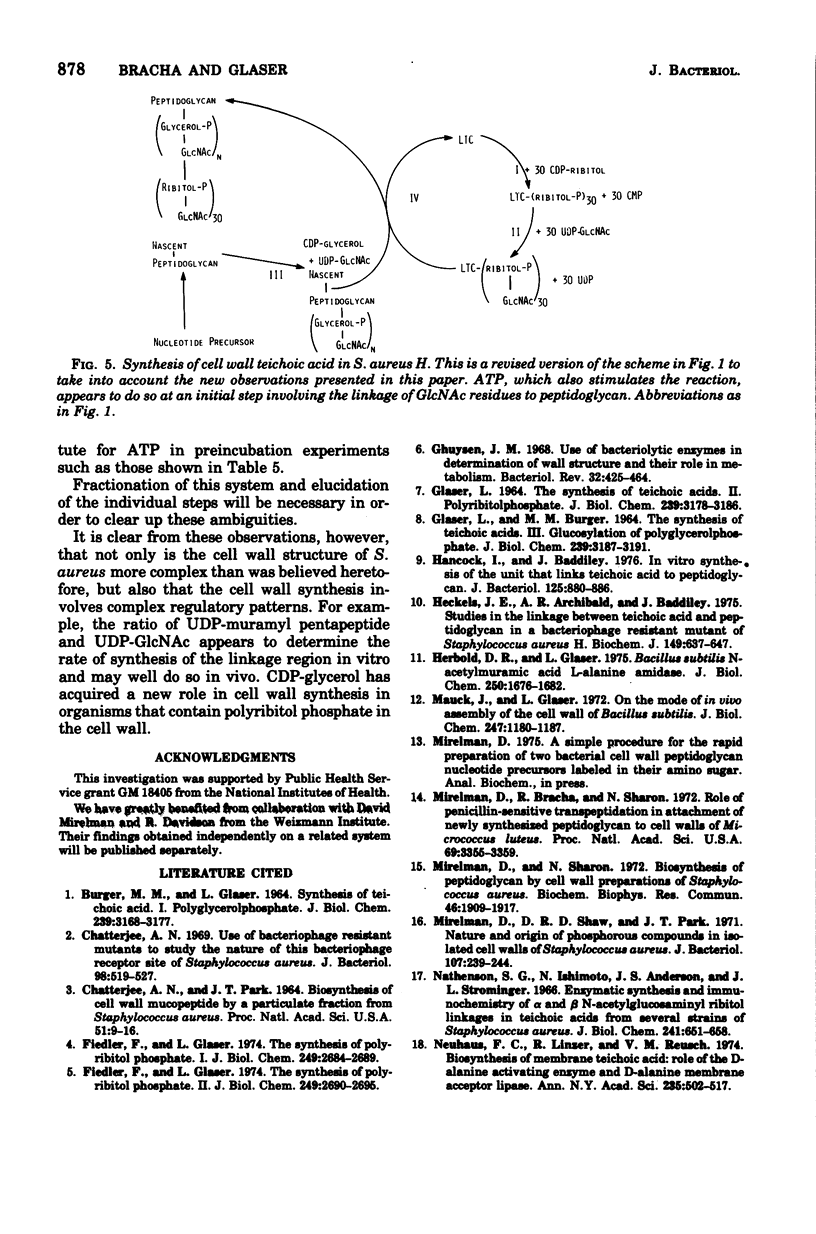
Abstract
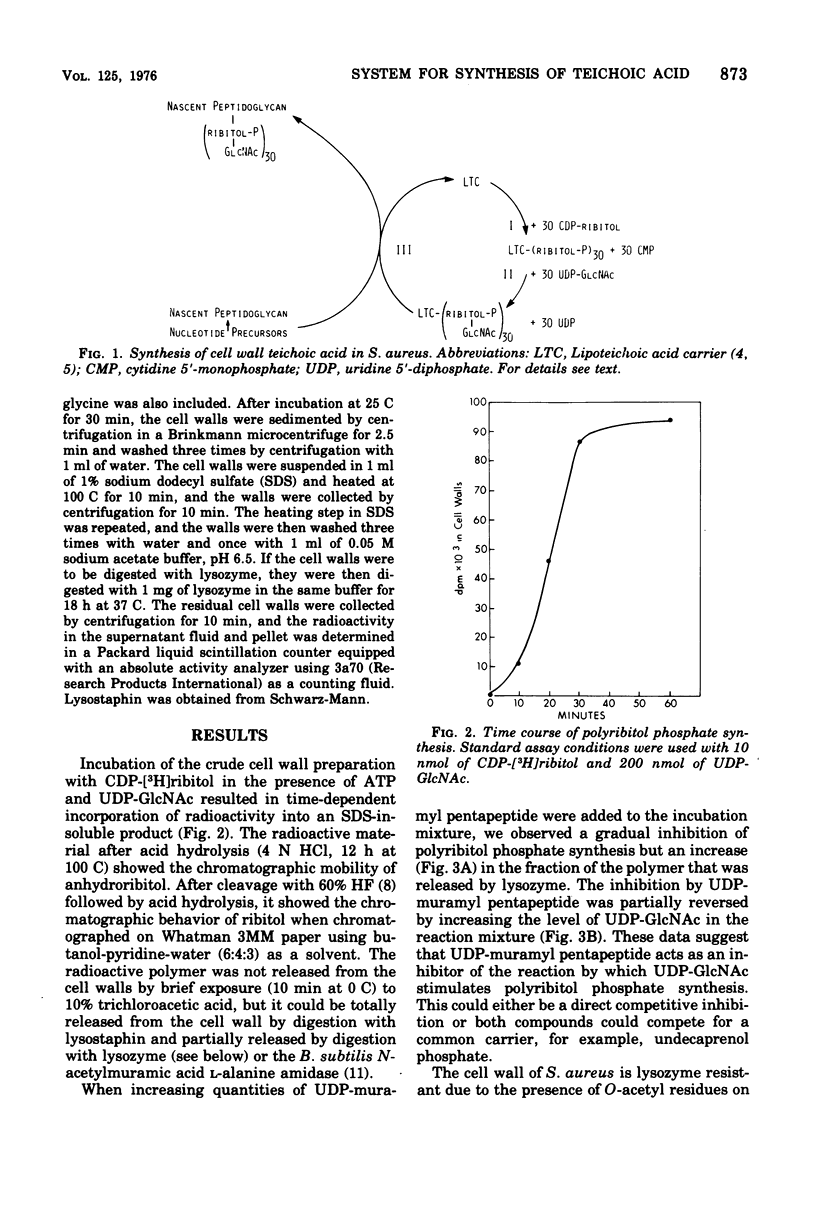
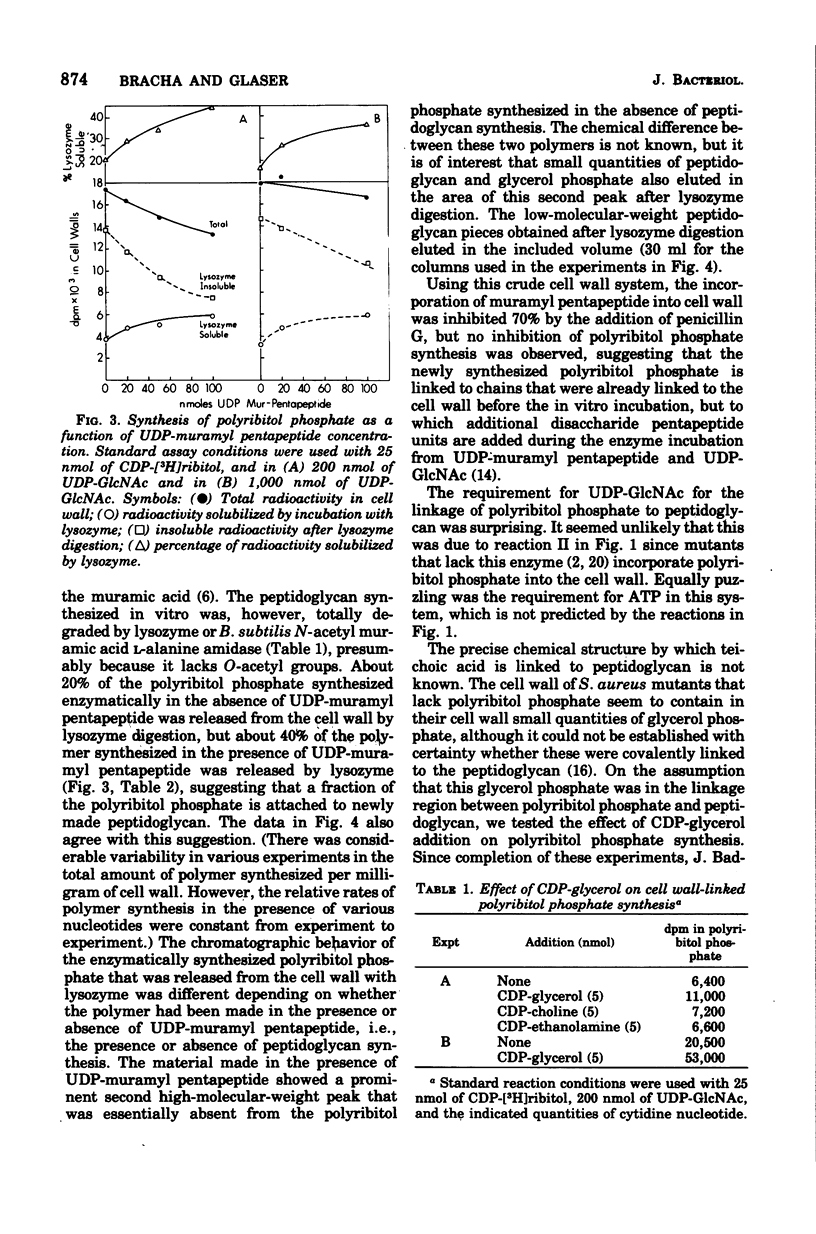
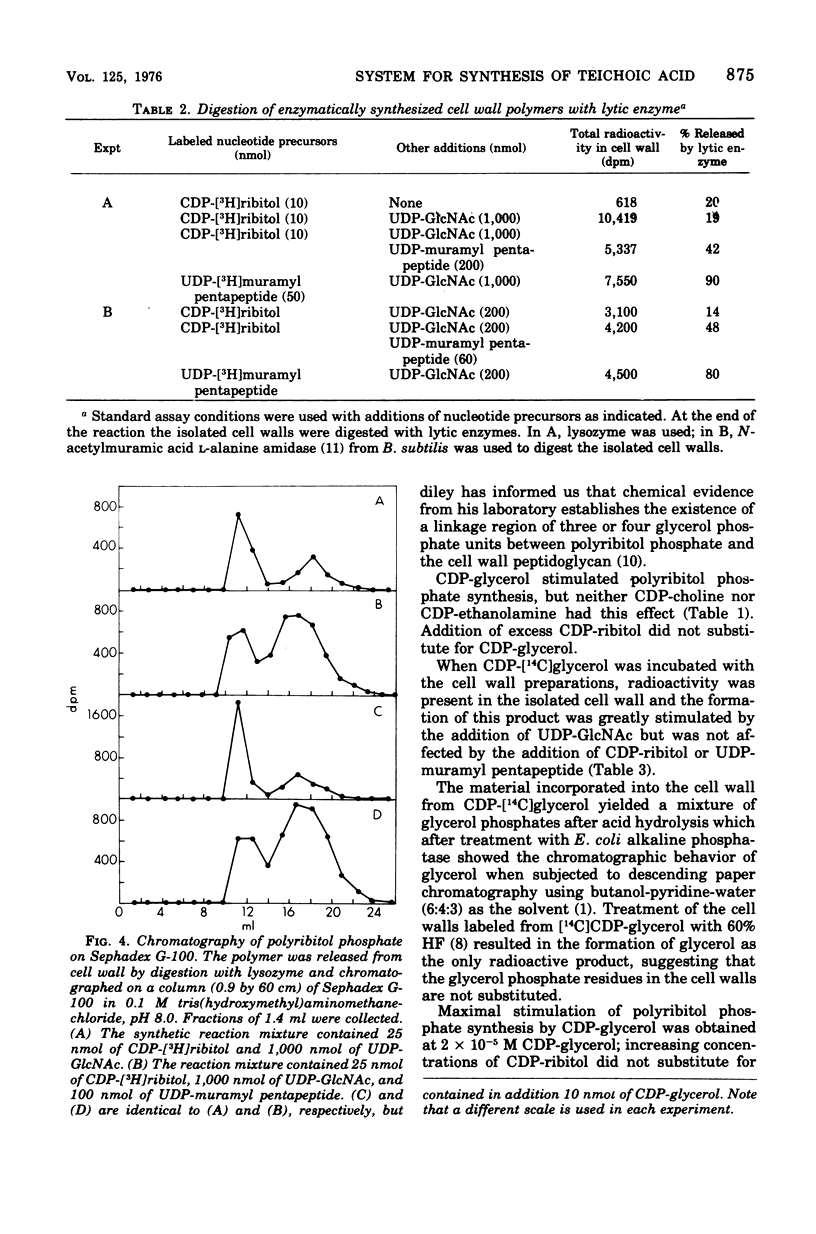
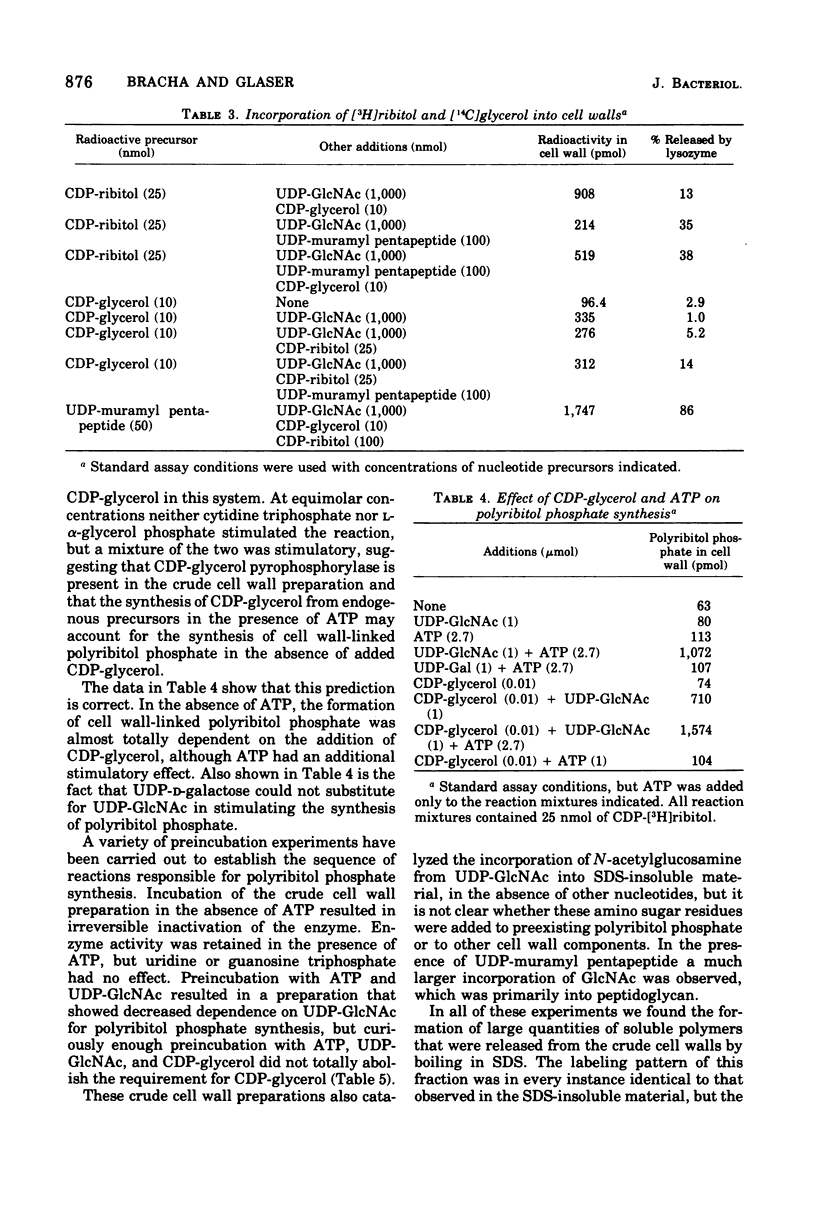
A crude cell wall preparation from Staphylococcus aureus H prepared by the method of Mirelman and Sharon (1972) was shown to catalyze the synthesis of polyribitol phosphate linked to the cell wall peptidoglycan. The reaction used cytidine diphosphate (CDP)-ribitol as a substrate and in addition required the presence of CDP-glycerol, uridine diphosphate (UDP)-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, and adenosine triphosphate. Incubation of radioactive CDP-glycerol with the crude cell wall preparation resulted in the transfer of glycerol phosphate residues to the cell wall; this reaction was greatly stimulated by the presence of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine. These data suggest that polyribitol phosphate is linked to the cell wall peptidoglycan