Abstract
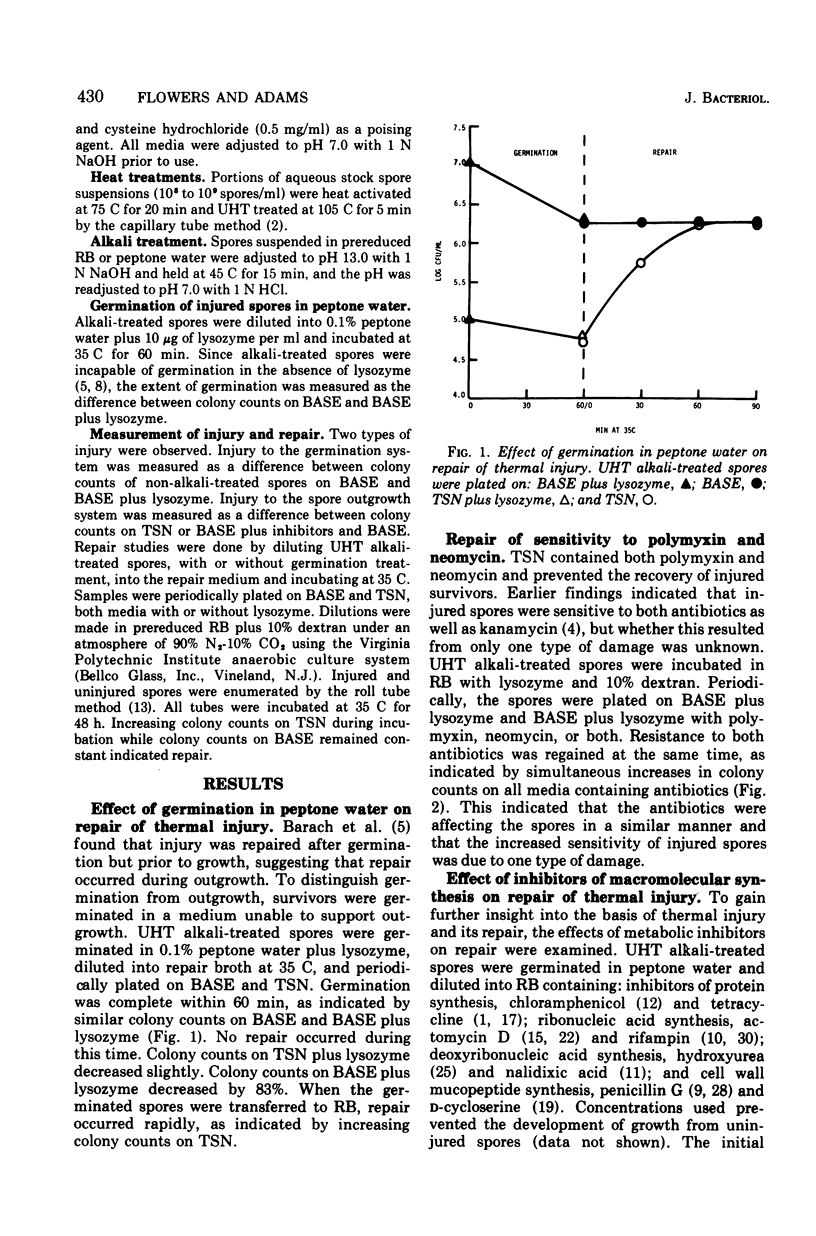
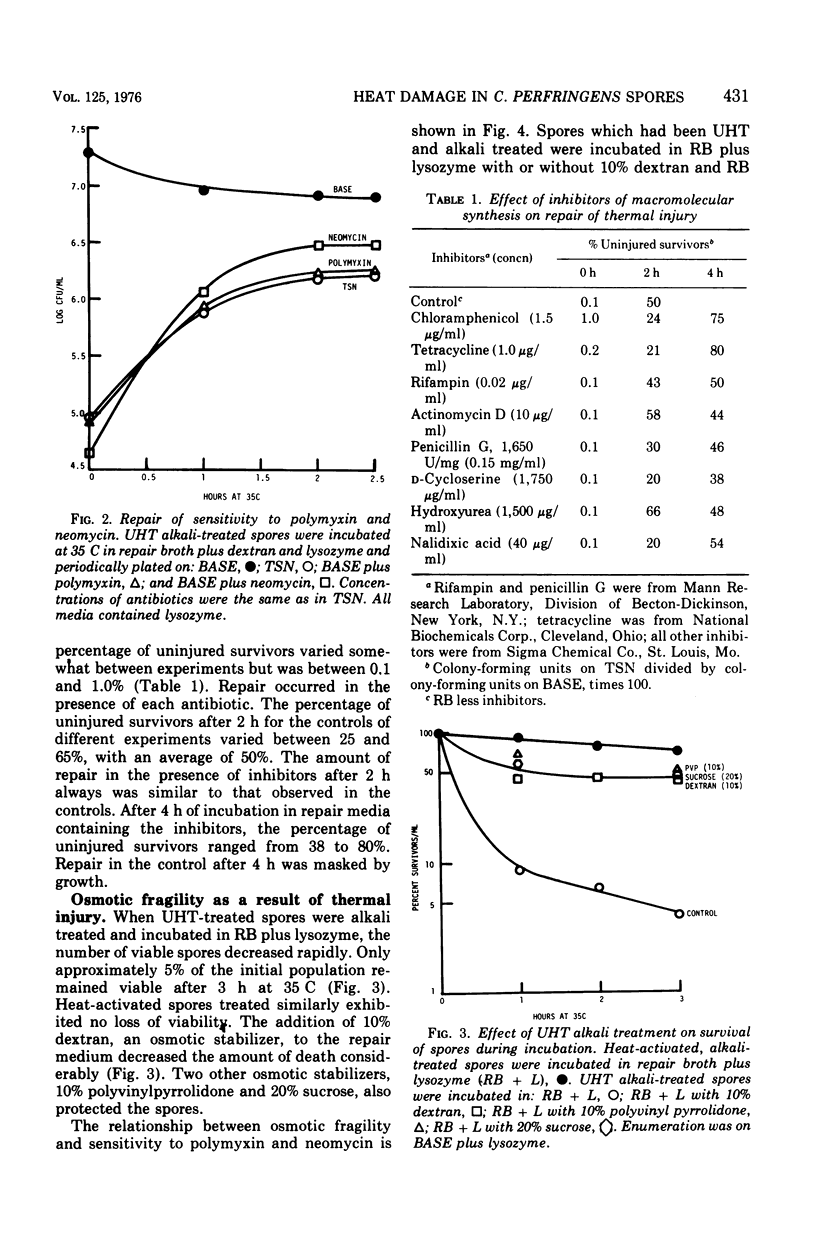
Clostridium perfringens spores were injured by ultrahigh-temperature treatment at 105 C for 5 min. Injury was manifested as an increased sensitivity to polymyxin and neomycin. Since many of the survivors could not germinate normally the ultrahigh-temperature-treated spores were sensitized to and germinated by lysozyme. Polymyxin reportedly acts upon the cell membrane. Neomycin may inhibit protein synthesis and has surface-active properties. Injured spores were increasingly sensitive to known surface-active agents, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium deoxycholate, and Roccal, a quaternary ammonium compound. Injured spores sensitive to polymyxin and neomycin also were osmotically fragile and died during outgrowth in a liquid medium unless the medium was supplemented with 20% sucrose, 10% dextran, or 10% polyvinylpyrrolidone. The results suggested that a spore structure destined to become cell membrane or cell wall was the site of injury. Repair of injury during outgrowth in the presence of protein, deoxyribonucleic acid, ribonucleic acid and cell wall synthesis inhibitors was consistent with this hypothesis.
