Abstract
The enzymes of naphthalene metabolism are induced in Pseudomonas putida ATCC 17484, PpG7, NCIB 9816, and PG and in Pseudomonas sp. ATCC 17483 during growth on naphthalene or salicylate; 2-aminobenzoate is a gratuitous inducer of these enzymes. The meta-pathway enzymes of catechol metabolism are induced in ATCC 17483 and PPG7 during growth on naphthalene or salicylate or during growth in the presence of 2-aminobenzoate, but in ATCC 17484 and NCIB 9816 the ortho-pathway enzymes of catechol metabolism are induced during growth on naphthalene or salicylate. 2-Aminobenzoate does not induce any enzymes of catechol metabolism in the latter two organisms. In Pseudomonas PG the meta-pathway enzymes are present at high levels under all conditions of growth, but this organism and PpG7 can induce ortho-pathway enzymes during naphthalene or salicylate metabolism. Salicylate appears to be the inducer of the enzymes of naphthalene metabolism in all of the organisms studied and, where they are inducible, of the meta-pathway enzymes, but the properties of Pseudomonas PG suggest that separate, regulatory systems may exist.
Full text
PDF
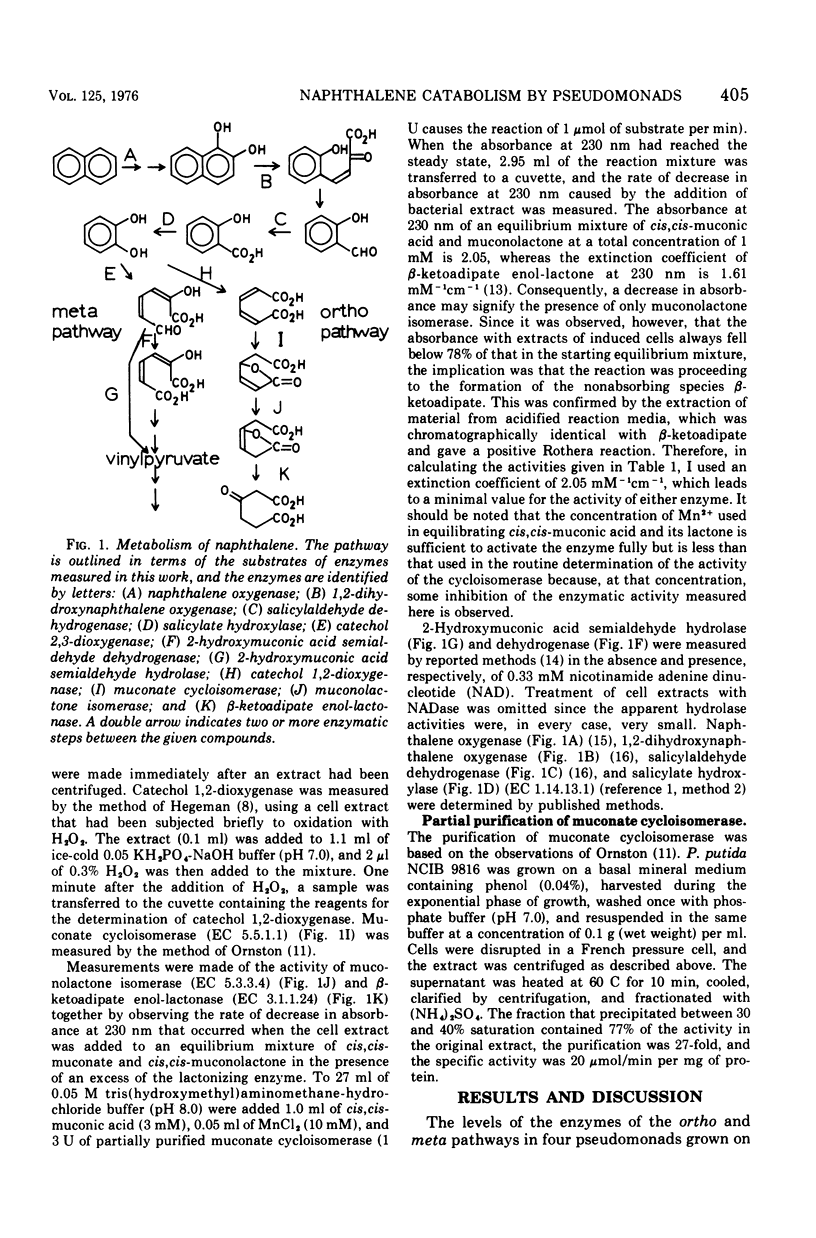
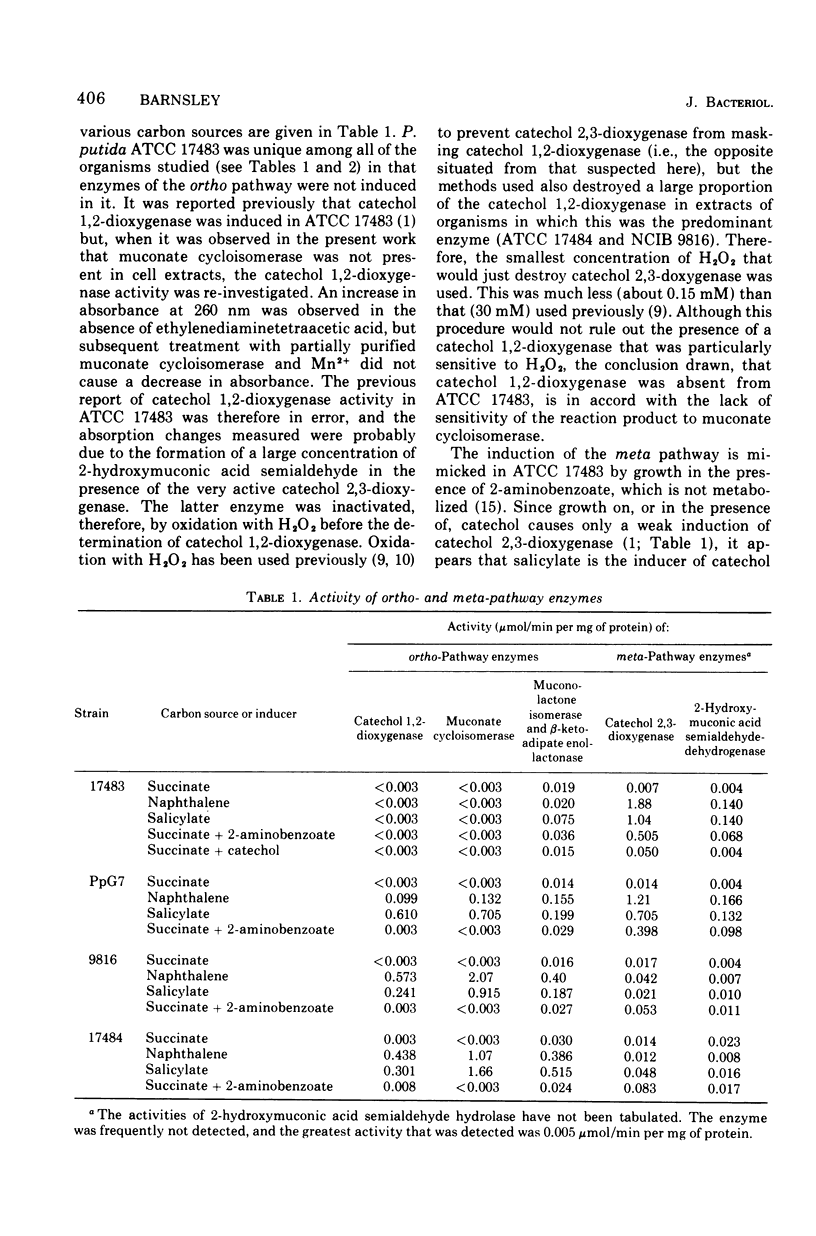

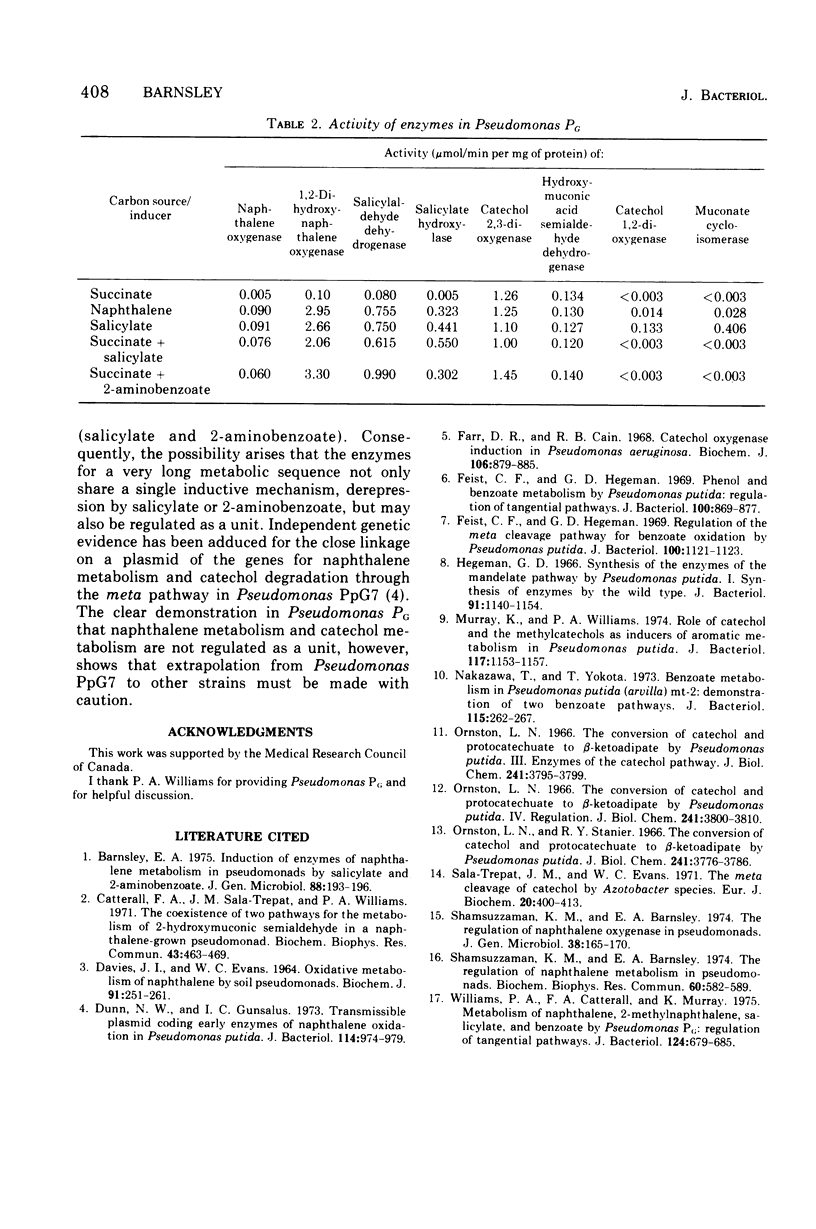
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnsley E. A. The induction of the enzymes of naphthalene metabolism in pseudomonads by salicylate and 2-aminobenzoate. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):193–196. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall F. A., Sala-Trepat J. M., Williams P. A. The coexistence of two pathways for the metabolism of 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde in a naphthalene-grown pseudomonad. