Abstract
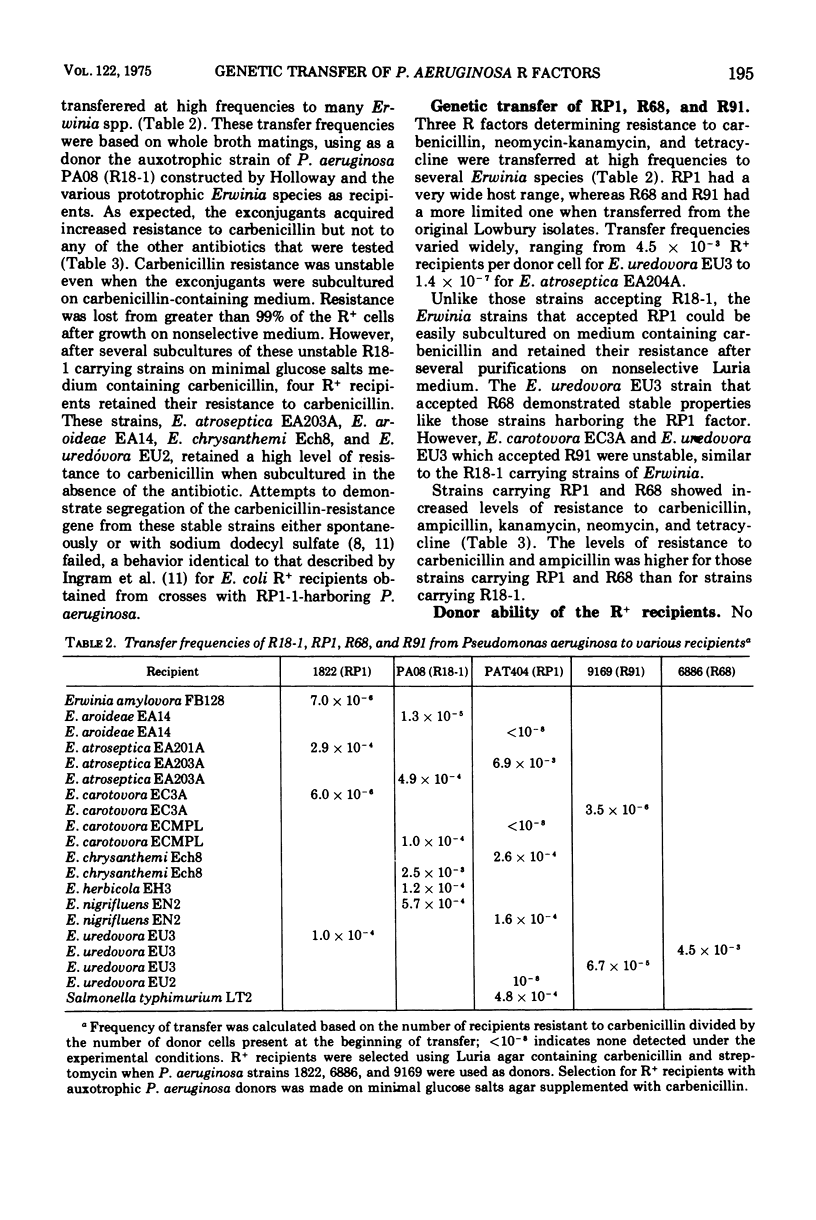
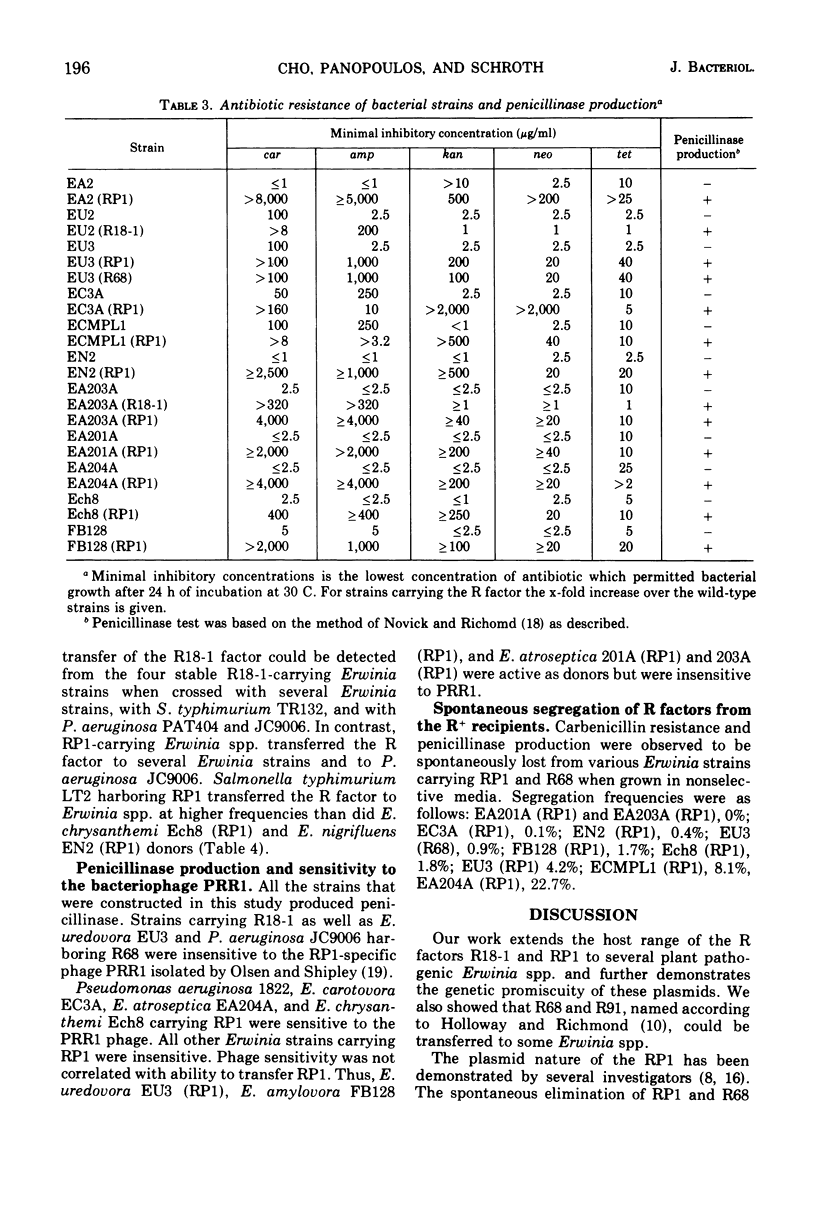
The R factors RP1, R68 and R91 were freely transmissible to and from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella typhimurium, and various plant pathogenic Erwinia spp. The antibiotic resistance spectrum of R+ Erwinia recipients was similar to those of other bacteria harboring these R factors, but maximum resistance levels differed with each recipient. The sponstaneous elimination of these factors from the Erwinia strains and the ability to transfer multiple antibiotic resistance suggest that these exist as plasmids in these hosts. Several, but not all, RP1-carrying Erwinia strains were sensitive to the RP1 specific phage PRR1. The R factor R18-1 was also transferred from P. aeruginosa to Erwinia spp. R18-1 was unstable in all Erwinia strains. Stable strains were isolated in which R18-1 could not be eliminated by sodium dodecyl sulfate and could not be transferred to other strains.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatterjee A. K., Starr M. P. Gene transmission among strains of Erwinia amylovora. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1100–1106. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1100-1106.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. K., Starr M. P. Genetic transfer of episomic elements among Erwinia species and other enterobacteria: F'Lac+. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):169–176. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.169-176.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. K., Starr M. P. Transfer among Erwinia spp. and other enterobacteria of antibiotic resistance carried on R factors. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):576–584. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.576-584.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W. Host ranges of R factors. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):453–460. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W., Shaw E. J., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of an R factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1244–1249. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1244-1249.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., Saunders J. R., Ingram L. C., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of a R factor which originated in Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1822. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):529–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.529-537.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L., Sykes R. B., Grinsted J., Saunders J. R., Richmond M. H. A transmissible resistance element from a strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa containing no detectable extrachromosomal DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):269–279. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominos S. D., Copeland C. E., Grosiak B., Postic B. Introduction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa into a hospital via vegetables. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):567–570. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.567-570.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., ADAMS J. N., TING R. C. Transduction of lactose-utilizing ability among strains of E. coli and S. dysenteriae and the properties of the transducing phage particles. Virology. 1960 Nov;12:348–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewontin R. C., Krakauer J. Distribution of gene frequency as a test of the theory of the selective neutrality of polymorphisms. Genetics. 1973 May;74(1):175–195. doi: 10.1093/genetics/74.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A., Kidson A., Ayliffe G. A., Jones R. J. Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antibiotics: emergence of strains highly resistant to carbenicillin. Lancet. 1969 Aug 30;2(7618):448–452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P., RICHMOND M. H. NATURE AND INTERACTIONS OF THE GENETIC ELEMENTS GOVERNING PENICILLINASE SYNTHESIS IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:467–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.467-480.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Shipley P. Host range and properties of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa R factor R1822. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):772–780. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.772-780.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The chromosomal integration of a -lactamase gene derived from the P-type R-factor RP1 in Escherichia coli. Genet Res. 1972 Oct;20(2):231–237. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300013732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. R., Grinsted J. Properties of RP4, an R factor which originated in Pseudomonas aeruginosa S8. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):690–696. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.690-696.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A., Holloway B. W. Chromosome transfer in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mediated by R factors. Genet Res. 1971 Apr;17(2):169–172. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300012179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Intergeneric transfer of a beta-lactamase gene between Ps. aeruginosa and E. coli. Nature. 1970 Jun 6;226(5249):952–954. doi: 10.1038/226952a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. B., Glaser D. A. Evidence for multiple growing points on the genome of rapidly growing E. coli B-r. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):800–804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



