Abstract
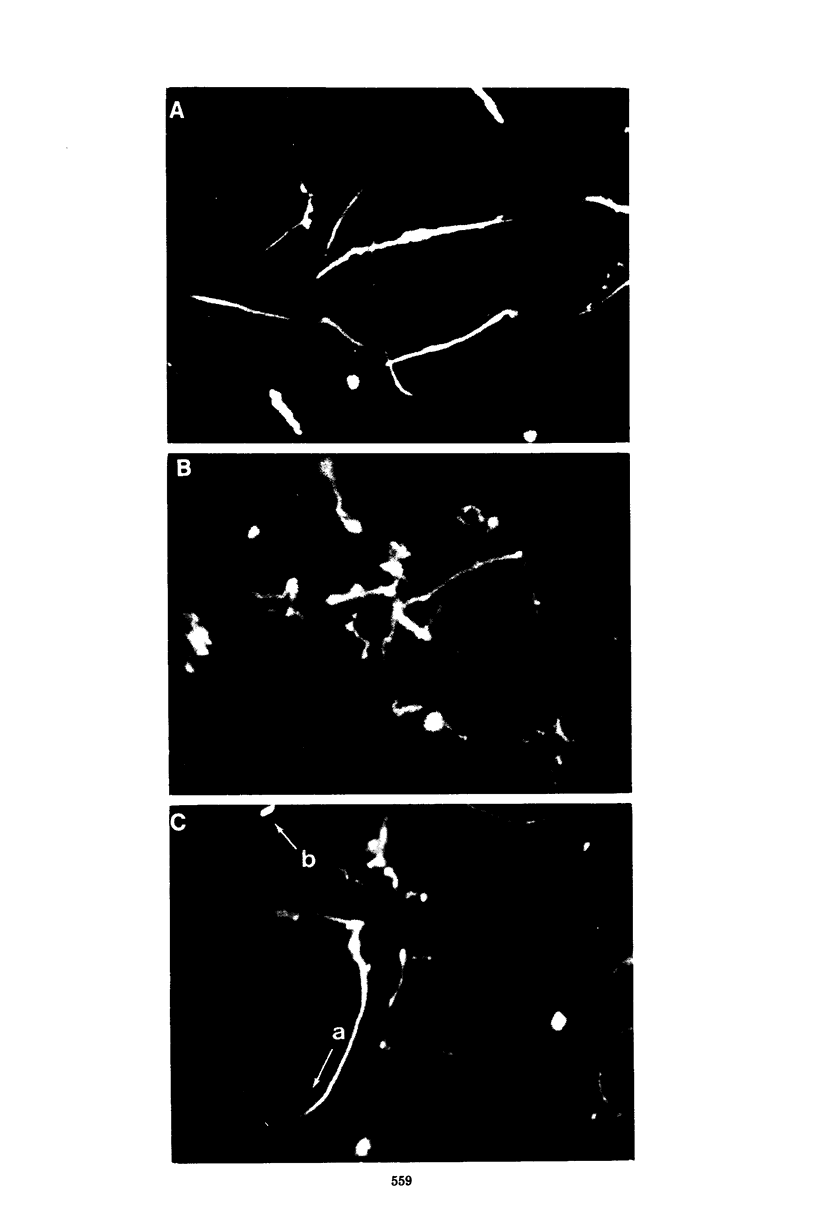
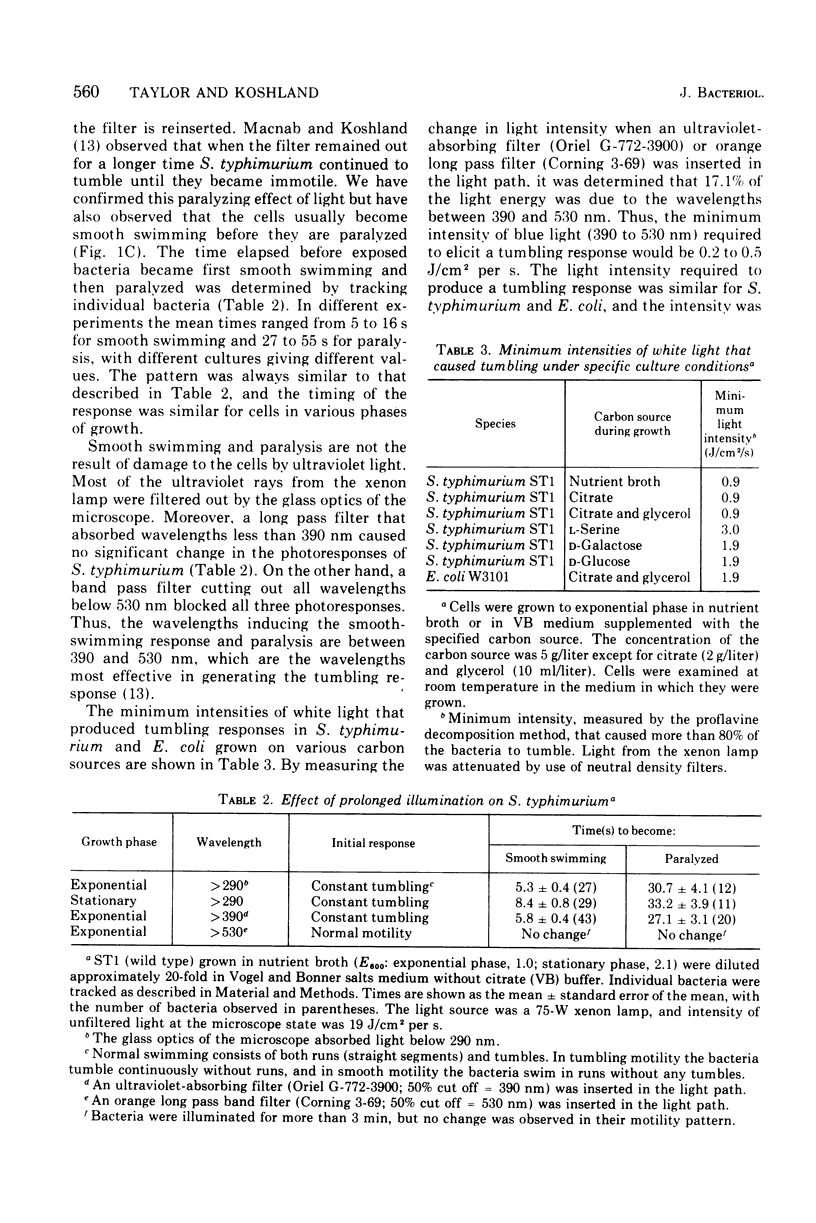
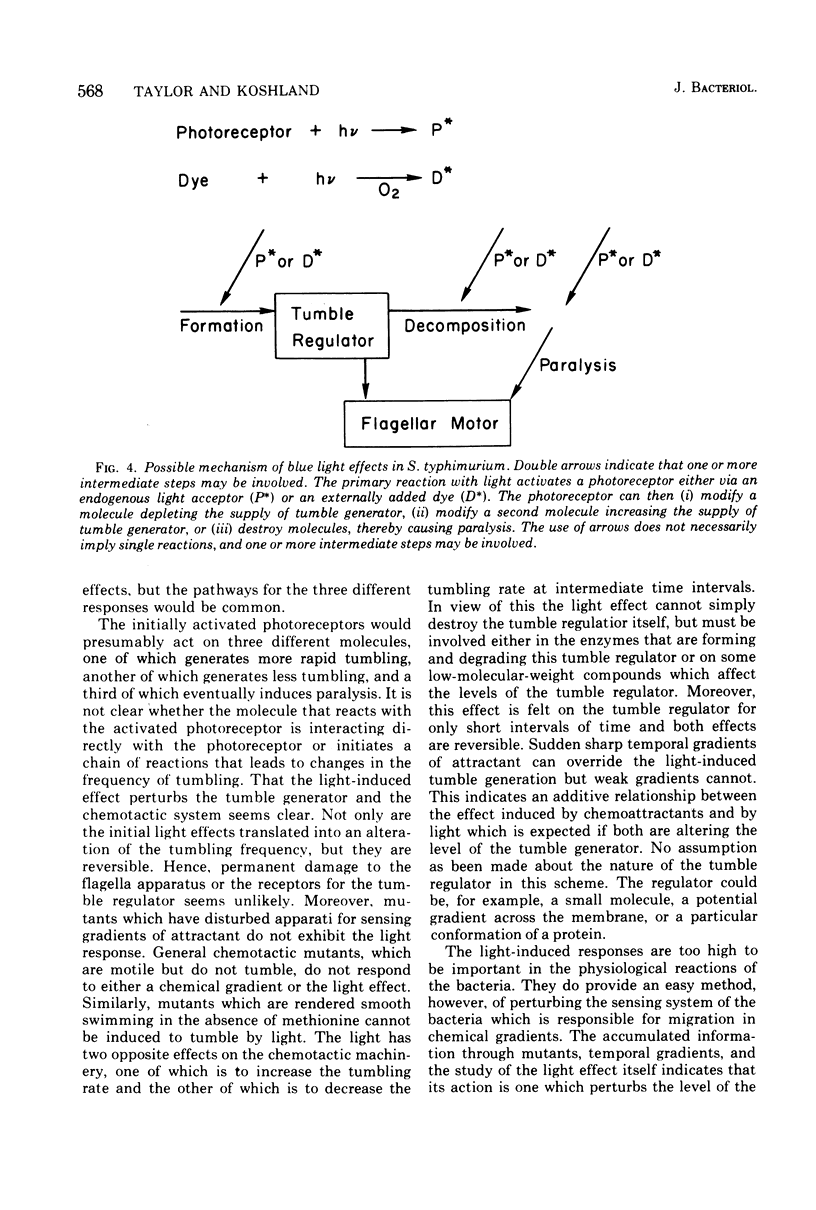
Exposure to intense light in the region between 390 and 530 nm has been shown to have three effects on the motility of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Short pulses of light initiate continuous tumbling. Longer exposures to light induce smooth swimming, and prolonged exposures induced paralysis. The tumbling response is intimately connected with the chemical gradient-sensing apparatus of the bacterium and can be overcome by strong temporal gradients of attractant. Some mutants of S. typhimurium which are defective in the tumble-generating mechanism for chemotaxis are also unable to tumble in intense light. This intrinsic light effect can be mimicked by the addition of external dyes (the classical photodynamic effect), but it can be shown that the two phenomena are distinct. The extrinsic (photodynamic) effect can be inhibited by histidine or by anaerobic conditions, whereas the intrinsic effect is not. The observation that the extrinsic effect can also produce the three types of light responses listed above suggests a common pathway after an intial event on either an endogenous or an externally added photoreceptor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J. Complementation of nonchemotactic mutants of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1969 Jan;61(1):61–66. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J., Dahl M. M. Nonchemotactic mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):390–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.390-398.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B. An S-adenosylmethionine requirement for chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Nov;18(11):1695–1701. doi: 10.1139/m72-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswad D., Koshland D. E., Jr Role of methionine in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):640–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.640-645.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Berg H. C. Temporal stimulation of chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1388–1392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote C. S. Mechanisms of photosensitized oxidation. There are several different types of photosensitized oxidation which may be important in biological systems. Science. 1968 Nov 29;162(3857):963–970. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3857.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Adler J., Gargus J. J., Hogg R. W. Chemomechanical coupling without ATP: the source of energy for motility and chemotaxis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Bacterial motility and chemotaxis: light-induced tumbling response and visualization of individual flagella. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Persistence as a concept in the motility of chemotactic bacteria. J Mechanochem Cell Motil. 1973;2(3):141–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesibov R., Adler J. Chemotaxis toward amino acids in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):315–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.315-326.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY W. J., Jr, KOSHLAND D. E., Jr Identification of amino acids involved in phosphoglucomutase action. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2493–2505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. R., Doetsch R. N. Velocity measurements of motile bacteria by use of a videotape recording technique. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):283–284. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.283-284.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Quantitation of the sensory response in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):710–713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Reversal of flagellar rotation in monotrichous and peritrichous bacteria: generation of changes in direction. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):640–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.640-642.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang N., Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Common mechanism for repellents and attractants in bacterial chemotaxis. Science. 1973 Jul 6;181(4094):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4094.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]