Abstract
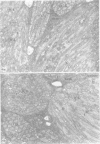
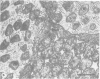
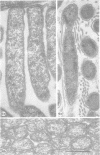
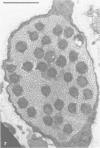
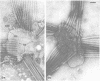
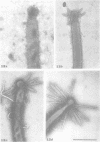
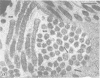
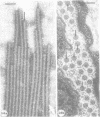
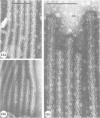
Nodules found in the superficial tissues of laboratory-maintained snails (Bulinus jousseaumei) contained a bacterium of two forms. This nonmotile microorganism occurred in intracellular packets as a simple gram-negative rod that appeared to undergo intrapacket transition to a cephalotrichous form. The latter is characterized by a "head" from which emerge long, thick, rigid, flagella-like, helically constituted filamentous organelles with a core and an outer component that is not an extension of the bacterial envelope. Neither form was successfully cultured, but clean snails derived from eggs removed before hatching developed nodules within 1 to 3 months of exposure to infected snails. The infectivity was specific for the host snail, and no transmission occurred to snails of 5 other genera tested. The presence of nodules did not interfere with longevity or reproduction of infected snails. Details of infectivity, transition, and taxonomic position of the bacterium remain to be explored, but it is reported because of unique morphological and ultrastructural features not previously known.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abram D., Davis B. K. Structural properties and features of parasitic Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):948–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.948-965.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abram D., Koffler H., Vatter A. E. Basal structure and attachment of flagella in cells of Proteus vulgaris. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1337-1354.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham J. C., Hashimoto T., Conti S. F. Ultrastructure and cell division of a facultatively parasitic strain of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):997–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.997-1004.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNIN E. A method of securing bacteriologically sterile snails (Australorbis glabratus). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Oct;96(1):204–210. doi: 10.3181/00379727-96-23433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUZ FILHO O., DIAS E. Bacillus pinottii sp. n. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1953 Nov;47(6):581–582. doi: 10.1016/s0035-9203(53)80012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Bazire G., London J. Basal organelles of bacterial flagella. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):458–465. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.458-465.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. M., Popkin T. J., Boylan R. J., Mendelson N. H. Ultrastructure of a temperature-sensitive rod- mutant of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):793–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.793-810.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAS E., DAWOOD M. M. Preliminary trials on the biological snail control with Bacillus pinottii in Egypt. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1955 May;53(1):13–29. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02761955000100002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean W. W., Mead A. R., Northey S. T. Aeromonas liquefaciens in the giant African snail, Achantina fulica. J Invertebr Pathol. 1970 Nov;16(3):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(70)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst J. A., Hayward A. C. The sheathed flagellum of Pseudomonas stizolobii. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Oct;58(2):239–245. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-2-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAUERT A. M., KERRIDGE D., HORNE R. W. THE FINE STRUCTURE AND MODE OF ATTACHMENT OF THE SHEATHED FLAGELLUM OF VIBRIO METCHNIKOVII. J Cell Biol. 1963 Aug;18:327–336. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeniger J. F., Van Iterson W., Van Zanten E. N. Basal bodies of bacterial flagella in Proteus mirabilis. II. Electron microscopy of negatively stained material. J Cell Biol. 1966 Dec;31(3):603–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.31.3.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen K. H., Birch-Andersen A. Electron microscopy of endoflagella and microtubules in Treponema reiter. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(1):37–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHELSON E. H. Studies on the biological control of schistosome-baring snails; predators and parasites of fresh-water mollusca: a review of the literature. Parasitology. 1957 Dec;47(3-4):413–426. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000022101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REPASKE R. Lysis of gram-negative bacteria by lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Oct;22(1):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. S. Shell mats associated with microsporida in Biomphalaria glabrata: genetic studies. J Invertebr Pathol. 1974 Nov;24(3):337–343. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(74)90141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Starr M. P. Structure of the flagellum of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1952–1955. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1952-1955.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]