by an oligomer contaning N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and glycerol phosphate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGER M. M., GLASER L. THE SYNTHESIS OF TEICHOIC ACIDS. I. POLYGLYCEROPHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3168–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATTERJEE A. N., PARK J. T. BIOSYNTHESIS OF CELL WALL MUCOPEPTIDE BY A PARTICULATE FRACTION FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jan;51:9–16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. N. Use of bacteriophage-resistant mutants to study the nature of the bacteriophage receptor site of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):519–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.519-527.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F., Glaser L. The synthesis of polyribitol phosphate. I. Purification of polyribitol phosphate polymerase and lipoteichoic acid carrier. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2684–2689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F., Glaser L. The synthesis of polyribitol phosphate. II. On the mechanism of polyribitol phosphate polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2690–2695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASER L., BURGER M. M. THE SYNTHESIS OF TEICHOIC ACIDS. 3. GLUCOSYLATION OF POLYGLYCEROPHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3187–3191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASER L. THE SYNTHESIS OF TEICHOIC ACIDS. II. POLYRIBITOL PHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3178–3186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Use of bacteriolytic enzymes in determination of wall structure and their role in cell metabolism. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):425–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock I., Baddiley J. In vitro synthesis of the unit that links teichoic acid to peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):880–886. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.880-886.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. Studies on the linkage between teichoic acid and peptidoglycan in a bacteriophage-resistant mutant of Staphylococcus aureus H. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):637–647. doi: 10.1042/bj1490637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbold D. R., Glaser L. Bacillus subtilis N-acetylmuramic acid L-alanine amidase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1676–1682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J., Glaser L. On the mode of in vivo assembly of the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1180–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Sharon N. Biosynthesis of peptidoglycan by a cell wall preparation of Staphylococcus aureus and its inhibition by penicillin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1909–1917. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Shaw D. R., Park J. T. Nature and origins of phosphorus compounds in isolated cell walls of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.239-244.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus F. C., Linzer R., Reusch V. M., Jr Biosynthesis of membrane teichoic acid: role of the D-alanine-activating enzyme and D-alanine: membrane acceptor ligase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):502–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., McDonnell M., Westphal M., Zanati E. Coordinated incorporation of nascent peptidoglycan and teichoic acid into pneumococcal cell walls and conservation of peptidoglycan during growth. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke A. W., Ward J. B. The synthesis of covalently-linked teichoic acid and peptidoglycan by cell-free preparations of Bacillus licheniformis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 4;65(3):877–885. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80467-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