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90636-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. I., Evans W. C. Oxidative metabolism of naphthalene by soil pseudomonads. The ring-fission mechanism. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):251–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0910251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn N. W., Gunsalus I. C. Transmissible plasmid coding early enzymes of naphthalene oxidation in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):974–979. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.974-979.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr D. R., Cain R. B. Catechol oxygenase induction in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(4):879–885. doi: 10.1042/bj1060879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist C. F., Hegeman G. D. Phenol and benzoate metabolism by Pseudomonas putida: regulation of tangential pathways. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.869-877.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist C. F., Hegeman G. D. Regulation of the meta cleavage pathway for benzoate oxidation by Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1121–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1121-1123.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. I. Synthesis of enzymes by the wild type. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1140–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1140-1154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K., Williams P. A. Role of catechol and the methylcatechols as inducers of aromatic metabolism in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1153–1157. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1153-1157.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa T., Yokota T. Benzoate metabolism in Pseudomonas putida(arvilla) mt-2: demonstration of two benzoate pathways. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):262–267. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.262-267.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Stanier R. Y. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3776–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. 3. Enzymes of the catechol pathway. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3795–3799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. IV. Regulation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3800–3810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Evans W. C. The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species. 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):400–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamsuzzaman K. M., Barnsley E. A. The regulation of naphthalene metabolism in pseudomonads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):582–589. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamsuzzaman K. M., Barnsley E. A. The regulation of naphthalene oxygenase in pseudomonads. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jul;83(0):165–170. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Catterall F. A., Murray K. Metabolism of naphthalene, 2-methylnaphthalene, salicylate, and benzoate by Pseudomonas PG: regulation of tangential pathways. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):679–685. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.679-685.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


