Abstract
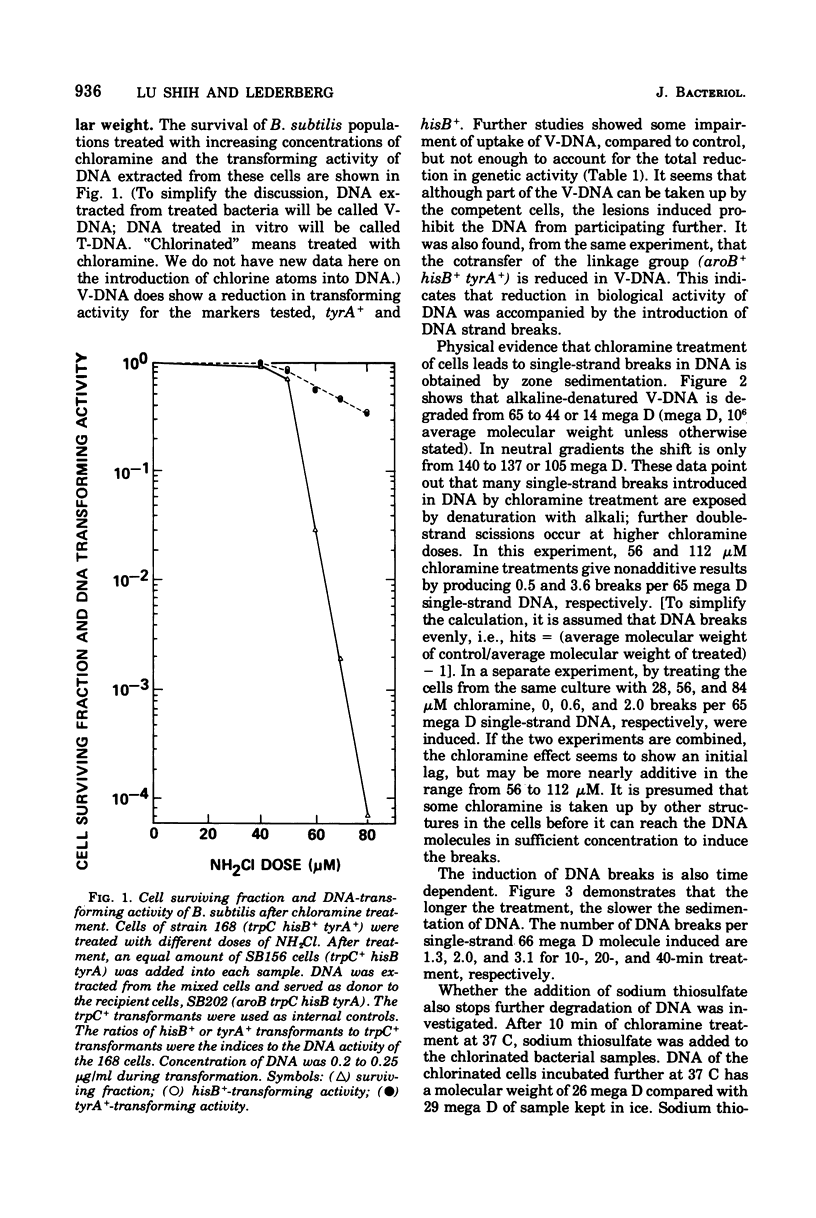
