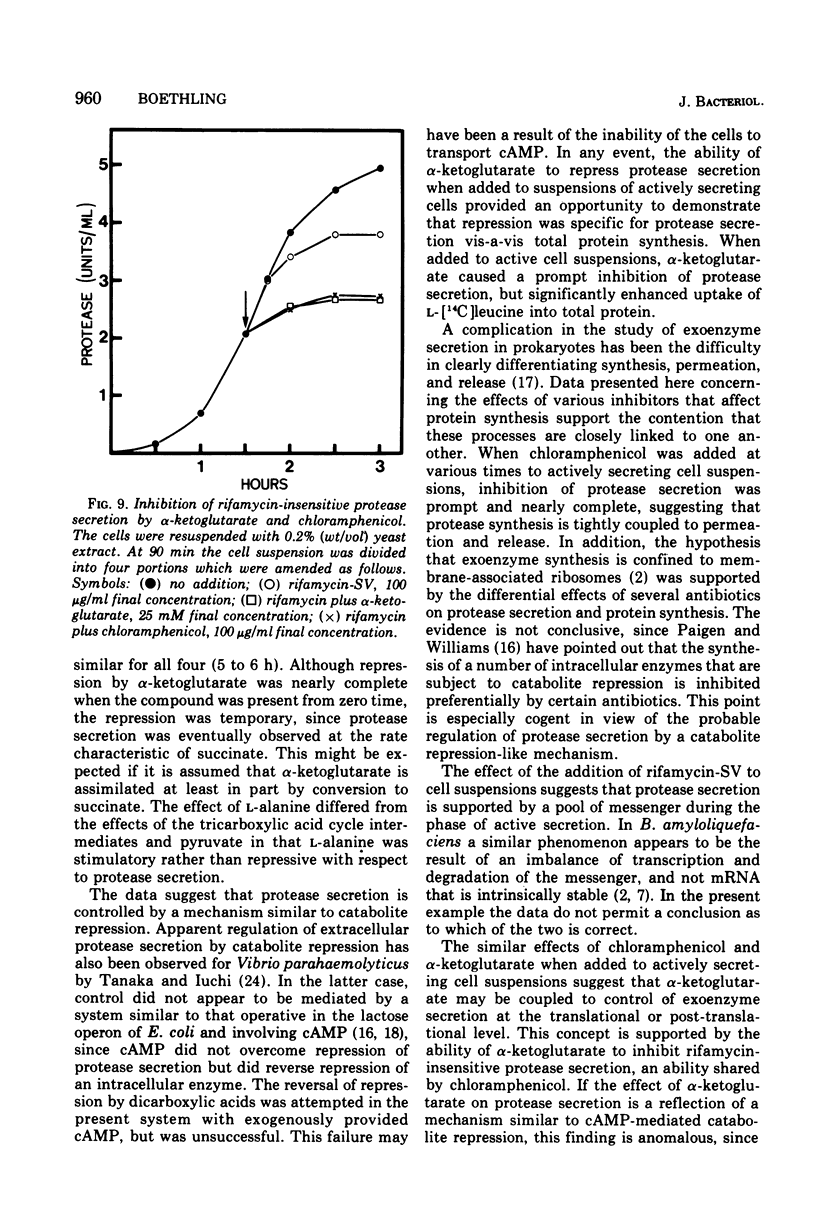
Abstract
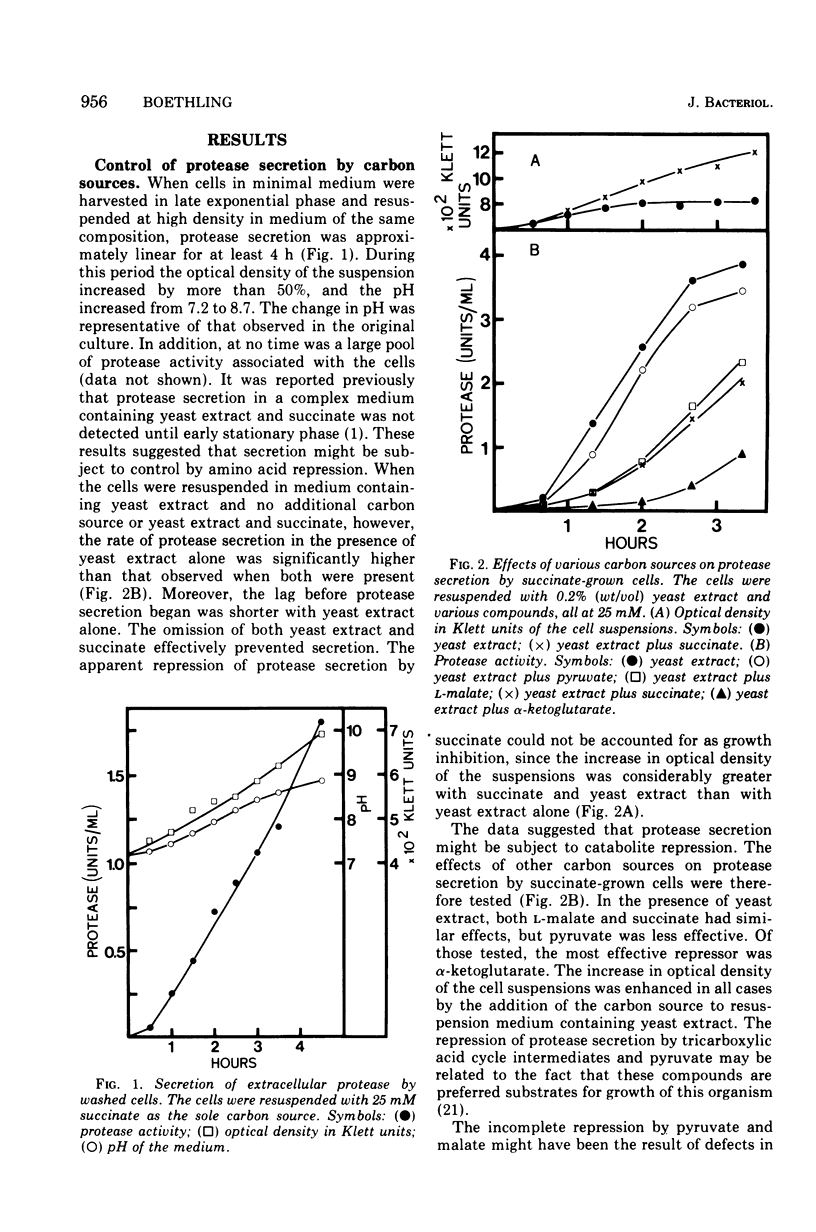
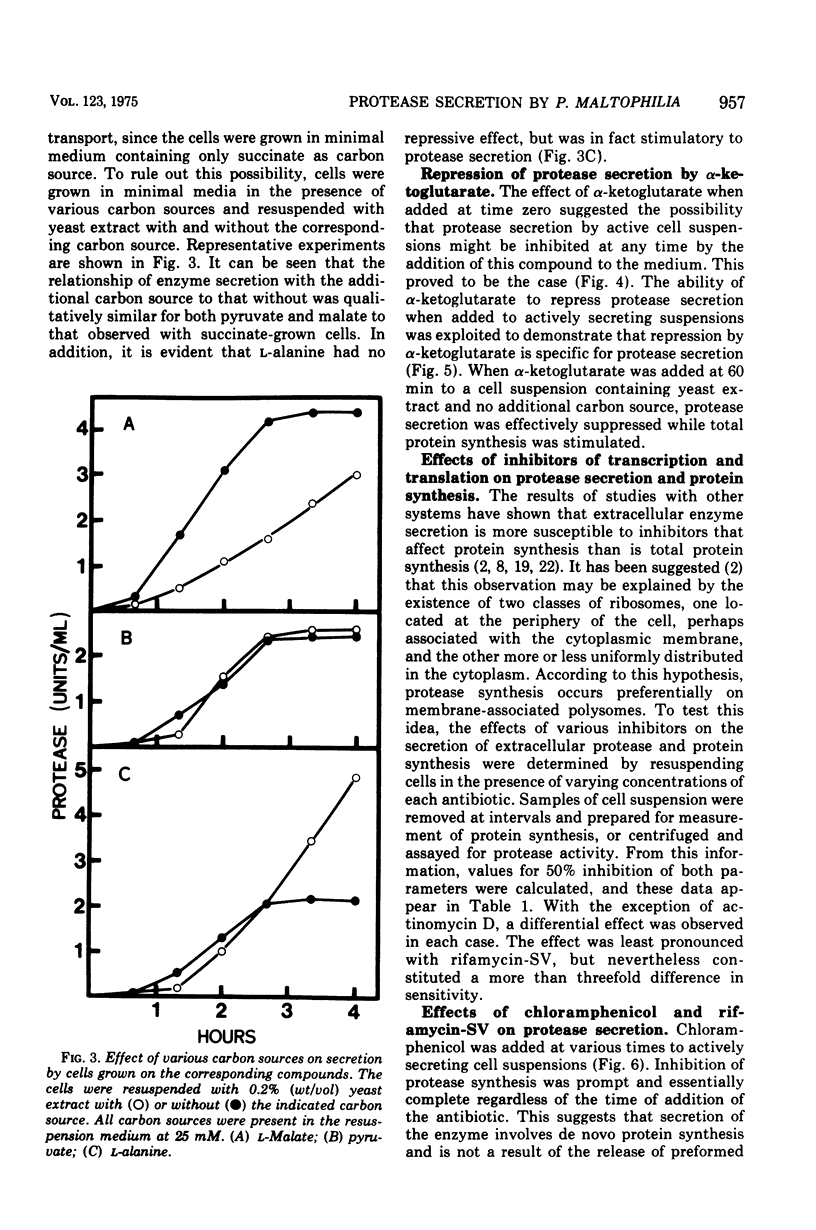
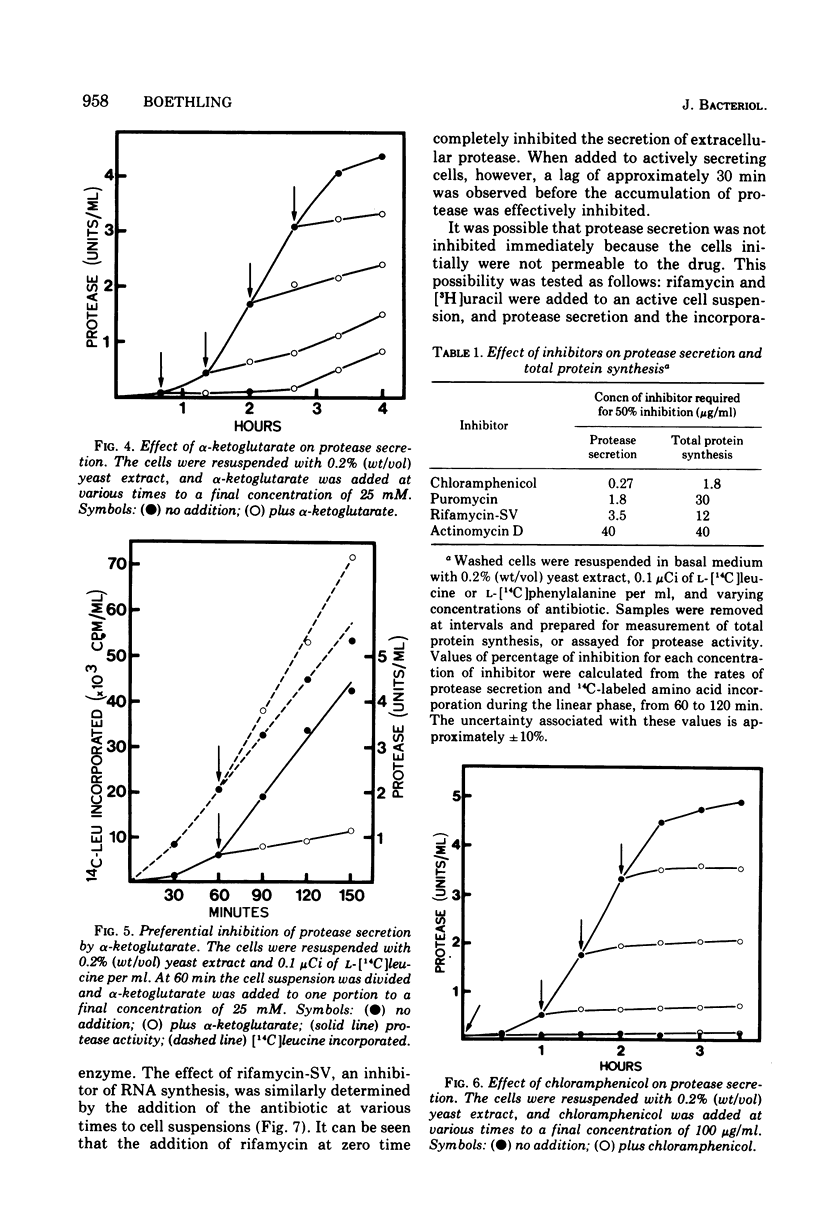
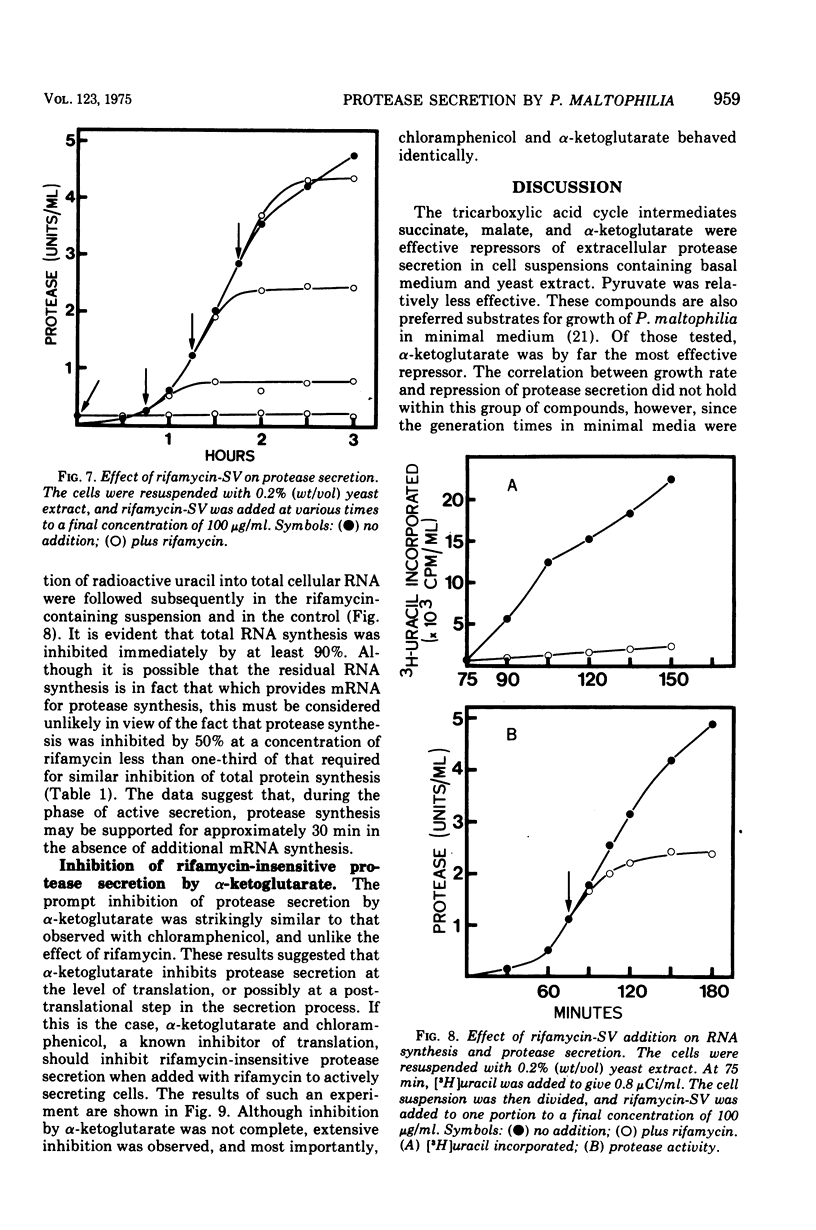
Cells grown in minimal medium and harvested in late exponential phase secreted extracellular protease linearly when suspended at high density in fresh medium. If the cells were suspended with 0.2% (wt/vol) yeast extract and no additional carbon source, the rate of exoenzyme production was increased several-fold. When pyruvate, L-malate, succinate, or alpha-ketoglutarate was added, repression of exoenzyme secretion was observed. The most effective repressor was alpha-ketoglutarate. These compounds were also preferred substrates for growth of Pseudomonas maltophilia. The data suggest that exoenzyme secretion is controlled by a mechanism similar to catabolite repression. In support of this was the observation that alpha-ketoglutarate repressed exoenzyme secretion preferentially with respect to total protein synthesis. The addition of inhibitors that affect protein synthesis indicated that exoenzyme secretion is several times more sensitive than is total protein synthesis. The addition of chloramphenicol and rifamycin-SV to actively secreting cell suspensions suggested that de novo protein synthesis is required, but