Abstract
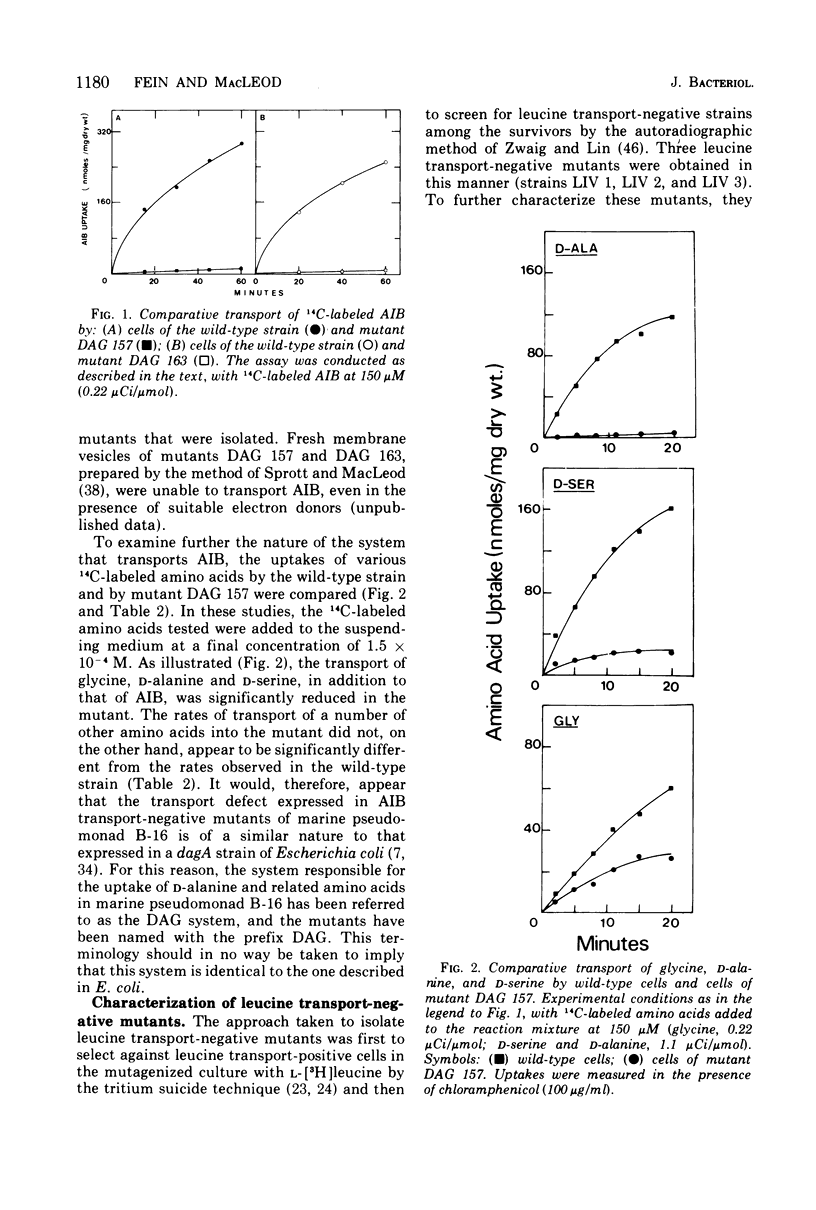
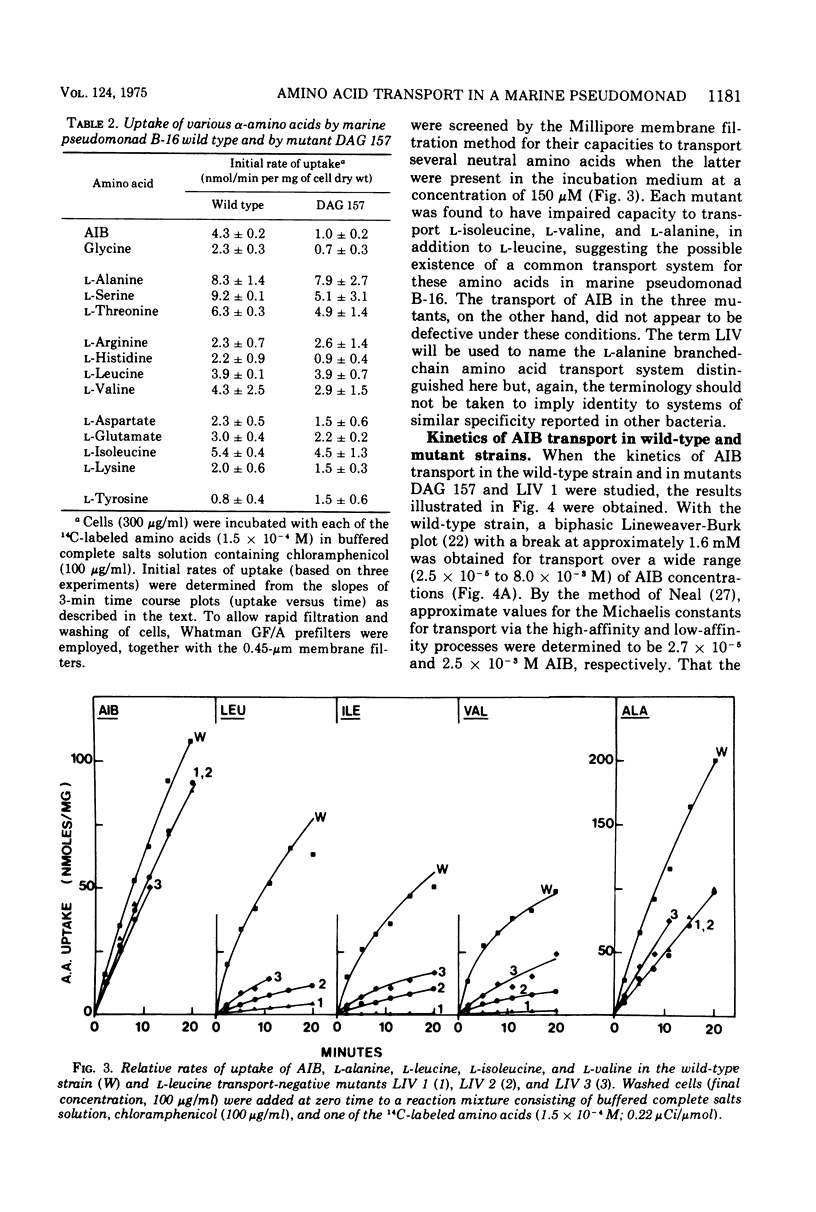
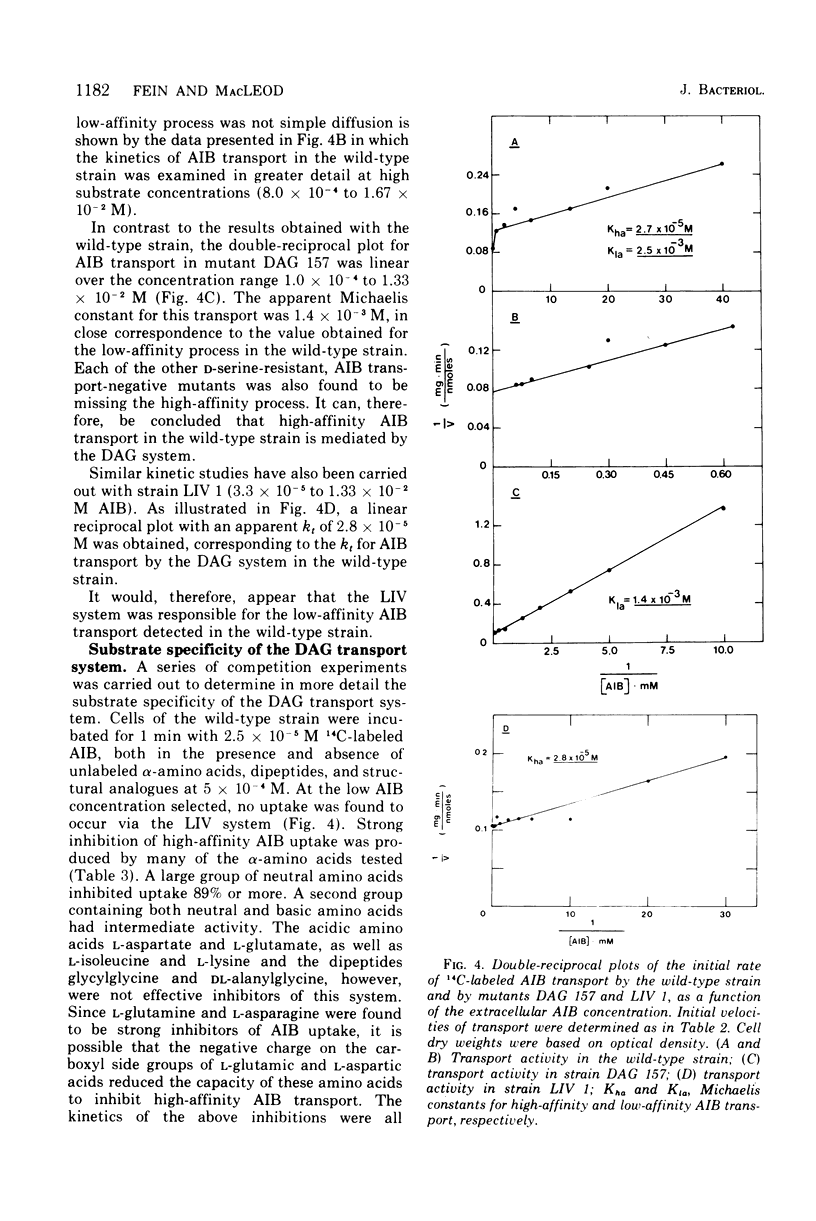
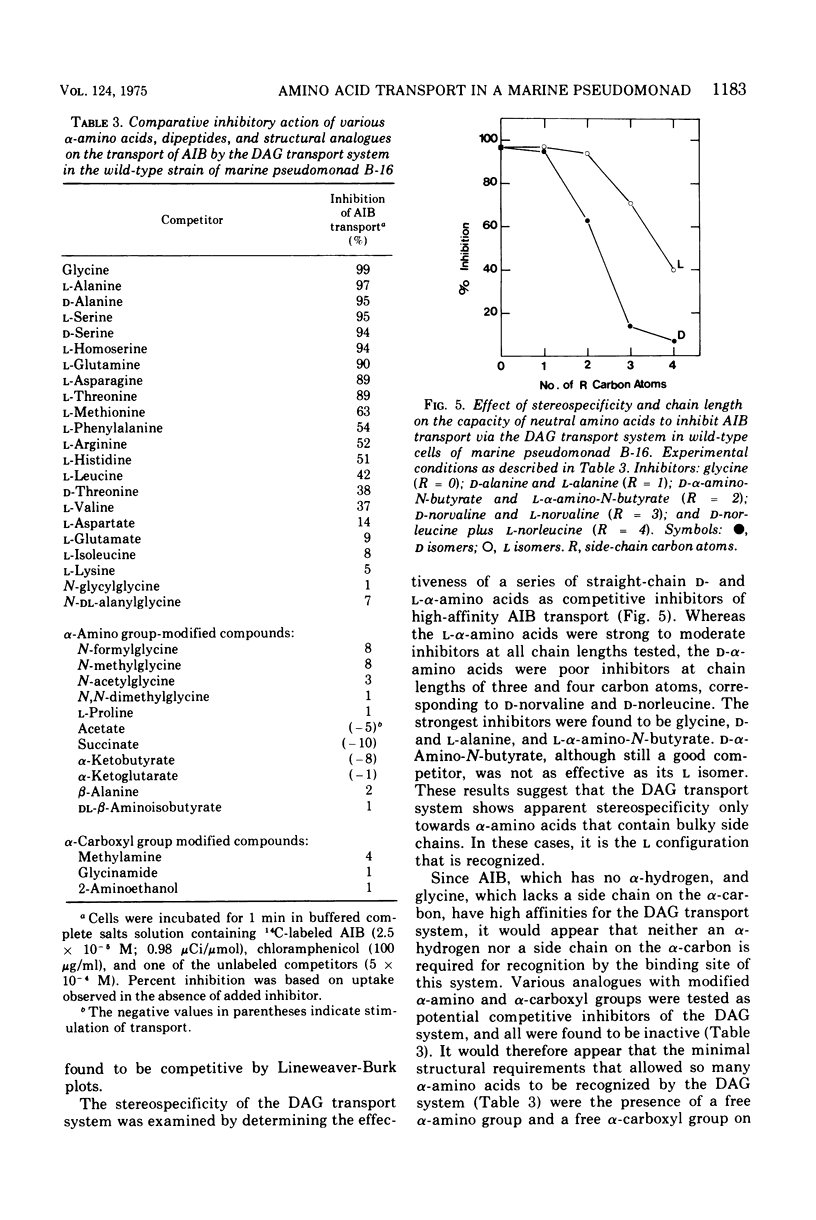
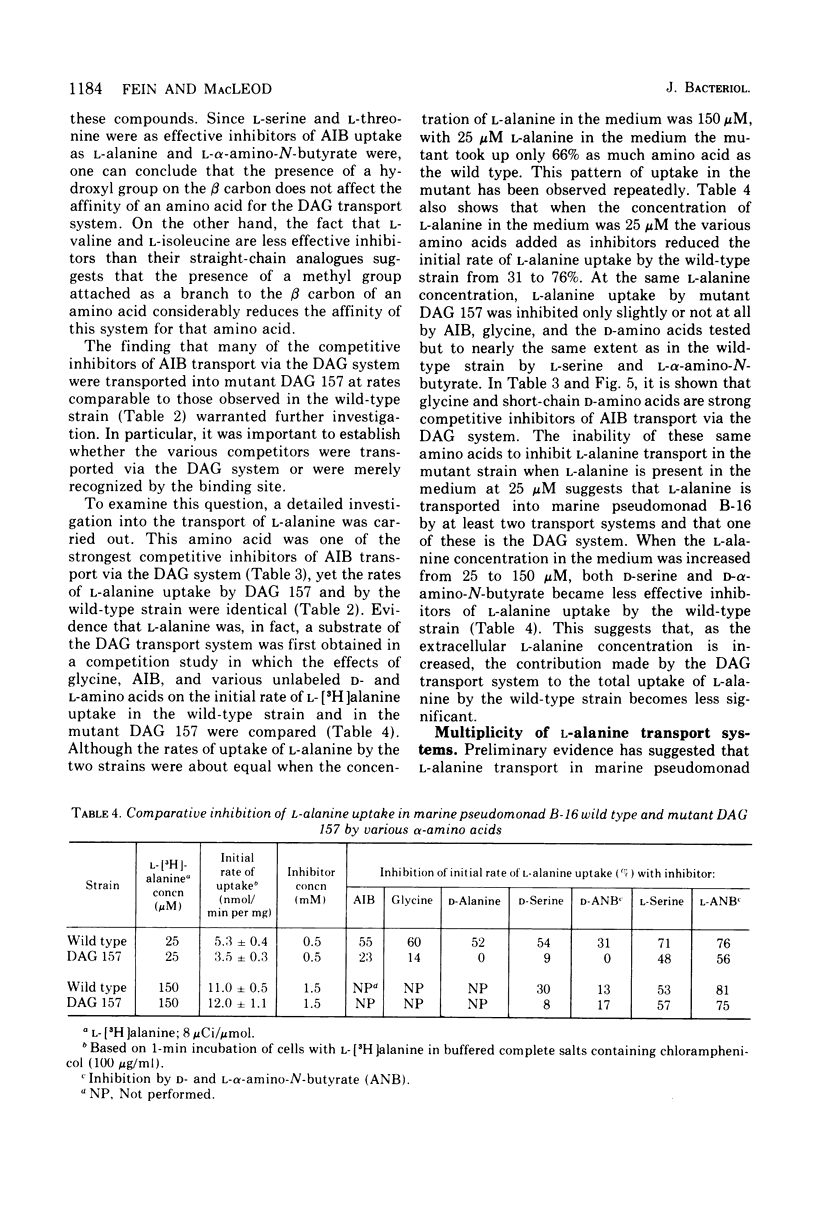
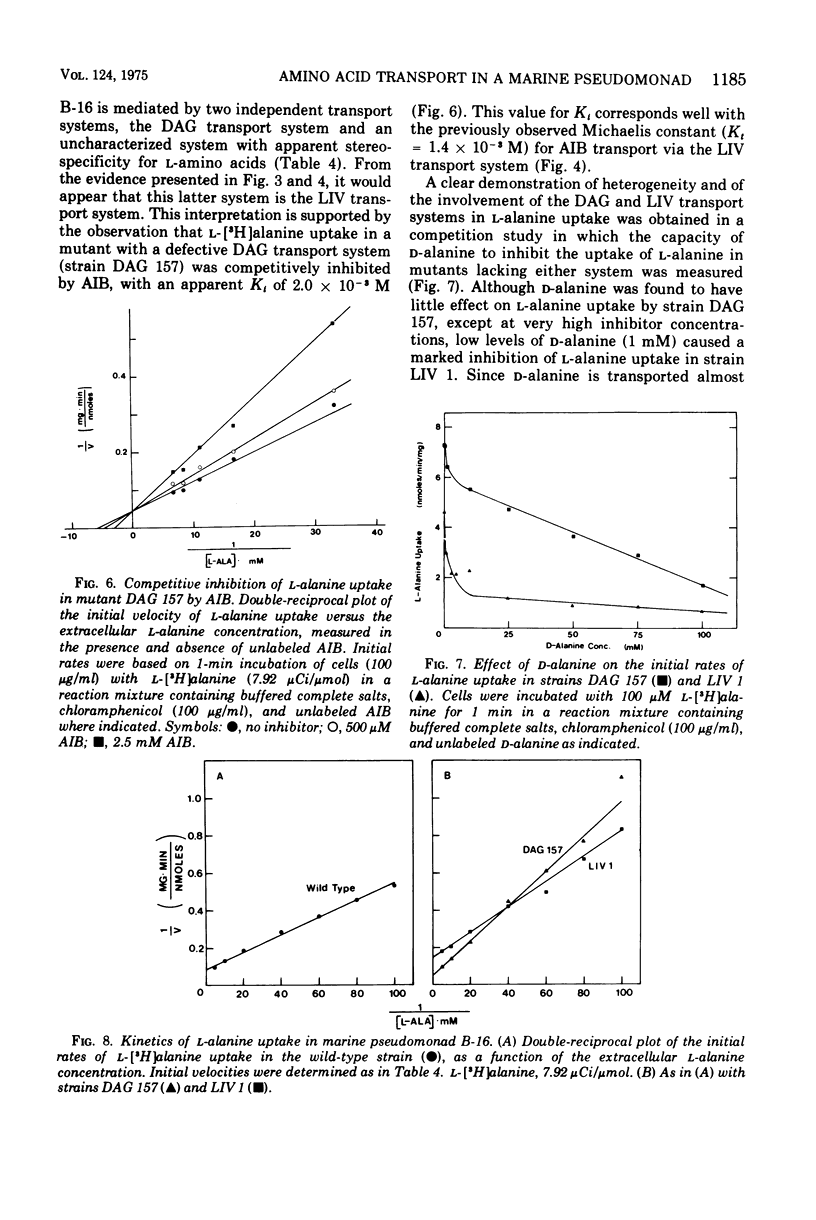
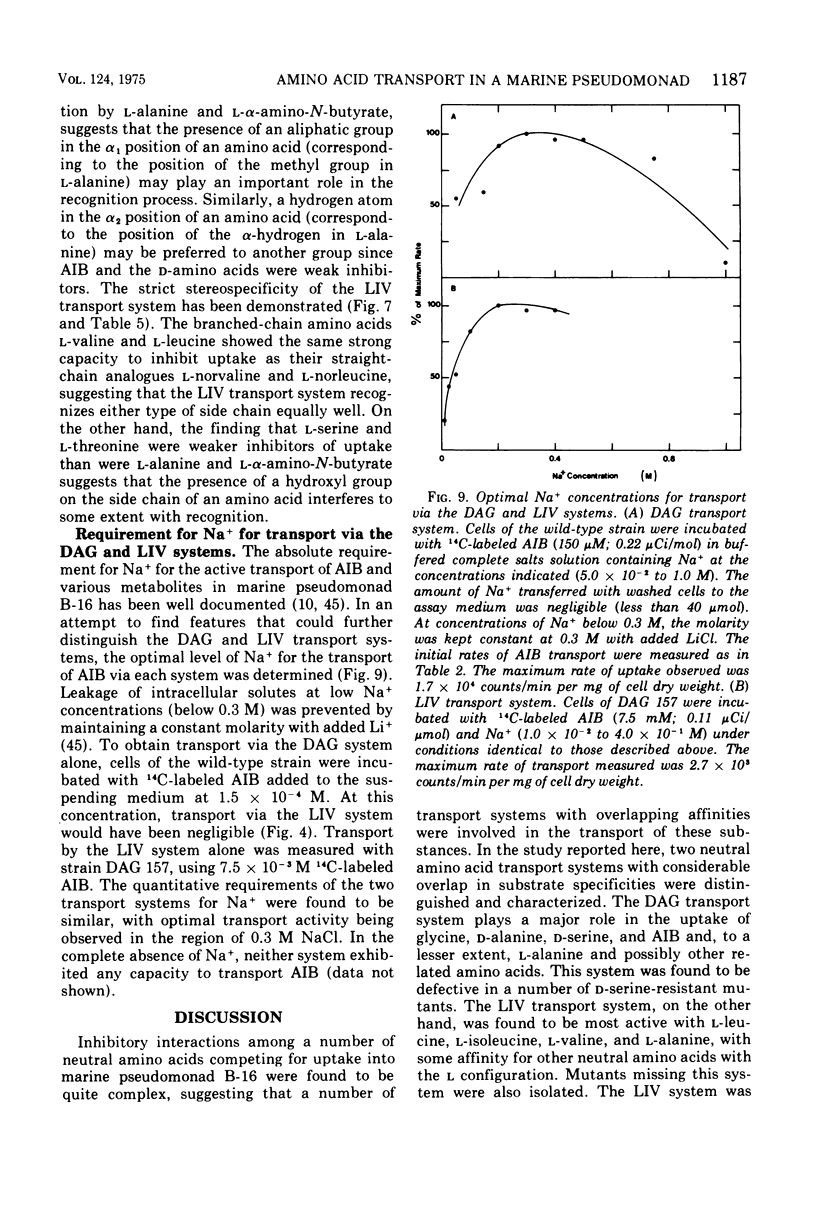
The transport of neutral amino acids in marine pseudomonad B-16 (ATCC 19855) has been investigated. From patterns of competitive inhibition, mutant analysis, and kinetic data, two active transport systems with overlapping substrate specificities were distinguished and characterized. One system (DAG) served glycine, D-alanine, D-serine, and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid (AIB) and, to a lesser extent, L-alanine and possibly other related neutral D- and L-amino acids. The other system (LIV) showed high stereospecificity for neutral amino acids with the L configuration and served primarily to transport L-leucine, L-isoleucine, L-valine, and L-alanine. This system exhibited low affinity for alpha-aminoisobutyric acid. Neither system was able to recognize structural analogues with modified alpha-amino or alpha-carboxyl groups. The kinetic parameters for L-alanine transport by the DAG and LIV systems were determined with appropriate mutants defective in either system. For L-alanine, Kt values