Abstract
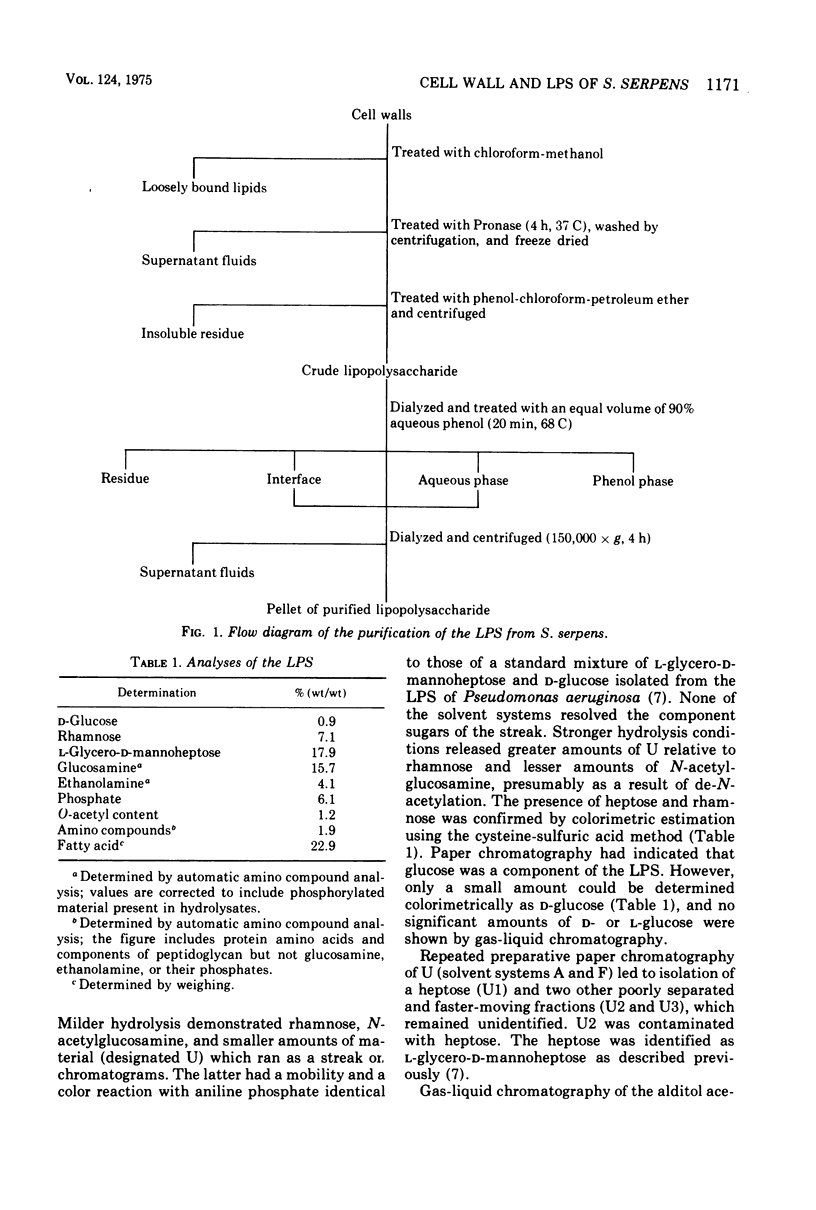
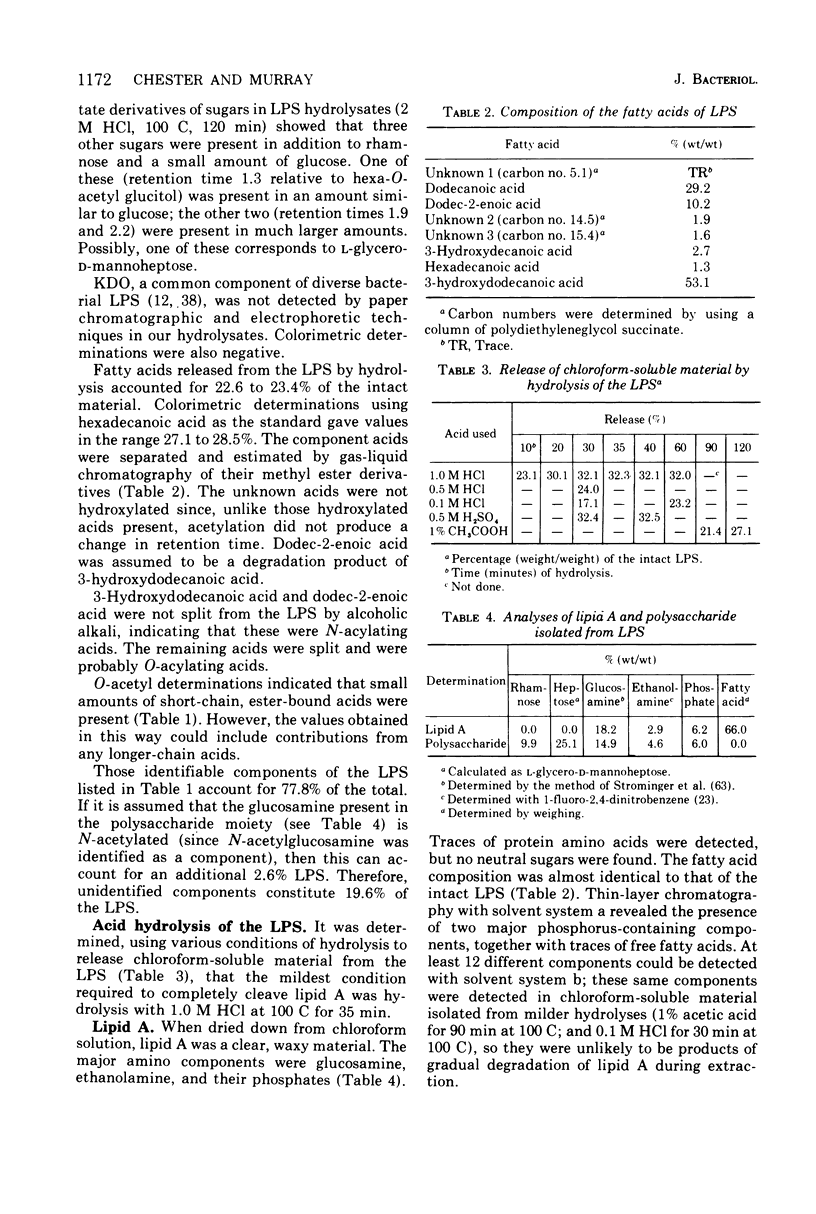
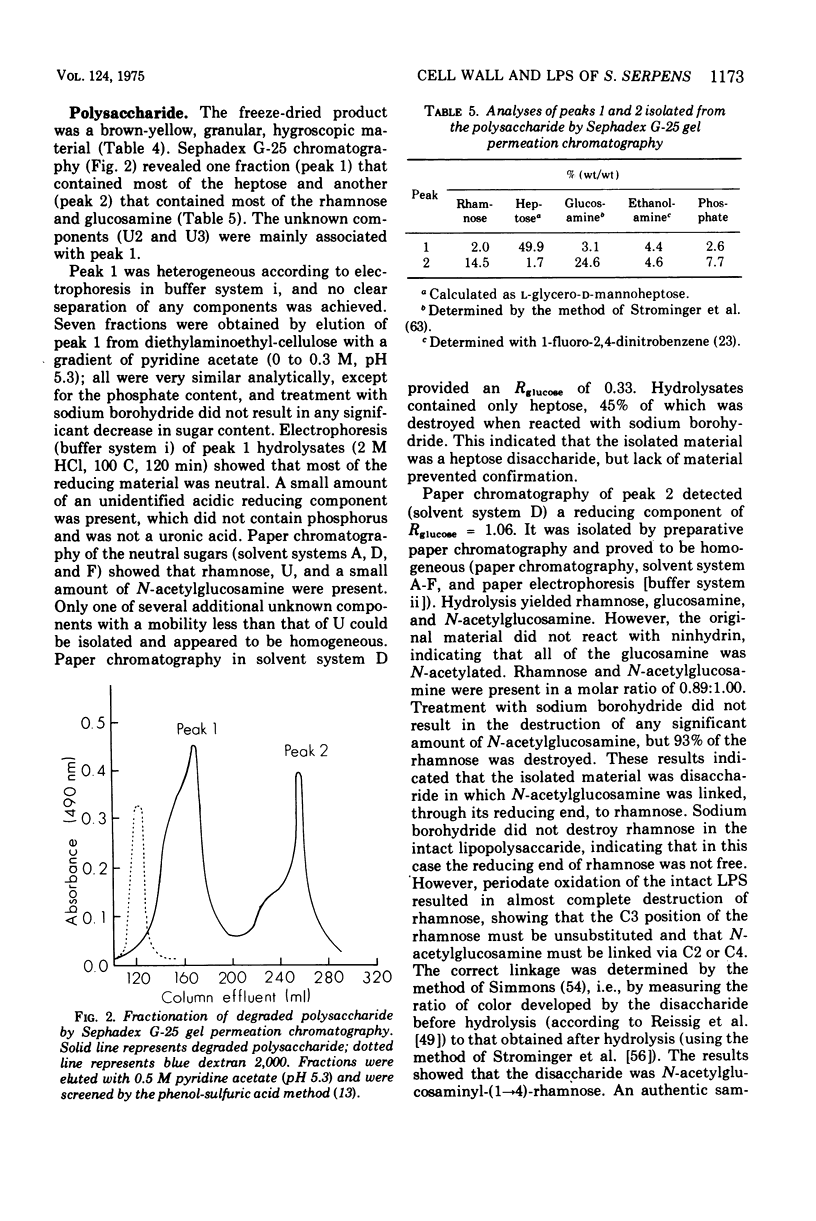
Isolated walls of Spirillum serpens VHA contained lipid, lipopolysaccharide, and protein in amounts similar to those of other gram-negative organisms. The loosely bound lipids consisted mainly of phosphatidylethanolamine, lyso-phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, and diphosphatidylglycerol. Lipopolysaccharide was tightly bound to the wall and could only be removed in a substantial amount after digestion of the wall with Pronase. The lipopolysaccharide contained L-glycero-D-mannoheptose, rhamnose, glucosamine, ethanolamine, and phosphate in common with many of the lipopolysaccharides isolated from the Enterobacteriaceae. However, 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonic acid was not detected. Several unidentified sugars were present. The fatty acid composition resembled that found in lipopolysaccharides isolated from various pseudomonads. Two major regions were identified in the polysaccharide moiety, one apparently corresponding to the core polysaccharide and the other corresponding to the side-chain polysaccharide as in enterobacterial and pseudomonad lipopolysaccharides. The side chains were obtained as low-molecular-weight material and their structure was partially elucidated by the isolation and partial characterization of N-acetylglucosaminyl-(1 leads to 4)-rhamnose.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Quadling C., Yaguchi M., Tornabene T. G. The chemical composition of cell-wall lipopolysaccharides from Moraxella duplex and Micrococcus calco-aceticus. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;16(1):1–8. doi: 10.1139/m70-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams G. A., Tornabene T. G., Yaguchi M. Cell wall lipopolysaccharides from Neisseria catarrhalis. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Apr;15(4):365–374. doi: 10.1139/m69-067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmire F. L., Murray R. G. Studies on the cell wall of Spirillum serpens. 1. Isolation and partial purification of the outermost cell wall layer. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Oct;16(10):1011–1022. doi: 10.1139/m70-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester I. R., Meadow P. M., Pitt T. L. The relationship between the O-antigenic lipopolysaccharides and serological specificity in strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa of different O-serotypes. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):305–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. New color reactions for determination of sugars in polysaccharides. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:313–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Structural investigations on the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C. The distribution of 2-keto-3-deoxy-octonic acid in bacterial walls. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):373–380. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fensom A. H., Gray G. W. The chemical composition of the lipopolyacarideof Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(2):185–196. doi: 10.1042/bj1140185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fensom A. H., Meadow P. M. Evidence for two regions in the polysaccharide moiety of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 8602. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jul 29;9(2):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formanek H., Formanek S., Wawra H. A three-dimensional atomic model of the murein layer of bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 15;46(2):279–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHUYSEN J. M., STROMINGER J. L. STRUCTURE OF THE CELL WALL OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS, STRAIN COPENHAGEN. I. PREPARATION OF FRAGMENTS BY ENZYMATIC HYDROLYSIS. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:1110–1119. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUWINK A. L. A macromolecular mono-layer in the cell wall of Spirillum spec. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Mar;10(3):360–366. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock I. C., Humphreys G. O., Meadow P. M. Characterisation of the hydroxy acids of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 8602. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 10;202(2):389–391. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90204-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstad T., Kristoffersen T. Chemical characteristics of endotoxin from Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Apr;61(1):15–19. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITAYA K., UI M. COLORIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF FREE FATTY ACIDS IN BIOLOGICAL FLUIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jan;6:16–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai N. Chemical studies on the lipid component of endotoxin, with special emphasis on its relation to biological activities. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):486–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai N., Nowotny A. Endotoxic glycolipid from a heptoseless mutant of Salmonella minnesota. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1824–1836. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1824-1836.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key B. A., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. The purification and chemical composition of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas alcaligenes. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(3):559–566. doi: 10.1042/bj1200559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeltzow D. E., Conrad H. E. Structural heterogeneity in the lipopolysaccharide of Aerobacter aerogenes NCTC 243. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 19;10(2):214–224. doi: 10.1021/bi00778a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Ensign J. C. Isolation and chemical structure of the peptidoglycan of Spirillum serpens cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):201–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.201-210.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamkin W. M., Ward D. N., Walborg E. F., Jr Quantitative determination of neutral monosaccharide residues in glycoproteins and glycopeptides by thin-layer densitometry. Anal Biochem. 1966 Dec;17(3):485–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Galanos C., Risse H. J., Ruschmann E., Schlecht S., Schmidt G., Schulte-Holthausen H., Wheat R., Westphal O., Schlosshardt J. Structural relationship of Salmonella O and R antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):349–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Seitz E., Jann B., Jann K. Degradation studies on the lipopolysaccharide from E. coli 071:K?:H12. Separation and investigation of O-specific and core polysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 1968 Oct;1(5):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J. Structure and biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:501–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISSIG J. L., STORMINGER J. L., LELOIR L. F. A modified colorimetric method for the estimation of N-acetylamino sugars. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapin A. M., Mayer H. Complex polysaccharides in different strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):425–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. M., Conrad H. E. Structural heterogeneity in the lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella newington. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jun;162(2):530–535. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. Studies of the bacterial cell wall. VII. Monosaccharide constituents of the walls of gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 4;45:364–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91459-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., PARK J. T., THOMPSON R. E. Composition of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: its relation to the mechanism of action of penicillin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. A. The immunochemistry of Shigella flexneri O-antigens. The structure and biosynthesis of the O-specific side chains of some representative serotypes. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(3):554–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaskovsky V. E., Kostetsky E. Y. Modified spray for the detection of phospholipids on thin-layer chromatograms. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):396–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk W. A., Salomonsky N. L., Hunt D. Xanthomonas sinensis cell wall lipopolysaccharide. I. Isolation of 4,7-anhydro- and 4,8-anhydro-3-deoxy-octulosonic acid following acid hydrolysis of Xanthomonas sinensis lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3881–3887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. Thiobarbituric acid spray reaction for deoxy sugars and sialic acids. Nature. 1960 Apr 16;186:237–237. doi: 10.1038/186237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat R. W., Berst M., Ruschmann E., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella T mutants. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1366–1380. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1366-1380.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G. Studies on the cell walls of pseudomonas species resistant to ethylenediaminetetra-acetic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(2):195–213. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


