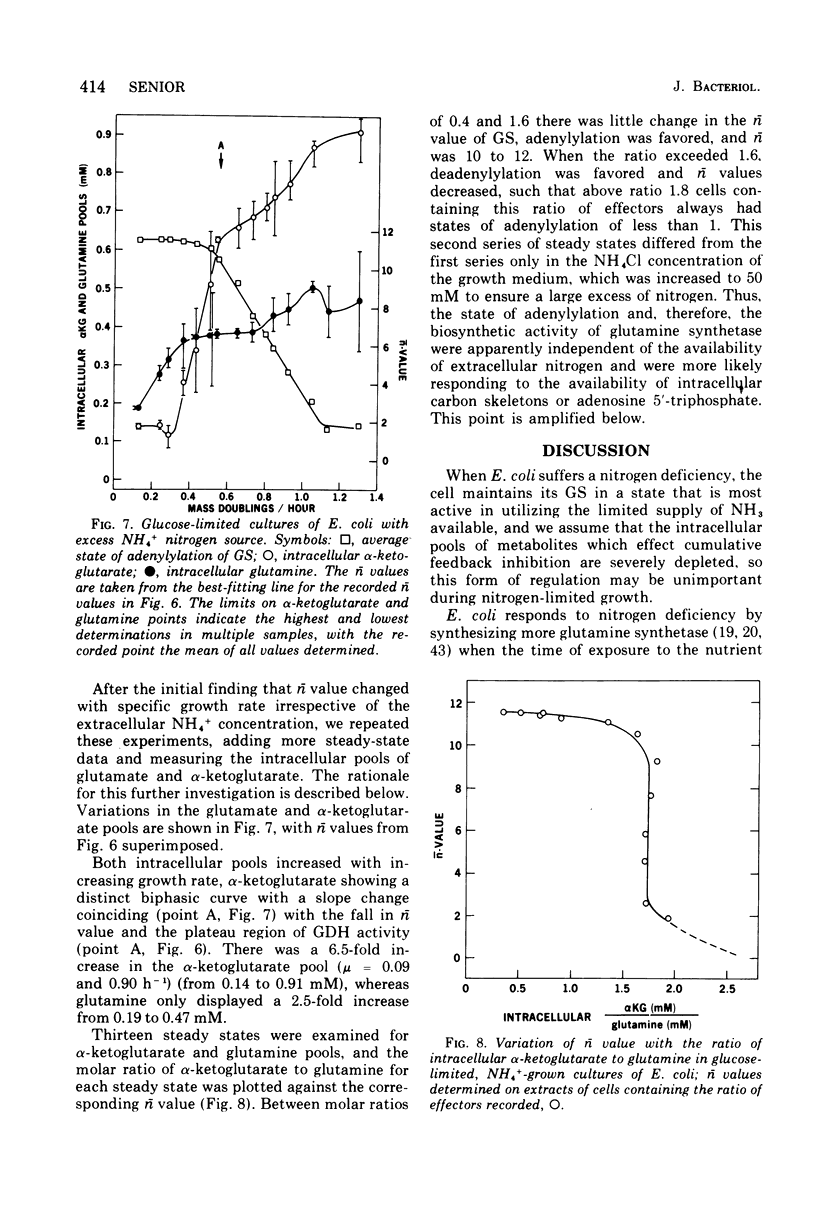
Abstract
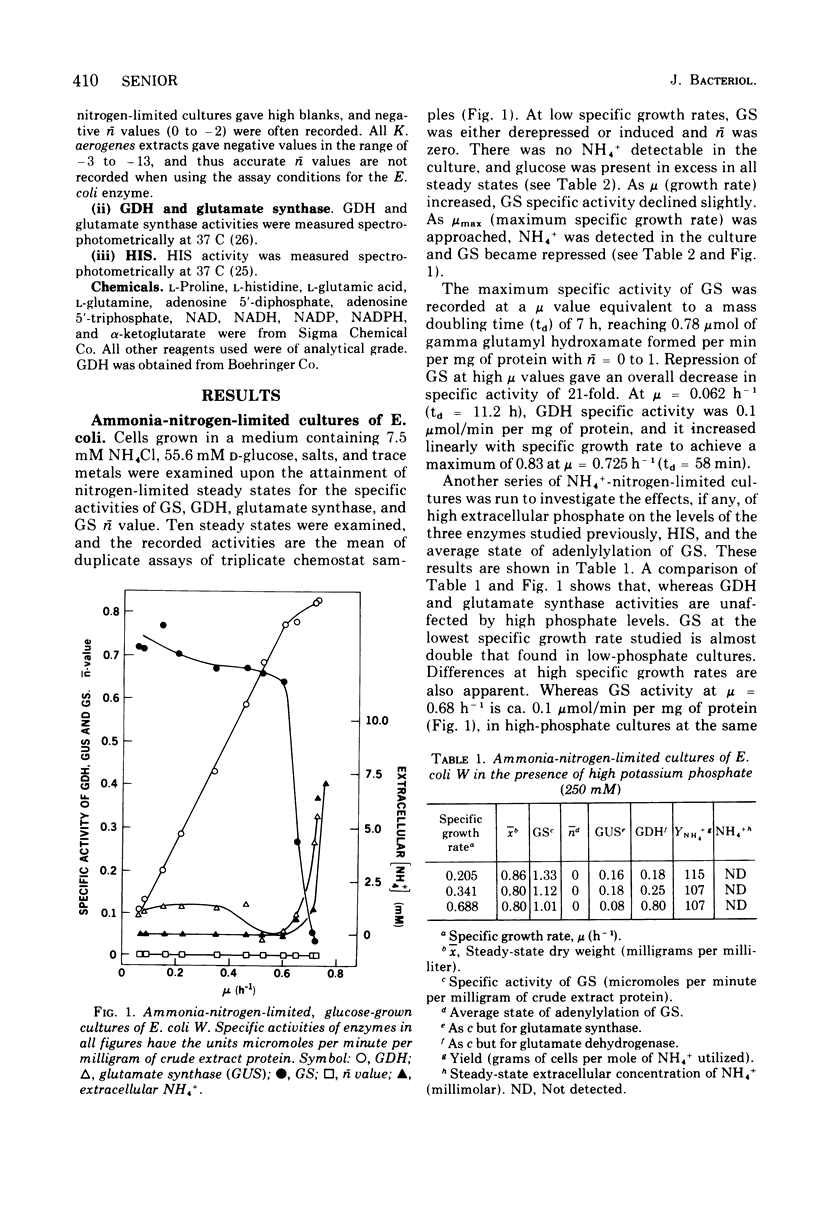
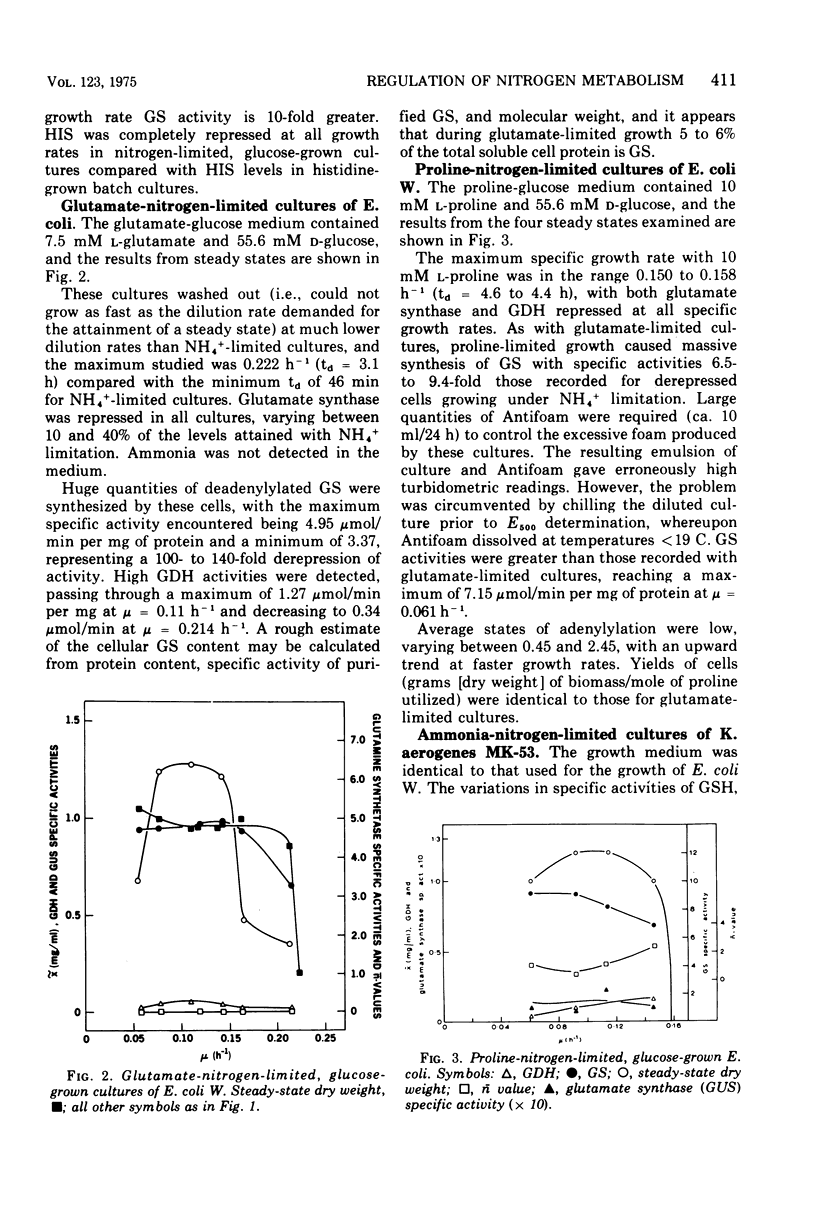
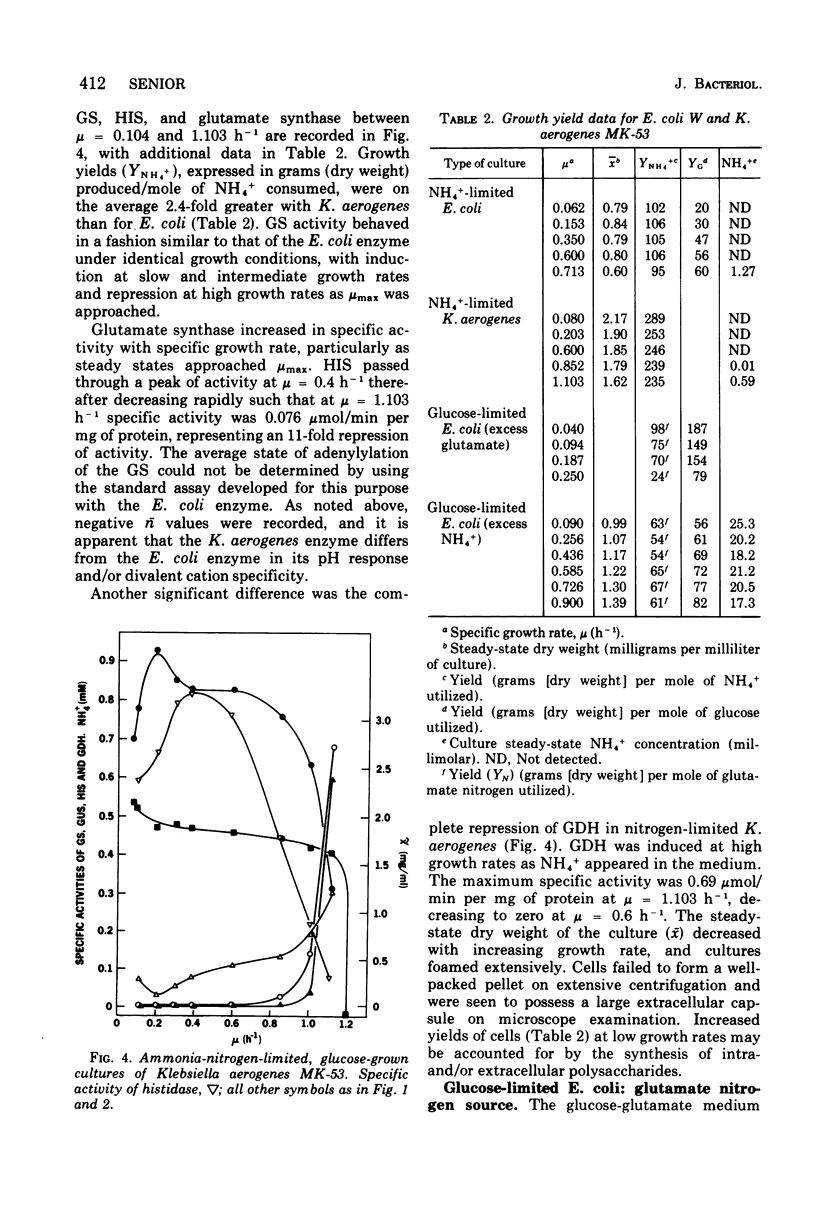
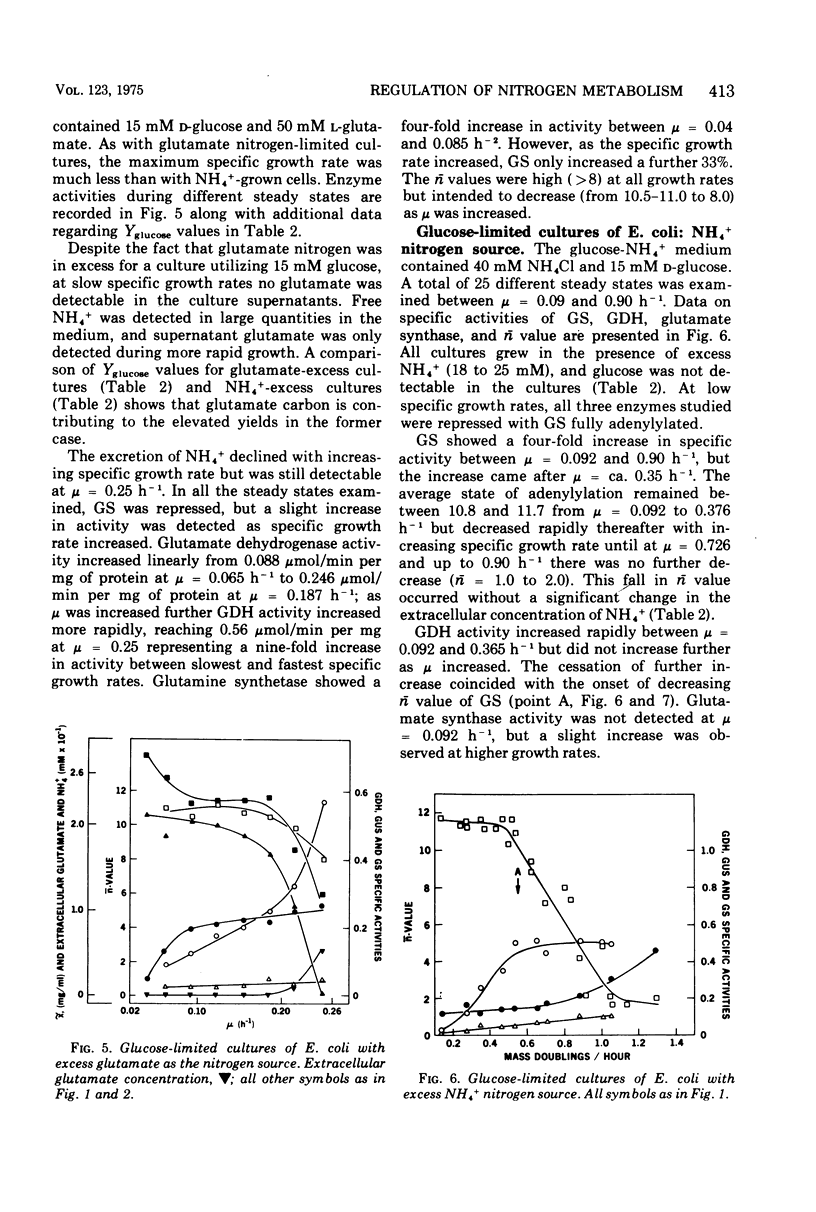
Ammonia-nitrogen-limited continuous cultures of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella aerogenes contain induced levels of glutamine synthetase that is deadenylyated (i.e., fully active). In the presence of excess ammonia or glutamate in glucose-limited cultures of E. coli, glutamine synthetase is repressed and adenylylated (inactive). The average state of adenylylation (n) is a linear function of the specific growth rate. At low specific growth rates, glutamine synthetase is adenylylated; as the specific growth rate increases, n decreases, approaching 0 to 2 at rapid growth rates. The average state of adenylylation correlates well with the intracellular concentrations and ratios of alpha-ketoglutarate and glutamine, which are key effectors in the adenylylation-deadenylylation systems. E. coli and K. aerogenes differ markedly in their growth yields, growth rates, and enzymatic composition during nitrogen limitation. The data suggest that, unlike K. aerogenes, E. coli W uses glutamate dehydrogenase to incorporate ammonia during nitrogen limitation. In E. coli, glutamate dehydrogenase is progressively induced during nitrogen limitation when mu (growth rate) approaches mumax. In contrast, in K. aerogenes glutamate dehydrogenase is repressed during nitrogen limitation, whereas glutamate synthase, an alternative supplier of glutamate to the cell, is induced. Data are presented that support the regulatory schemes proposed for the control of glutamine synthetase activity by induction-repression phenomena and adenylylation-deadenylylation reaction. We propose that the intracellular ratio of alpha-ketoglutarate to glutamine may be the most important physiological parameter in determining the activity of glutamine synthetase.