of 4.6 X 10(-5) and 1.9 X 10(-4) M and Vmax values of 6.9 and 20.8 nmol/min per mg of cell dry weight were obtained for transport via the DAG and LIV systems respectively. alpha-Aminoisobutyric acid transport heterogeneity was also resolved with the mutants, and Kt values of 2.8 X 10(-5) and 1.4 X 10(-3) M AIB were obtained for transport via the DAG and LIV systems, respectively. Both systems required Na+ for activity (0.3 M Na+ optimal) and in this regard are distinguished from systems of similar substrate specificity reported in nonmarine bacteria.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asghar S. S., Levin E., Harold F. M. Accumulation of neutral amino acids by Streptococcus faecalis. Energy coupling by a proton-motive force. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5225–5233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D., MOO-PENN G. An amino acid transport system in Streptococcus faecium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Aug;98:183–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Concentration spécifique réversible des amino acides chez Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Nov;91(5):693–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Methods for distinguishing amino acid transport systems of a given cell or tissue. Fed Proc. 1966 May-Jun;25(3):850–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark V. L., Young F. E. Active transport of D-alanine and related amino acids by whole cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1085–1092. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1085-1092.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosloy S. D. D-serine transport system in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):679–684. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.679-684.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosloy S. D., McFall E. Metabolism of D-serine in Escherichia coli K-12: mechanism of growth inhibition. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):685–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.685-694.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David H. L. Resistance to D-cycloserine in the tubercle bacilli: mutation rate and transport of alanine in parental cells and drug-resistant mutants. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):888–892. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.888-892.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R., Matula T. I., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XV. Relation of Na+-activated transport to the Na+ requirement of a marine pseudomonad for growth. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):63–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.63-71.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gow J. A., DeVoe U. W., MacLeod R. A. Dissociation in a marine pseudomonad. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jun;19(6):695–701. doi: 10.1139/m73-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guardiola J., De Felice M., Klopotowski T., Iaccarino M. Multiplicity of isoleucine, leucine, and valine transport systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):382–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.382-392.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guardiola J., De Felice M., Klopotowski T., Iaccarino M. Mutations affecting the different transport systems for isoleucine, leucine, and valine in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):393–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.393-405.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., MacLeod R. A. Kinetics of Na+-dependent K+ ion transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):160–164. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.160-164.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. T., Bunch J. M. Asparagine transport in Lactobacillus plantarum and Streptococcus faecalis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 25;307(3):640–655. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSEL D., LUBIN M. STABILITY OF ALPHA-HYDROGEN OF AMINO ACIDS DURING ACTIVE TRANSPORT. Biochemistry. 1965 Mar;4:561–565. doi: 10.1021/bi00879a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Gronlund A. F. Influence of carbon or nitrogen starvation on amino acid transport in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):276–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.276-282.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Freese E. Amino acid transport in membrane vesicles of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2408–2418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J., LEDERBERG E. M. Replica plating and indirect selection of bacterial mutants. J Bacteriol. 1952 Mar;63(3):399–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.3.399-406.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBIN M. Selection of auxotrophic bacterial mutants by tritium-labeled thymidine. Science. 1959 Mar 27;129(3352):838–839. doi: 10.1126/science.129.3352.