Abstract
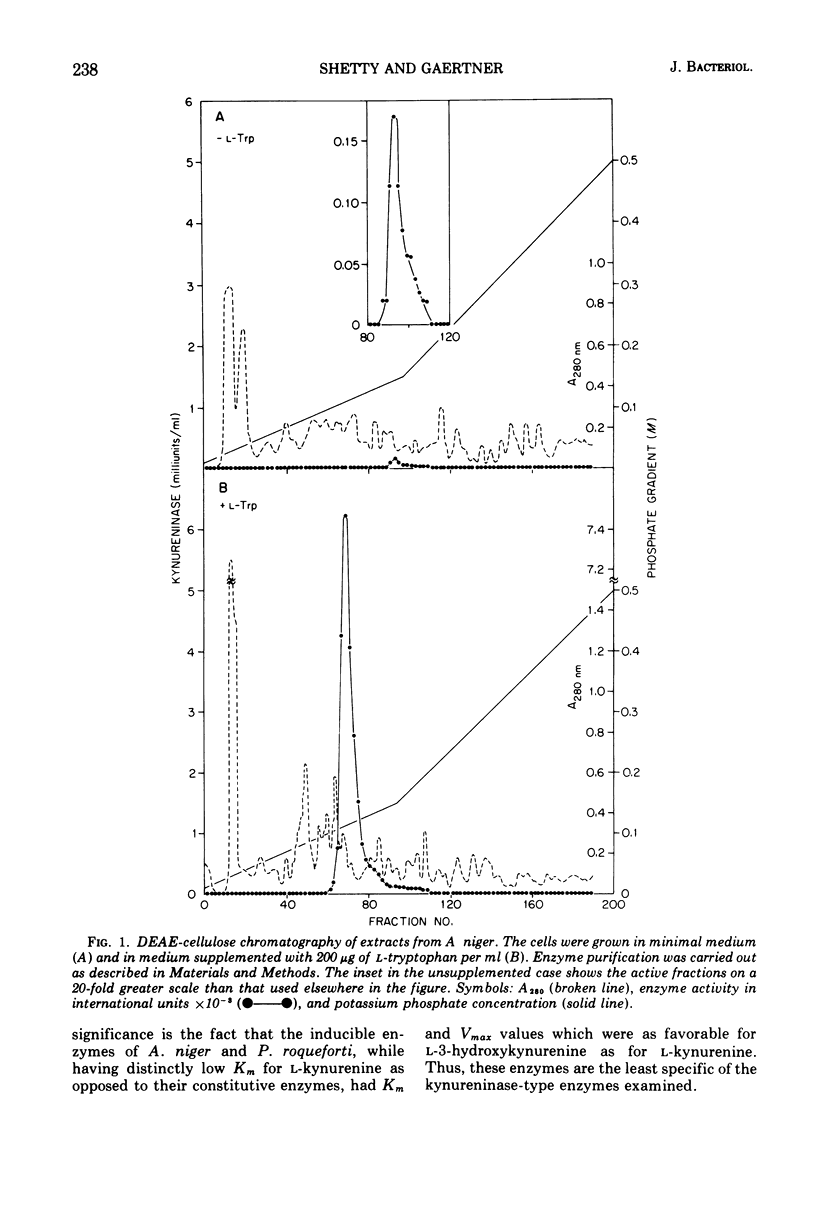
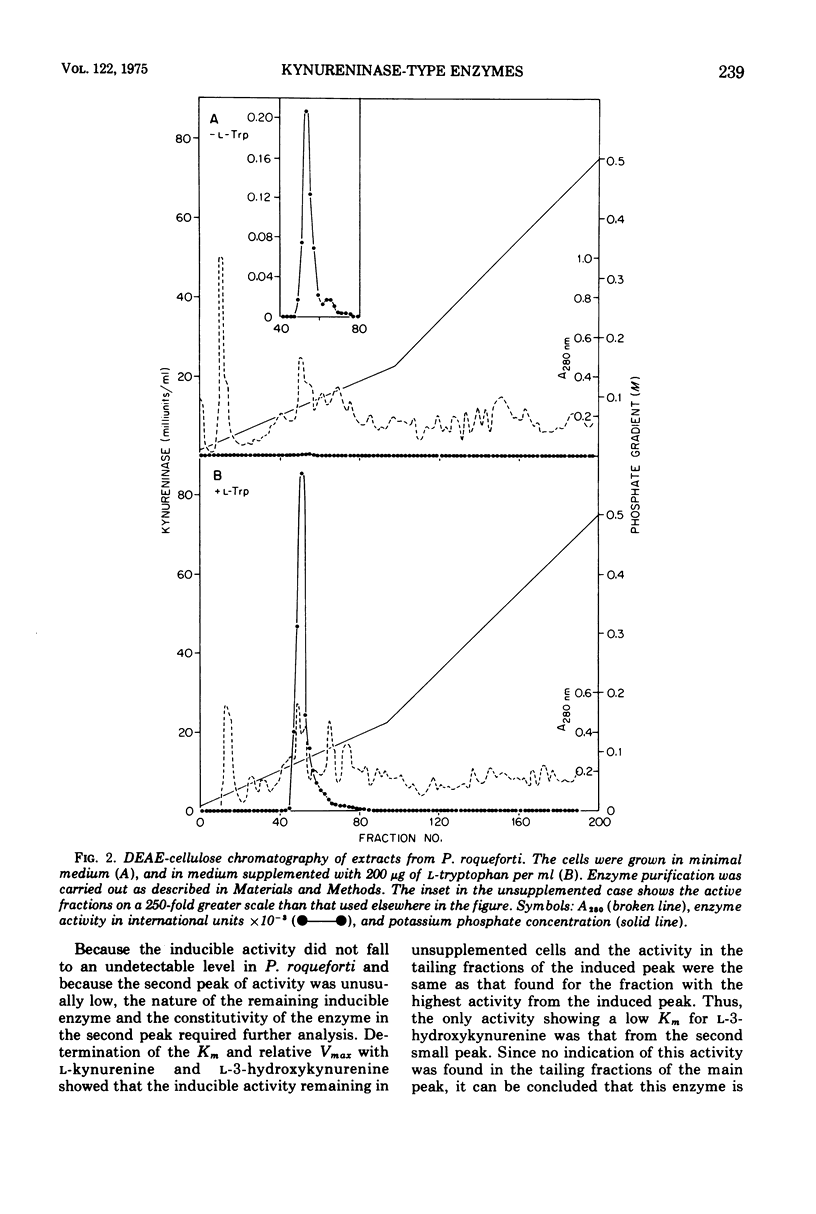
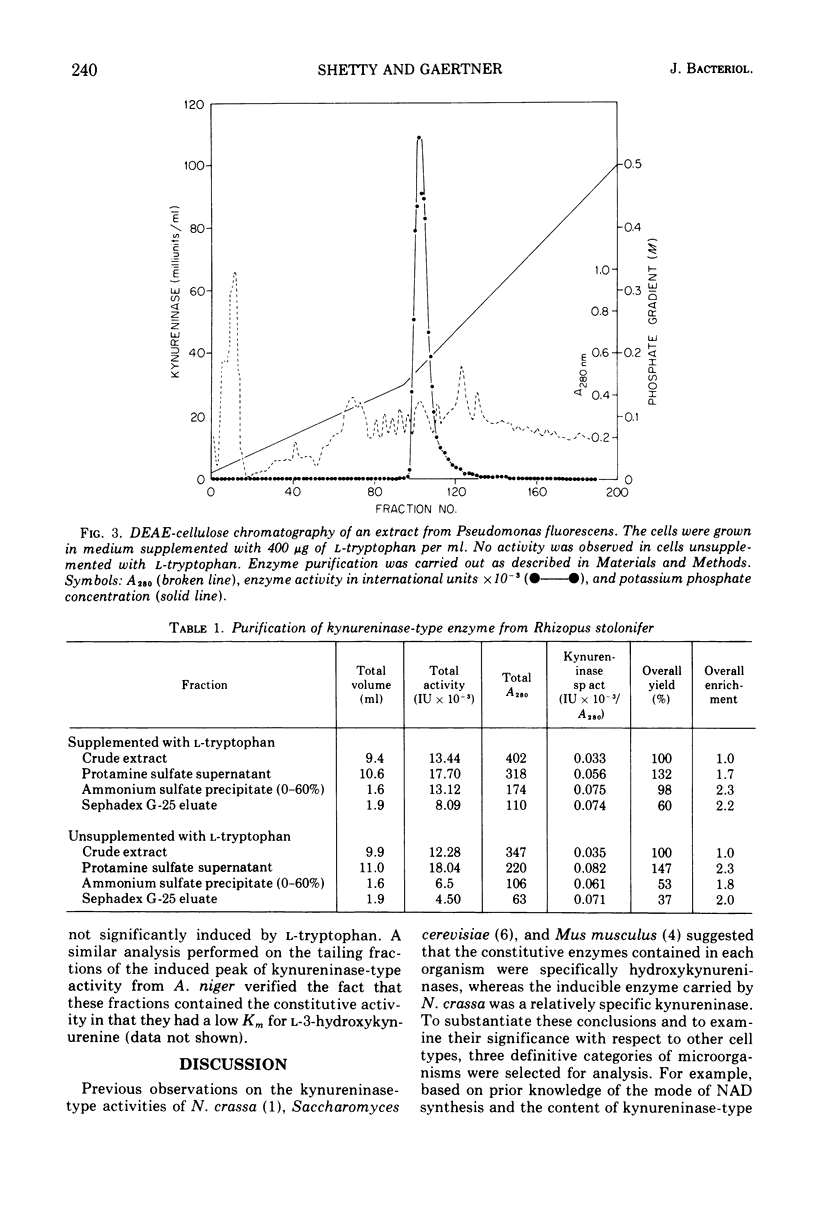
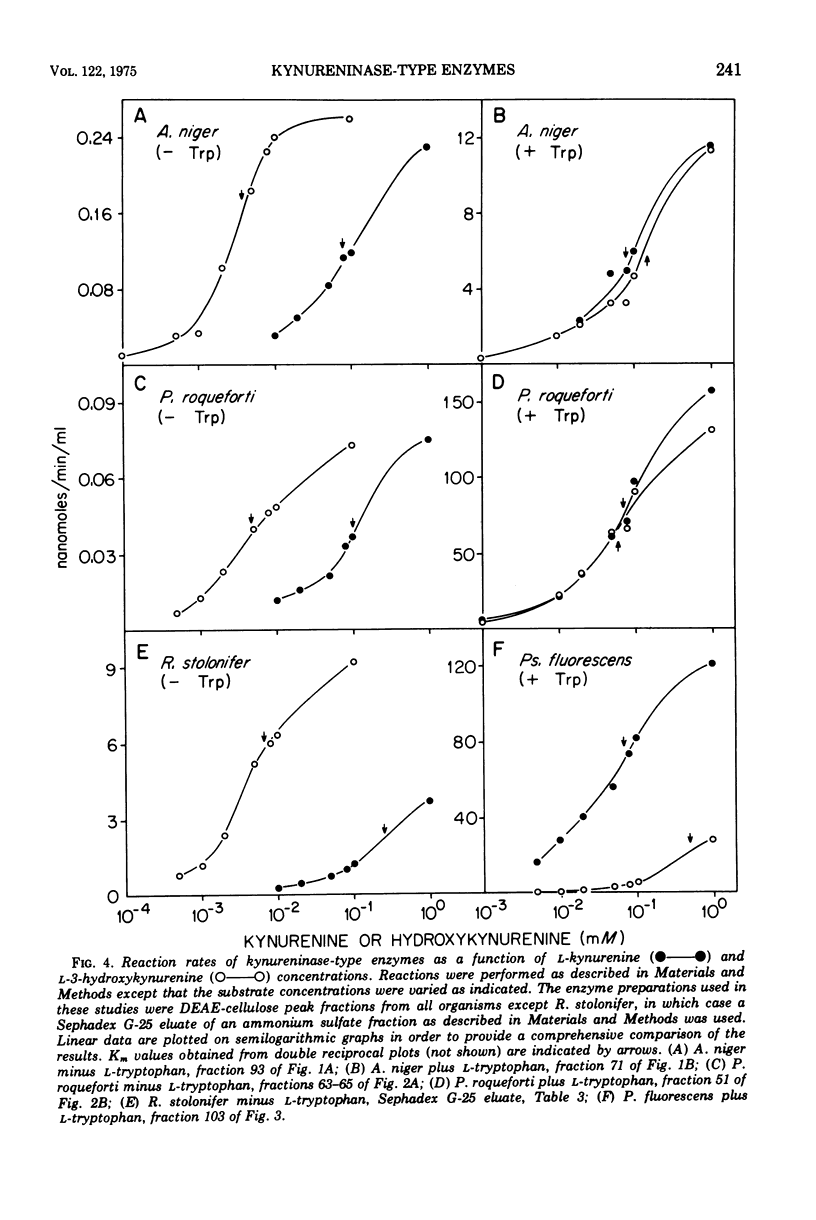
The kynureninase-type enzymes of three fungi and one bacterium were isolated and examined kinetically for their ability to catalyze the hydrolysis of L-kynurenine and L-3-hydroxykynurenine. The phycomycete Rhizopus stolonifer was found to contain a single, constitutive enzyme with Km for L-3-hydroxykynurenine and L-kynurenine of 6.67 times 10-minus 6 and 2.5 times 10-minus 4 M, respectively. The ascomycetes Aspergillus niger and Penicillium roqueforti each contain an enzyme, induced by L-tryptophan, with similar Km for L-3-hydroxykynurenine and L-kynurenine ranging from 5.9 times 10-minus 5 to 14.3 times 10-minus 5 M, as well as a constitutive enzyme with Km for the two substrates of similar to 4 times 10-minus 6 M and 10-minus 4 M. The bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens has a single, inducible enzyme with Km for L-3-hydroxykynurenine and L-kynurenine of 5 times 10-minus 4 and 7 times 10-minus 5 M. In addition, significant differences in maximal velocities (Vmax) were observed in two cases. The Vmax of the inducible activity from P. fluorescens was 4.5 times greater for L-kynurenine than L-3-hydroxykynurenine, whereas the Vmax of the constitutive activity from R. stolonifer was 2.5 times greater for L-3-hydroxykynurenine. It is concluded (i) that the constitutive activities are hydroxykynureninases involved in the biosynthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide from L-tryptophan, (ii) that the inducible activities are kynureninases involved in the catabolism of L-tryptophan to anthranilate, and (iii) that R. stolonifer and P. fluorescens, respectively, carry the most specific examples of each type of enzyme.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gaertner F. H., Cole K. W., Welch G. R. Evidence for distinct kynureninase and hydroxykynureninase activities in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):902–909. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.902-909.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYAISHI O., STANIER R. Y. The kynureninase of Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Biol Chem. 1952 Apr;195(2):735–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAKOBY W. B., BONNER D. M. Kynureninase from Neurospora: purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1953 Dec;205(2):699–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott C. E., Casciano D. A., Gaertner F. H. Isolation and characterization of an hydroxykynureninase from homogenates of adult mouse liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 2;51(3):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlitt S. C., Lester G., Russell P. J. Isolation and characterization of low-kynureninase mutants of Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1117–1120. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1117-1120.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shetty A. S., Gaertner F. H. Distinct kynureninase and hydroxykynureninase activities in microorganisms: occurrence and properties of a single physiologically discrete enzyme in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1127–1133. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1127-1133.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. R., Drucker H. Kynureninase from Neurospora: occurrence of two activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 19;42(4):698–704. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90544-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