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. B., Hennig S. B., Ginsburg A., Stadtman E. R. Association of ATP: glutamine synthetase adenylyltransferase activity with the P1 component of the glutamine synthetase deadenylylation system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1417–1424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. B., Stadtman E. R. Purification and functional roles of the P I and P II components of Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase deadenylylation system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Apr;143(2):428–443. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90229-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich M. A. A glutamate-dependent phenotype in E. coli K12: the result of two mutations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1498–1503. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Segal A., Stadtman E. R. Modulation of glutamine synthetase adenylylation and deadenylylation is mediated by metabolic transformation of the P II -regulatory protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2949–2953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton M. D., Ginsburg A. Some characteristics of the binding of substrates of glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 3;9(3):617–632. doi: 10.1021/bi00805a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebner E., Wolf D., Gancedo C., Elsässer S., Holzer H. ATP: glutamine synthetase adenylyltransferase from Escherichia coli B. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jul;14(3):535–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmerich C., Aubert J. P. Synthesis of glutamate by a glutamine: 2-oxo-glutarate amidotransferase (NADP oxidoreductase) in Bacillus megaterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 5;42(3):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gancedo C., Holzer H. Enzymatic inactivation of glutamine synthetase in Enterobacteriaceae. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Apr 3;4(2):190–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg A., Yeh J., Hennig S. B., Denton M. D. Some effects of adenylylation on the biosynthetic properties of the glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 3;9(3):633–649. doi: 10.1021/bi00805a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig S. B., Ginsburg A. ATP: glutamine synthetase adenylytransferase from Escherichia coli: purification and properties of a low-molecular weight enzyme form. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jun;144(2):611–627. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90368-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer H. Regulation of enzymes by enzyme-catalyzed chemical modification. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:297–326. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon H. S., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. 8. ATP: glutamine synthetase adenylyltransferase, an enzyme that catalyzes alterations in the regulatory properties of glutamine synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1703–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon H. S., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. X. Effect of growth conditions on the susceptibility of Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase to feedback inhibition. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):949–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.949-957.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry O. H., Carter J., Ward J. B., Glaser L. The effect of carbon and nitrogen sources on the level of metabolic intermediates in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6511–6521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecke D., Holzer H. Repression und inaktivierung von Glutaminsynthetase in Escherichia coli durch NH4+. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 10;122(2):341–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers J. L., Tempest D. W. Regulation of glutamine synthetase synthesis in some gram-negative bacteria. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(3):603–605. doi: 10.1042/bj1190603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E., Stadtman E. R. Glutamate synthase from Escherichia coli. An iron-sulfide flavoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7407–7419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prival M. J., Brenchley J. E., Magasanik B. Glutamine synthetase and the regulation of histidase formation in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4334–4344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prival M. J., Magasanik B. Resistance to catabolite repression of histidase and proline oxidase during nitrogen-limited growth of Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6288–6296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S., Miller R. E., Valentine R. C. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate control of the enzymes of glutamine metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2922–2926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebello J. L., Strauss N. Regulation of synthesis of glutamine synthase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):683–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.683-688.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutt H., Holzer H. Biological function of the ammonia-induced inactivation of glutamine synthetase in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 15;26(1):68–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior P. J., Beech G. A., Ritchie G. A., Dawes E. A. The role of oxygen limitation in the formation of poly- -hydroxybutyrate during batch and continuous culture of Azotobacter beijerinckii. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1193–1201. doi: 10.1042/bj1281193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. M., Kingdon H. S., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. VII. Adenylyl glutamine synthetase: a new form of the enzyme with altered regulatory and kinetic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):642–649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. M. The glutamine synthetase deadenylylating enzyme system from Escherichia coli. Resolution into two components, specific nucleotide stimulation, and cofactor requirements. Biochemistry. 1969 Feb;8(2):659–670. doi: 10.1021/bi00830a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R. Allosteric regulation of enzyme activity. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1966;28:41–154. doi: 10.1002/9780470122730.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Ginsburg A., Ciardi J. E., Yeh J., Hennig S. B., Shapiro B. M. Multiple molecular forms of glutamine synthetase produced by enzyme catalyzed adenylation and deadenylylation reactions. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1970;8:99–118. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(70)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Shapiro B. M., Ginsburg A., Kingdon H. S., Denton M. D. Regulation of glutamine synthetase activity in Escherichia coli. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1968 Jun;21(2):378–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Meers J. L., Brown C. M. Synthesis of glutamate in Aerobacter aerogenes by a hitherto unknown route. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(2):405–407. doi: 10.1042/bj1170405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B., Deleo A. B., Magasanik B. Activation of transcription of hut DNA by glutamine synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):225–229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfolk C. A., Shapiro B., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. I. Purification and properties of glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):177–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfolk C. A., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. 3. Cumulative feedback inhibition of glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Mar 20;118(3):736–755. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Yuan L. H. Regulation of synthesis of glutamine synthetase in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Apr;51(1):57–65. doi: 10.1099/00221287-51-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulff K., Mecke D., Holzer H. Mechanism of the enzymatic inactivation of glutamine synthetase from E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):740–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


