Abstract
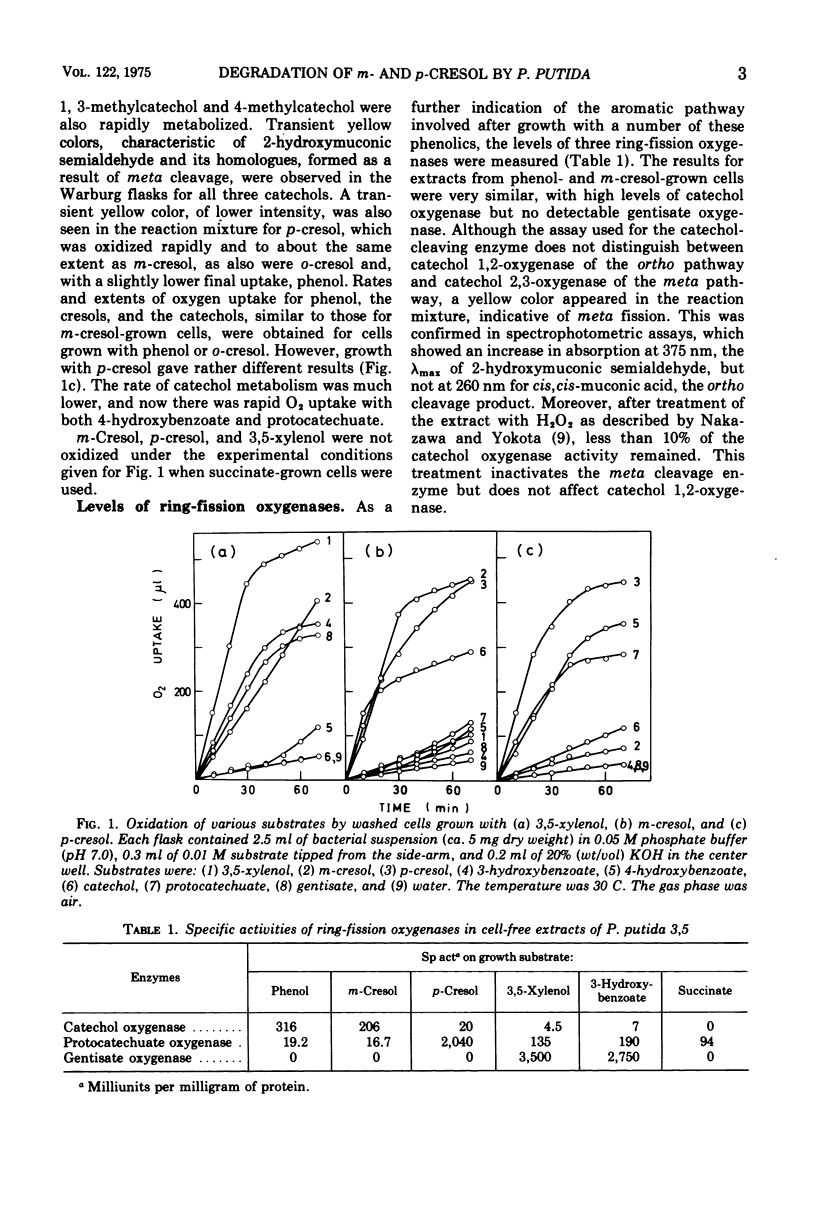
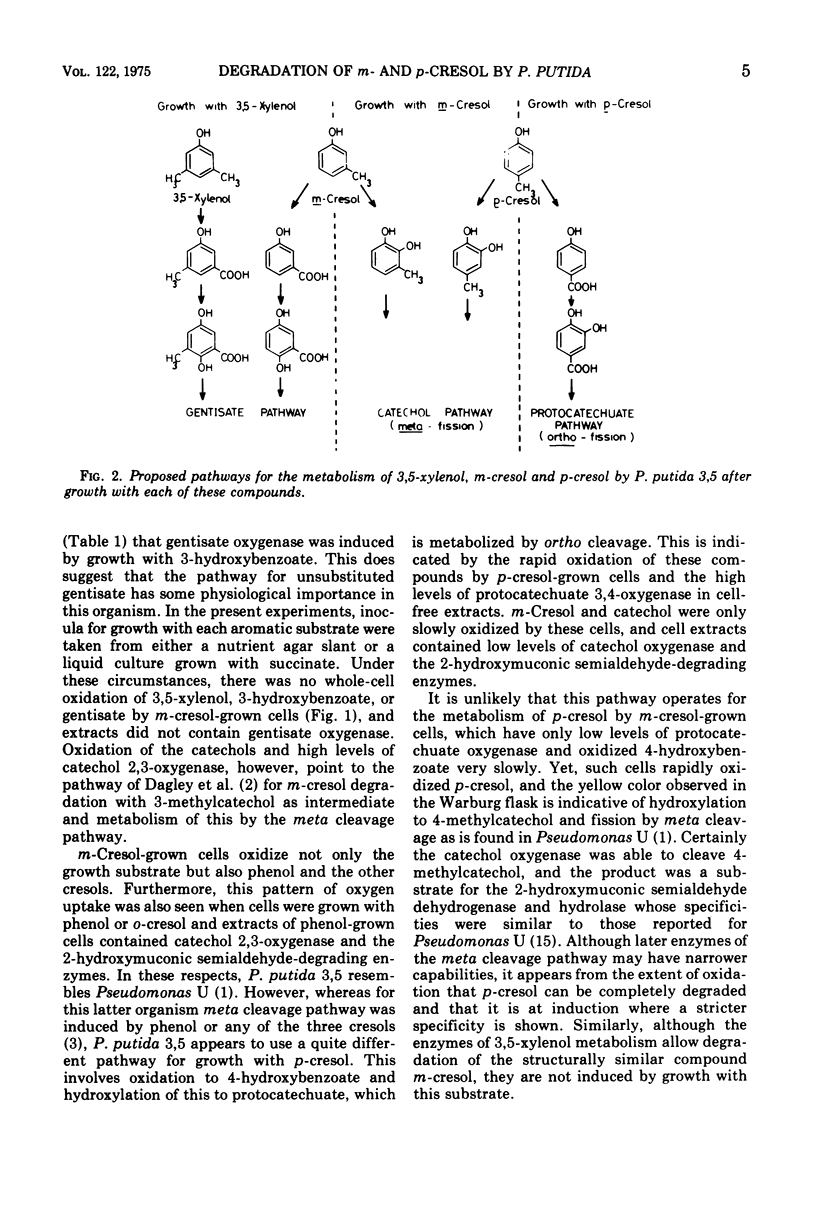
A comparison of the oxidation rates of various compounds by whole cells of Pseudomonas putida 3, 5 indicated that m-cresol is metabolized by oxidation to 3-hydroxybenzoate followed by hydroxylation to gentisate, the ring-fission substrate, when grown with 3, 5-xylenol. However, when m-cresol was the growth substrate, similar experiments suggested a different pathway involving a methyl-substituted catechol, and ring-fission by meta cleavage. Assays of ring-fission enzymes in cell-free extracts confirmed that different pathways are induced by the two growth substrates. 3, 5-Xylenol-grown cells contained high levels of gentisate oxygenase and only very small amounts of catechol oxygenase, whereas gentisate ocygenase could not be detected in m-cresol-grown cells, but levels of catechol oxygenase were greatly increased. Extracts of m-cresol-grown cells also contained 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde dehydrogenase and hydrolase, whose specificities enable them to metabolize the ring-fission products from catechol, 3-methylcatechol, and 4-methylcatechol. This catechol pathway is also used by m-cresol-grown cells for p-cresol metabolism. In contrast, the results for cells grown with p-cresol point to an alternative pathway involving oxidation to 4-hydroxybenzoate and hydrosylation to protocatechuate as ring-fission substrate. Extracts of these cells contained high levels of protocatechuate oxygenase and only small amounts of catechol oxygenase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S., Gibson D. T. The metabolism of cresols by species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):293–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1010293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., CHAPMAN P. J., GIBSON D. T., WOOD J. M. DEGRADATION OF THE BENZENE NUCLEUS BY BACTERIA. Nature. 1964 May 23;202:775–778. doi: 10.1038/202775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist C. F., Hegeman G. D. Phenol and benzoate metabolism by Pseudomonas putida: regulation of tangential pathways. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.869-877.