Abstract
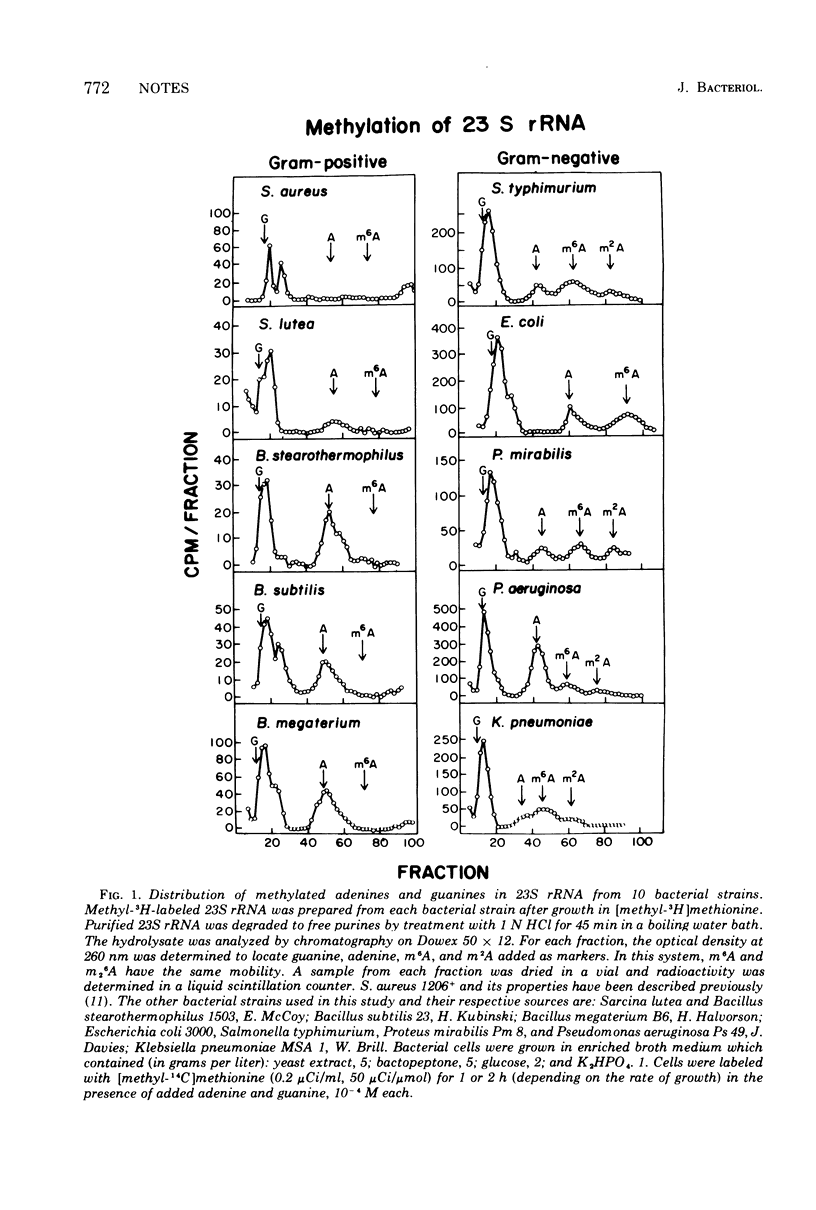
A survey of gram-positive and gram-negative organisms was performed to compare the distributionof N6-methylated adenine. It was found that (i) all the gram-positive strains tested, Staphylococcus aureus, Sarcina lutea, Bacillus stearothermophilus, Bacillus subtilis, and Bacillus megaterium, contain neither N6-monomethyl adenine (m6A) nor N6-dimethyladenine (m26A) in 23S ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA). In the case of S. aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes, strains which are clinically resistant to erythromycin contain m26A. (ii) The gram-negative strains Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella pneumoniae all contain m6A but not m23A in 23S rRNA. These observations suggest the existence of at least one systematic structural difference between the ribosomes of the two classes of bacteria. Because of the demonstrated relationship between N6-dimethylation of adenine in 23S rRNA and clinical resistance to macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin B-type antibiotics in staphylococci and streptococci, the observed systematic differences found in rRNA methylation combined with greater cellular permeability may be related to the relatively greater efficacy of macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin B-type antibiotics in treating infections caused by gram-positive organisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang F. N., Sih C. J., Weisblum B. Lincomycin, an inhibitor of aminoacyl sRNA binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):431–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Weisblum B. The specificity of lincomycin binding to ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):836–843. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Franke A. E. Characterization of a plasmid determining resistance to erythromycin, lincomycin, and vernamycin Balpha in a strain Streptococcus pyogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 May;5(5):534–537. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P. M., Carlier C., Chabbert Y. A. Plasmid-linked tetracycline and erythromycin resistance in group D "streptococcus". Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Dec;123(6):755–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyder S. L., Streitfeld M. M. Inducible and constitutive resistance to macrolide antibiotics and lincomycin in clinically isolated strains of Streptococcus pyogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):327–331. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Dahlberg J. E., Weisblum B. Structure of an inducibly methylatable nucleotide sequence in 23S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from erythromycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):457–460. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Weisblum B., Fahnestock S. R., Nomura M. Alteration of 23 S ribosomal RNA and erythromycin-induced resistance to lincomycin and spiramycin in Staphylococcus aureus. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 15;74(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malke H. Genetics of resistance to macrolide antibiotics and lincomycin in natural isolates of Streptococcus pyogenes. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;135(4):349–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00271149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBENECK U. Susceptibility of Proteus mirabilis and its stable L-forms to erythromycin and other macrolides. Nature. 1962 Oct 13;196:195–196. doi: 10.1038/196195b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Siddhikol C., Lai C. J., Demohn V. Erythromycin-inducible resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: requirements for induction. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):835–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.835-847.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