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo T. C., Rayman M. K., Sanwal B. D. Transport of succinate in Escherichia coli. I. Biochemical and genetic studies of transport in whole cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6323–6331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A. THE QUESTION OF THE EXISTENCE OF SPECIFIC MARINE BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:9–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal J. L. Analysis of Michaelis kinetics for two independent, saturable membrane transport functions. J Theor Biol. 1972 Apr;35(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(72)90196-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz R. H., Slade H. D., Neuhaus F. C. The biochemical mechanisms of resistance by streptococci to the antibiotics D-cycloserine and O-carbamyl-D-serine. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2561–2570. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Grossowicz N. Properties of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport in a thermophilic microorganism. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):414–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.414-424.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ J. H., MAAS W. K., SIMON E. J. An impaired concentrating mechanism for amino acids in mutants of Escherichia coli resistant to L-canavanine and D-serine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:582–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90650-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., White D. C., Kaback H. R. Active transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. V. The transport of amino acids by membrane vesicles prepared from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):298–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., MacLeod R. A. Nature of the specificity of alcohol coupling to L-alanine transport into isolated membrane vesicles of a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1043–1054. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1043-1054.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang S. L., Howard D. H. Uptake and utilization of glutamic acid by Cryptococcus albidus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):98–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.98-106.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Na+ and K+ gradients and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7106–7111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVII. Ion-dependent retention of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid and its relation to Na+ dependent transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1016–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