that exoenzyme secretion may be supported for at least 30 min in the absence of messenger synthesis. Rifamycin-insensitive protease secretion could be reversed by either alpha-ketoglutarate or chloramphenicol, suggesting that alpha-ketoglutarate is coupled to a post-transcriptional control mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boethling R. S. Purification and properties of a serine protease from Pseudomonas matophilia. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):933–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.933-941.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., McInnes J. L., Hanlon J. E., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Evidence for an accumulation of messenger RNA specific for extracellular protease and its relevance to the mechanism of enzyme secretion in bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 20;67(2):199–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Schlesinger M. J. Localization of polyribosomes containing alkaline phosphatase nascent polypeptides on membranes of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):290–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.290-301.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman G., Stormonth D. A. Stimulation of the differential rate of exoenzyme formation in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens by streptolydigin, an inhibitor of RNA chain elongation. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):194–196. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daatselaar M. C., Harder W. Some aspects of the regulation of the production of extracellular proteolytic enzymes by a marine bacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1974;101(1):21–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00455922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn A. R., Both G. W., McInnes J. L., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Dynamic state of the messenger RNA pool specific for extracellular protease in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens: its relevance to the mechanism of enzyme secretion. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jan 10;73(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90325-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Heath E. C. Studies on the extracellular alkaline phosphatase of Micrococcus sodonensis. II. Factors affecting secretion. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1566–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould A. R., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Accumulation of messenger RNA for extracellular enzymes as a general phenomenon in Bacillus amyloiquefaciens. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jan 10;73(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90324-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litchfield C. D., Prescott J. M. Regulation of proteolytic enzyme production by Aeromonas proteolytica. I. Extracellular endopeptidase. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;16(1):17–22. doi: 10.1139/m70-003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litchfield C. D., Prescott J. M. Regulation of proteolytic enzyme production by Aeromonas proteolytica. II. Extracellular aminopeptidase. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;16(1):23–27. doi: 10.1139/m70-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May B. K., Elliott W. H. Characteristics of extracellular protease formation by Bacillus subtilis and its control by amino acid repression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 21;157(3):607–615. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald I. J., Chambers A. K. Regulation of proteinase formation in a species of Micrococcus. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Dec;12(6):1175–1185. doi: 10.1139/m66-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):353–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G., Lampen J. O. A mechanism for penicillinasesecretion in Bacillus licheniformis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):962–969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semets E. V., Glenn A. R., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Accumulation of messenger ribonucleic acid specific for extracellular protease in Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):531–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.531-534.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Merrick J. M. Extracellular enzyme secretion by Pseudomonas lemoignei. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):152–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.152-161.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormonth D. A., Coleman G. Cellular changes accompanying the transition from minimal to maximal rate of extracellular enzyme secretion by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. J Appl Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;37(2):225–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1974.tb00434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Iuchi S. Induction and repression of an extracellular proteinase in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Biken J. 1971 Jun;14(2):81–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