Full text
PDF
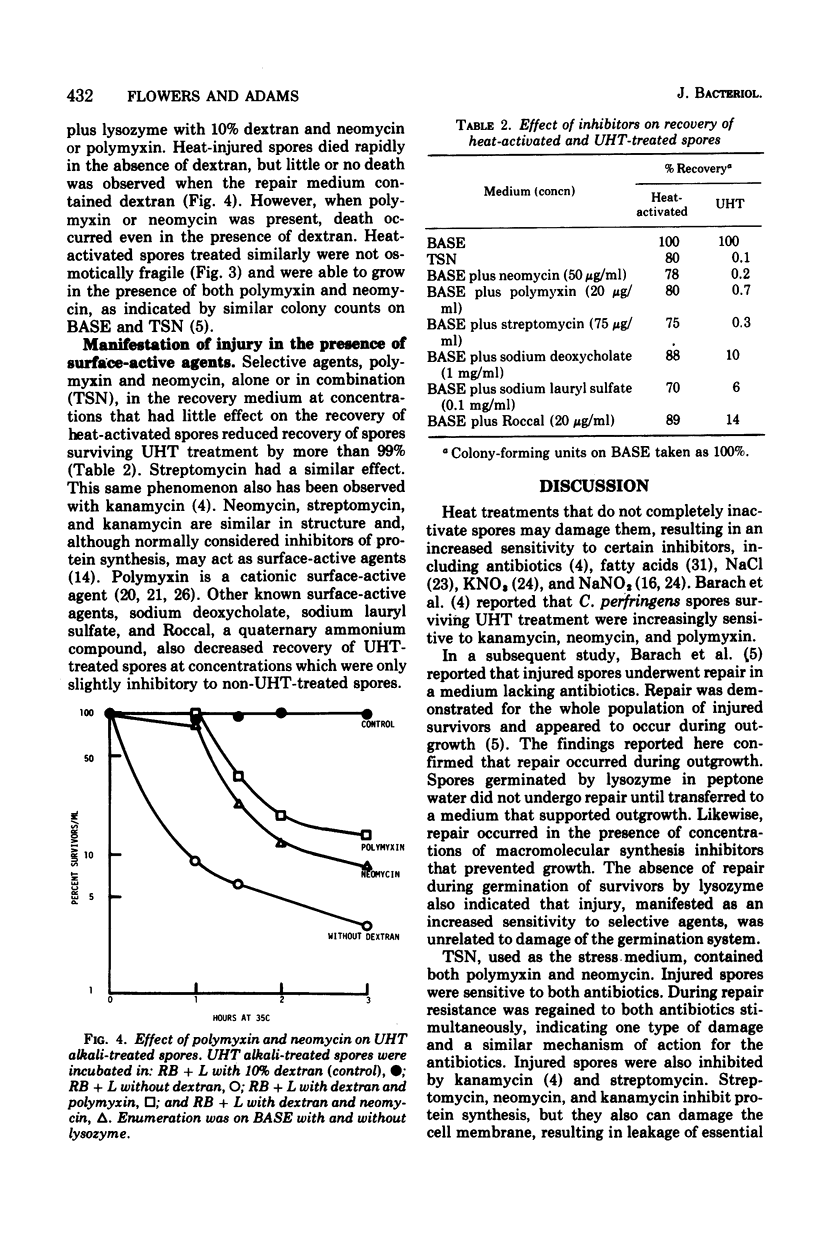


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Zeid A. Z. Tetracyclines. Zentralbl Bakteriol Parasitenkd Infektionskr Hyg. 1973;128(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/s0044-4057(73)80038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. M. Inactivation of Clostridium perfringens type A spores at ultrahigh temperatures. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):282–287. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.282-287.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. M. Requirement for and sensitivity to lysozyme by Clostridium perfringens spores heated at ultrahigh temperatures. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Apr;27(4):797–801. doi: 10.1128/am.27.4.797-801.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barach J. T., Adams D. M., Speck M. L. Recovery of heated Clostridium perfringens type A spores on selective media. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):793–797. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.793-797.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barach J. T., Flowers R. S., Adams D. M. Repair of heat-injured Clostridium perfringens spores during outgrowth. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Nov;30(5):873–875. doi: 10.1128/am.30.5.873-875.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassier M., Sebald M. Germination lysozyme-dépendante des spores de Clostridium perfringens ATCC 3624 après traitement thermique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Sep;117(3):312–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Labbe R. G., Reich R. R. Germination of heat- and alkali-altered spores of Clostridium perfringens type A by lysozyme and an initiation protein. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):550–559. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.550-559.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSS W. A., DEITZ W. H., COOK T. M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NALIDIXIC ACID ON ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1112–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1112-1118.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRK J. M. The mode of action of actinomycin D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 29;42:167–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90769-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe R. G., Duncan C. L. Growth from spores of Clostridium perfringens in the presence of sodium nitrite. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Feb;19(2):353–359. doi: 10.1128/am.19.2.353-359.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL R. S., STEENBERGEN J. F., MCCLUNG L. S. RAPID TECHNIQUE FOR THE ENUMERATION OF CLOSTRIDIUM PERFINGENS. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Jul;13:559–563. doi: 10.1128/am.13.4.559-563.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. The properties and mode of action of the polymyxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):14–27. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.14-27.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton B. A. Mechanisms of antibiotic action. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1965;19:209–240. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.19.100165.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENKRANZ H. S., LEVY J. A. HYDROXYUREA: A SPECIFIC INHIBITOR OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 11;95:181–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Staehelin M. Actions of the rifamycins. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Sep;35(3):290–309. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.290-309.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynne E. S., Foster J. W. Physiological Studies on Spore Germination with Special Reference to Clostridium botulinum: I. Development of a Quantitative Method. J Bacteriol. 1948 Jan;55(1):61–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


