Abstract
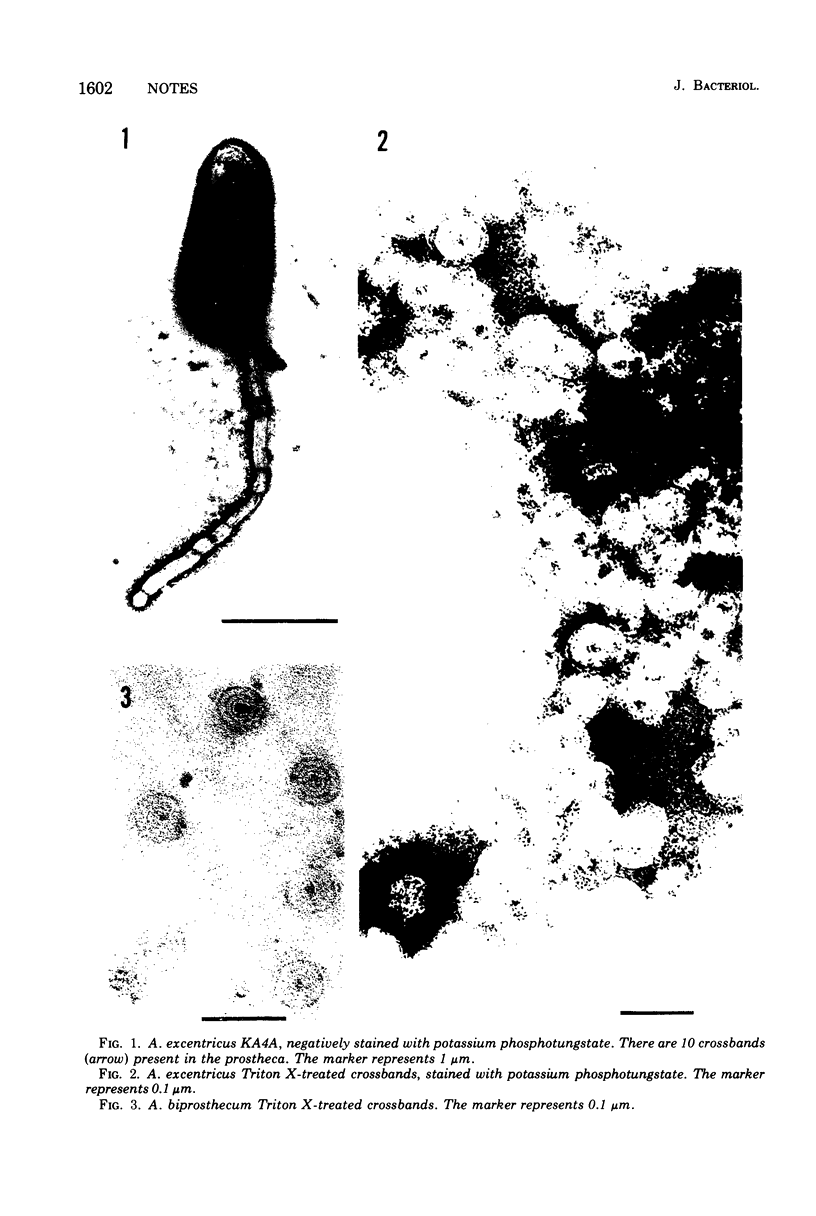
Triton X-treated prosthecae from Asticcacaulis excentricus and A. biprosthecum were sonicated and examined with a electron microscope. Crossbands had a substructure of concentric rings and were digested by lysozyme.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jordan T. L., Porter J. S., Pate J. L. Isolation and characterization of prosthecae of Asticcacaulis biprosthecum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Mar 1;96(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00590158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POINDEXTER J. S. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE CAULOBACTER GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:231–295. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.231-295.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. L., Ordal E. J. The fine structure of two unusual stalked bacteria. J Cell Biol. 1965 Oct;27(1):133–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. L., Porter J. S., Jordan T. L. Asticcacaulis biprosthecum sp.nov. Life cycle, morphology and cultural characteristics. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1973 Nov;39(4):569–583. doi: 10.1007/BF02578901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOVEPOINDEXTER J. L., COHEN-BAZIRE G. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF STALKED BACTERIA BELONGING TO THE FAMILY CAULOBACTERACEAE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Dec;23:587–607. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]