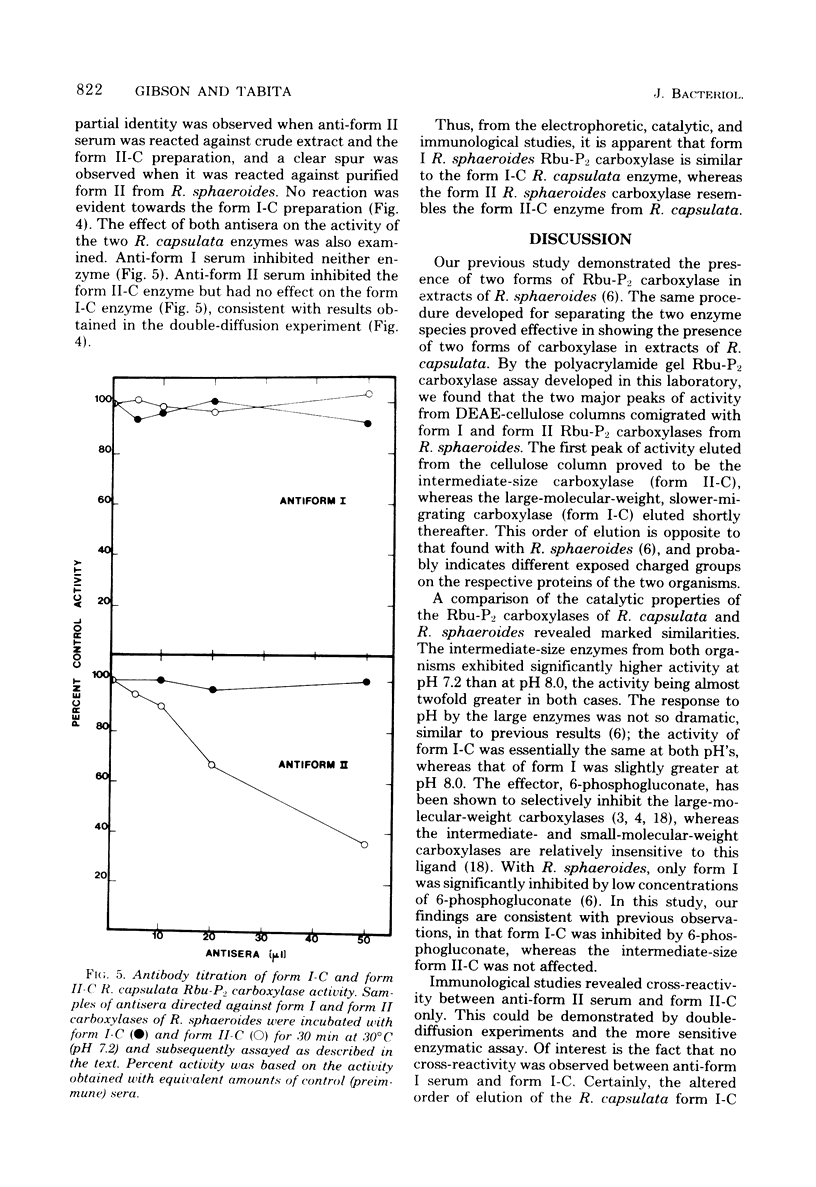
The presence of two distinct forms of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase has been demonstrated in extracts of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata, similar to the form I (peak I) and form II (peak II) carboxylases previously described from R. sphaeroides (J. Gibson and F. R. Tabita, J. Biol. Chem 252:943-949, 1977). The two activities, separated by diethylaminoethyl-cellulose chromatography, were shown to be of different molecular size after assay on polyacrylamide gels. The higher-molecular-weight carboxylase from R. capsulata was designated form I-C, whereas the smaller enzyme was designated form II-C. Catalytic studies revealed significant differences between the two enzymes in response to pH and the effector 6-phosphogluconate. Immunological studies with antisera directed against the carboxylases from R. sphaeroides demonstrated antigenic differences between the two R. capsulata enzymes; cross-reactivity was observed only between R. sphaeroides anti-form II serum and the corresponding R. capsulata enzyme, form II-C.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowien B., Mayer F., Codd G. A., Schlegel H. G. Purification, some properties and quaternary structure of the D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase of Alcaligenes eutrophus. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Nov 2;110(23):157–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00690223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Activation and inhibition of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phosphogluconate. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):373–379. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Inhibition of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phosphogluconate. Plant Physiol. 1972 Aug;50(2):224–227. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.2.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Characterization of antiserum directed against form II ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):1020–1022. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.1020-1022.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Different molecular forms of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):943–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs B. Genetic recombination in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):971–973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A. Autotrophic CO2 assimilation and the evolution of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):289–319. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.289-319.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Denend A. R. Ribulose diphosphate carboxylase from autotrophic microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):633–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.633-642.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tabita F. R. D-ribulose-1, 5-diphosphate carboxylase and the evolution of autotrophy. Biosystems. 1974 Oct;6(2):93–112. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(74)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tabita F. R., Kuehn G. D. Ribulose-diphosphate carboxylase from the hydrogen bacteria and Rhodospirillum rubrum. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:461–472. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMEROD J. G., ORMEROD K. S., GEST H. Light-dependent utilization of organic compounds and photoproduction of molecular hydrogen by photosynthetic bacteria; relationships with nitrogen metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:449–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr M. D., Blakley R. L., Panagou D. Discontinuous buffer systems for analytical and preparative electrophoresis of enzymes on polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jan;45(1):68–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A., Cohen A. L. Purification, quaternary structure, composition, and properties of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Thiobacillus intermedius. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):505–515. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.505-515.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A. Quaternary structure and oxygenase activity of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Hydrogenomonas eutropha. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):415–421. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.415-421.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spomer G. G. Molecular diversity of the ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from photosynthetic microorganisms. Science. 1968 Aug 2;161(3840):482–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. I. Levels, purification, and effects of metallic ions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3453–3458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. II. Quaternary structure, composition, catalytic, and immunological properties. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3459–3464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. Molecular and catalytic properties of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from the photosynthetic extreme halophile Ectothiorhodospira halophila. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1271–1277. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1271-1277.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A., Pfennig N. D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum Tassajara. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 21;341(1):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. Regulation of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phospho-D-gluconate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1153–1159. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90831-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., Stevens S. E., Jr, Gibson J. L. Carbon dioxide assimilation in blue-green algae: initial studies on the structure of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.531-539.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita R. F., Stevens S. E., Jr, Quijano R. D-ribulose 1, 5-diphosphate carboxylase from blue-green algae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 6;61(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Akazawa T. Catalytic role of subunit A in ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Chromatium strain D. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jul;157(1):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Nishimura M., Akazawa T. Presence of two subunit types in ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from blue-green algae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91179-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall J. D., Weaver P. F., Gest H. Genetic transfer of nitrogenase-hydrogenase activity in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):630–631. doi: 10.1038/258630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman W., Tabita F. R. Inhibition of D-ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1034–1039. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90758-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]