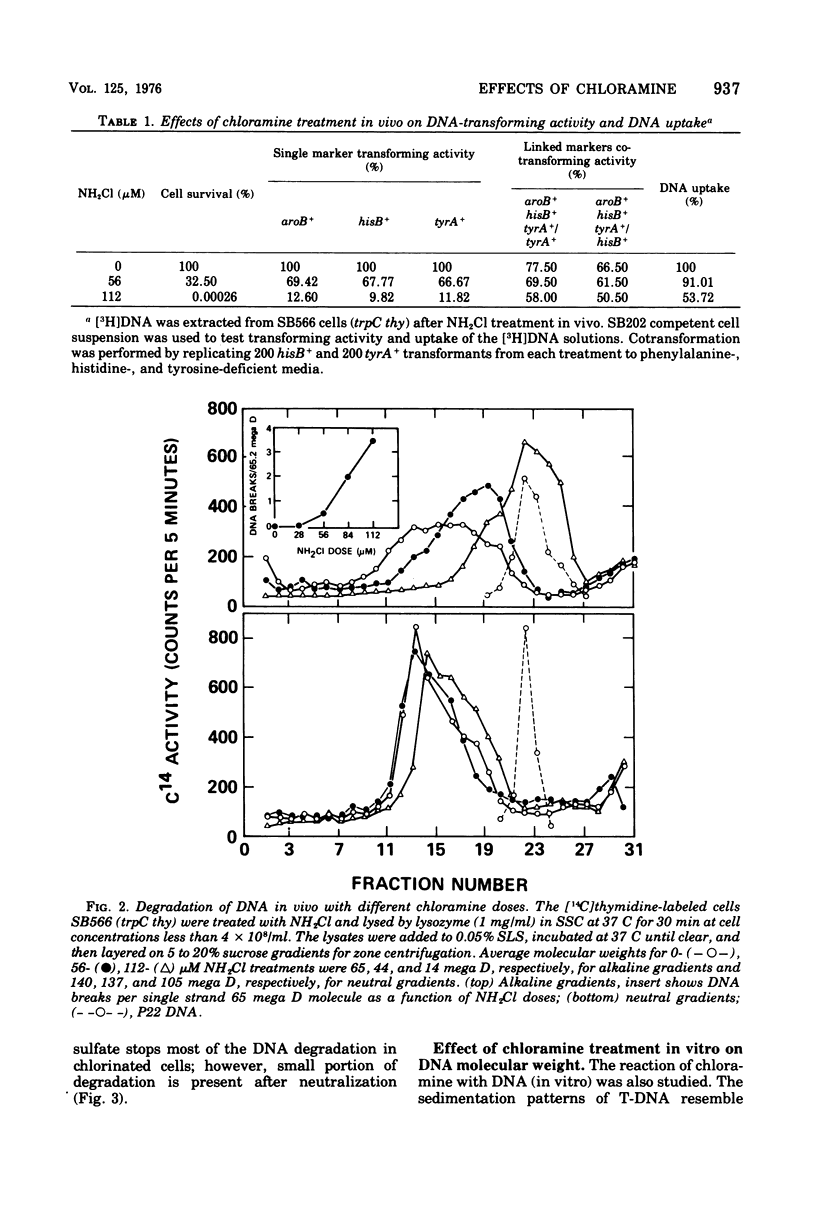
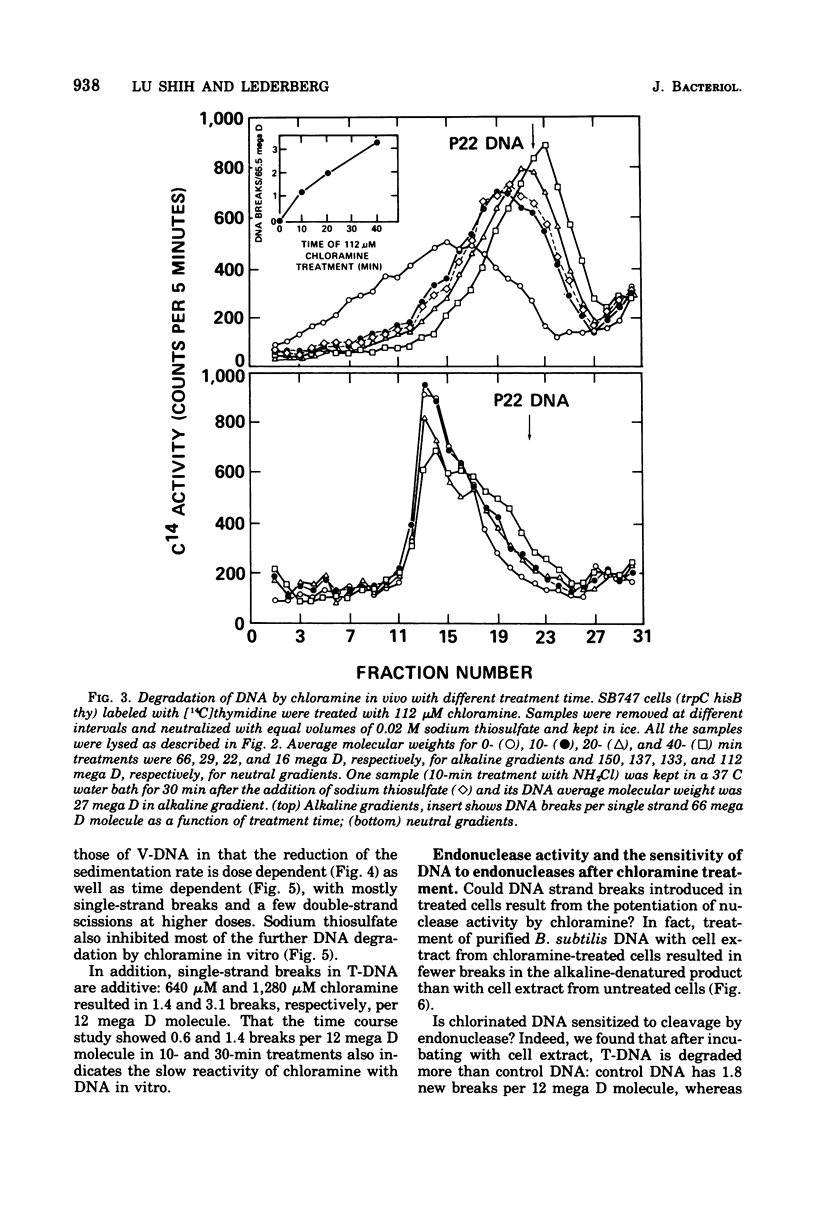
