Abstract
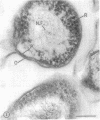
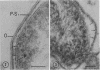
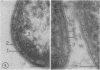
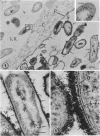
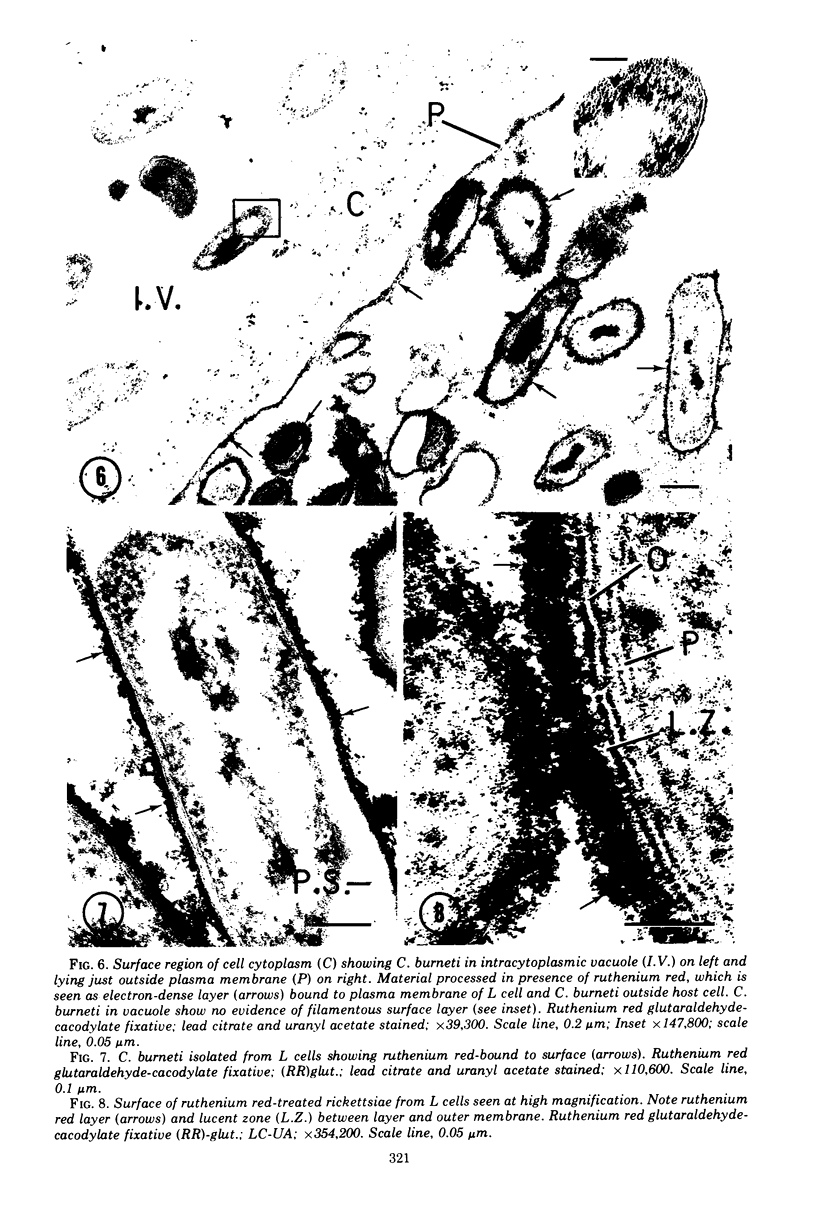
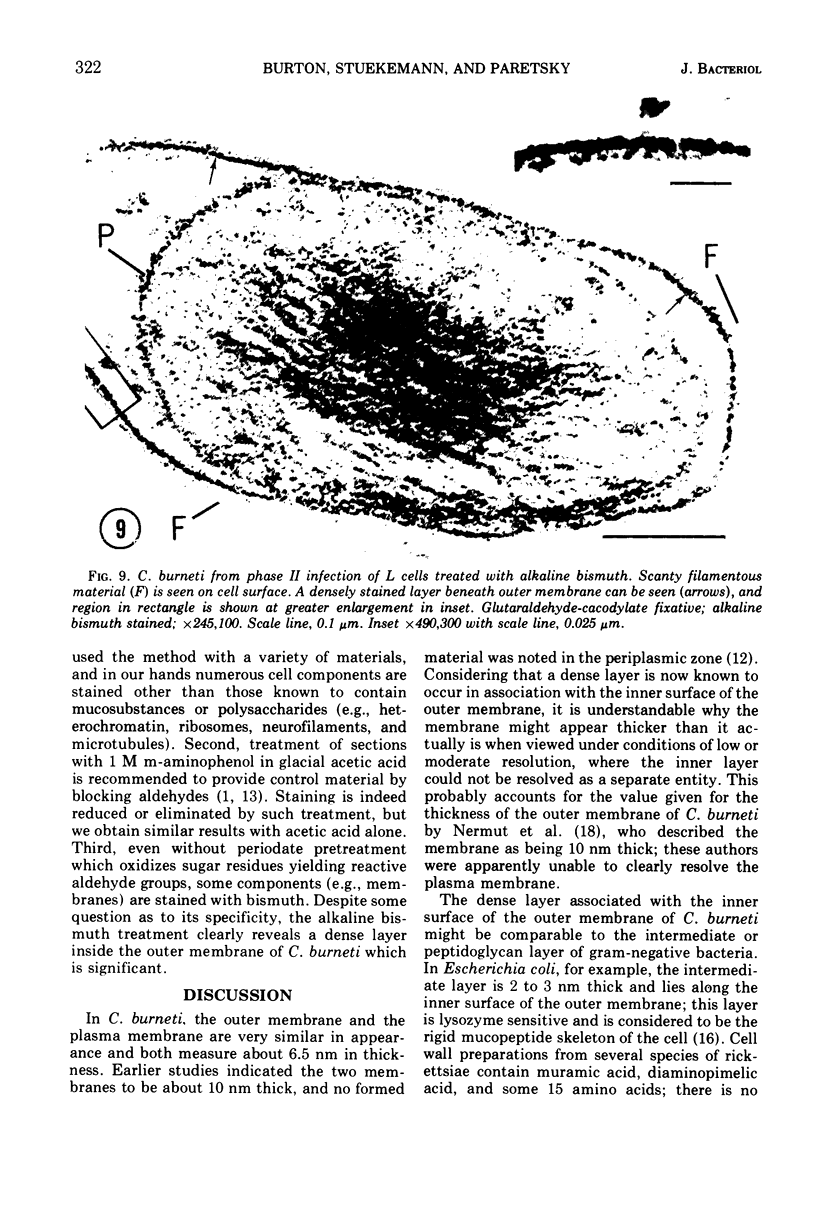
Surface layers of Coxiella burneti studied at a high resoulution reveal a plasma membrane and an outer surface membrane 6 to 7 nm thick, and a thin, moderately electron-dense intermediate layer associated with the inner surface of the outer membrane of many cells. This layer appears to be unaffected by lysozyme treatment. Ruthenium red staining was used to delineate a layer of filamentous material external to the outer membrane; this fuzzy layer has a mean thickness of 20 nm and is not often seen on the surface of cells prepared by conventional means. Both antigenic phase I and II cells show a ruthenium red-binding surface layer. It is suggested that this fuzzy layer may be, among other possibilities, a highly branched mucopolysaccharide.
Full text
PDF

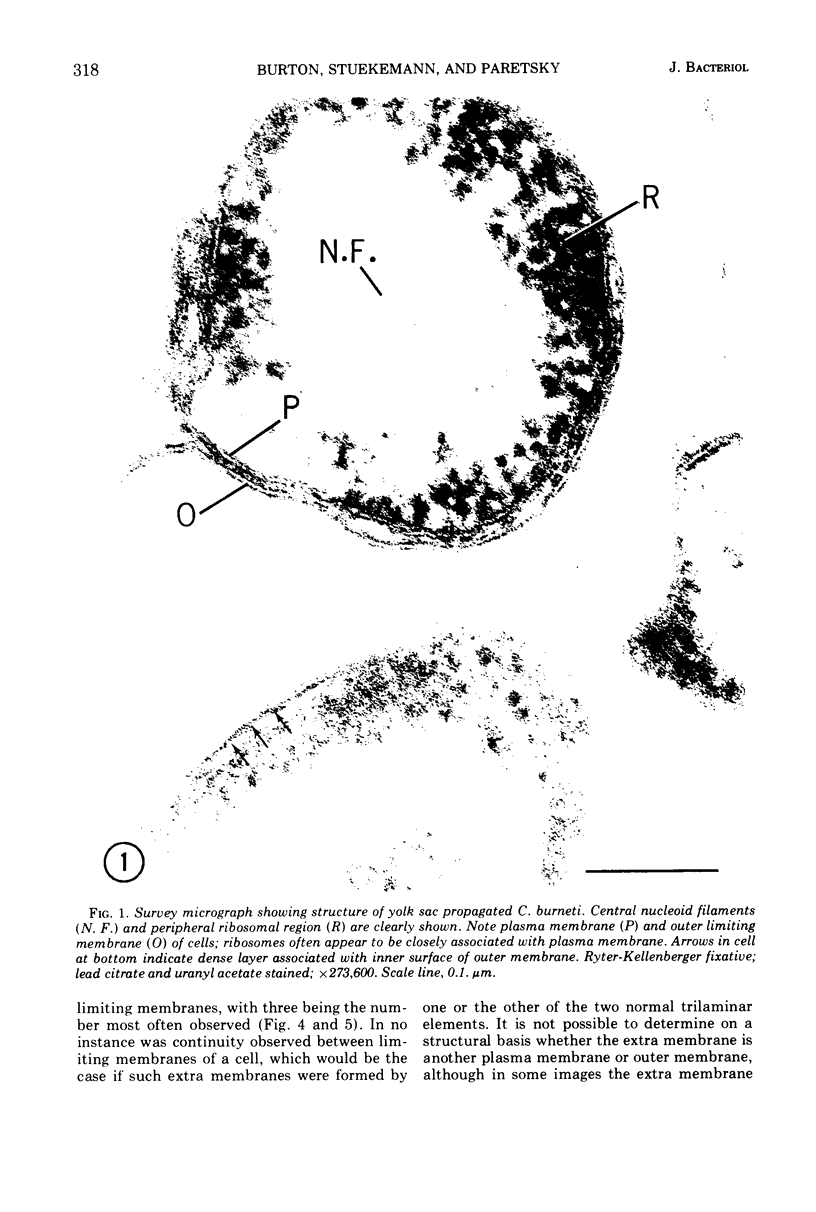


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANACKER R. L., FUKUSHI K., PICKENS E. G., LACKMAN D. B. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF COXIELLA BURNETII IN THE CHICK YOLK SAC. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1130–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1130-1138.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth S. K., Ito S., Karnovsky M. J. Alkaline bismuth reagent for high resolution ultrastructural demonstration of periodate-reactive sites. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Dec;20(12):995–1005. doi: 10.1177/20.12.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Partial chemical characterization of a toxic lipopolysaccharide from Coxiella burneti. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):959–961. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.959-961.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Some physiological and biochemical effects of a Coxiella burneti lipopolysaccharide preparation on guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):939–945. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.939-945.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton L. P., Burgdorfer W. Fine structure of Rickettsia canada in tissues of Dermacentor andersoni Stiles. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1149–1159. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1149-1159.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R., Kordová N., Paretsky D. Electron microscopic studies of the rickettsia Coxiella burneti: entry, lysosomal response, and fate of rickettsial DNA in L-cells. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Feb;17(2):143–150. doi: 10.1139/m71-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciampor F., Schramek S., Brezina R. Electron microscopy of ruthenium red-stained phase I and II Coxiella burneti. Acta Virol. 1972 Nov;16(6):503–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Costerton J. W., Macleod R. A. Separation and localization of cell wall layers of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1338–1353. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1338-1353.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITO S., VINSON J. W. FINE STRUCTURE OF RICKETTSIA QUINTANA CULTIVATED IN VITRO AND IN THE LOUSE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:481–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.481-495.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):369–415. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., STEED P., ELSON H. E. THE LOCATION OF THE MUCOPEPTIDE IN SECTIONS OF THE CELL WALL OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:547–560. doi: 10.1139/m65-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nermut M. V., Schramek S., Brezina R. Electron microscopy of Coxiella burneti phase I and II. Acta Virol. 1968 Sep;12(5):446–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKINS H. R., ALLISON A. C. Cell-wall constituents of rickettsiae and psittacosis-lymphogranuloma organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:469–480. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. L., Ordal E. J. The fine structure of Chondrococcus columnaris. 3. The surface layers of Chondrococcus columnaris. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):37–51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. A., Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Presence of ribosomal ribonucleic acid in the rickettsia Coxiella burneti. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):365–366. doi: 10.1042/bj1250365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebe M. E., Burton P. R., Shankel D. M. Isolation and characterization of two cell types of Coxiella burneti phase I. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):368–377. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.368-377.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. H., Jr, Wisseman C. L., Jr The cell wall of Rickettsia mooseri. I. Morphology and chemical composition. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1113–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1113-1118.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]