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Metabolism of l-Malate and d-Malate by a Species of Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1197–1202. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1197-1202.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. The enzymic degradation of alkyl-substituted gentisates, maleates and malates. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;122(1):29–40. doi: 10.1042/bj1220029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J. Gentisic acid and its 3- and 4-methyl-substituted homologoues as intermediates in the bacterial degradation of m-cresol, 3,5-xylenol and 2,5-xylenol. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;122(1):19–28. doi: 10.1042/bj1220019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa T., Yokota T. Benzoate metabolism in Pseudomonas putida(arvilla) mt-2: demonstration of two benzoate pathways. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):262–267. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.262-267.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTON L. N., STANIER R. Y. MECHANISM OF BETA-KETOADIPATE FORMATION BY BACTERIA. Nature. 1964 Dec 26;204:1279–1283. doi: 10.1038/2041279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERGER R. F., ELSDEN S. R. The yields of Streptococcus faecalis grown in continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Jun;22:726–739. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-3-726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothera A. C. Note on the sodium nitro-prusside reaction for acetone. J Physiol. 1908 Dec 15;37(5-6):491–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1908.sp001285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Evans W. C. The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species. 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):400–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Murray K., Williams P. A. The metabolic divergence in the meta cleavage of catechols by Pseudomonas putida NCIB 10015. Physiological significance and evolutionary implications. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):347–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