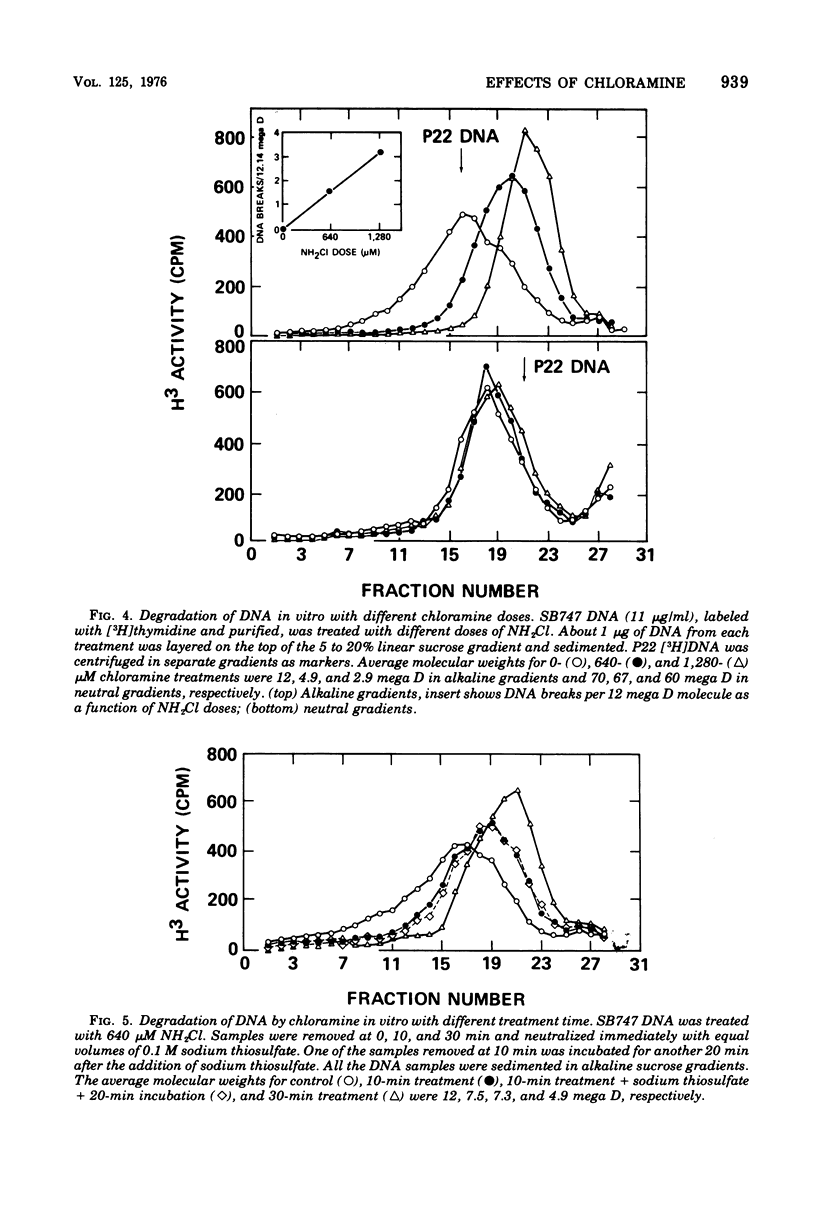
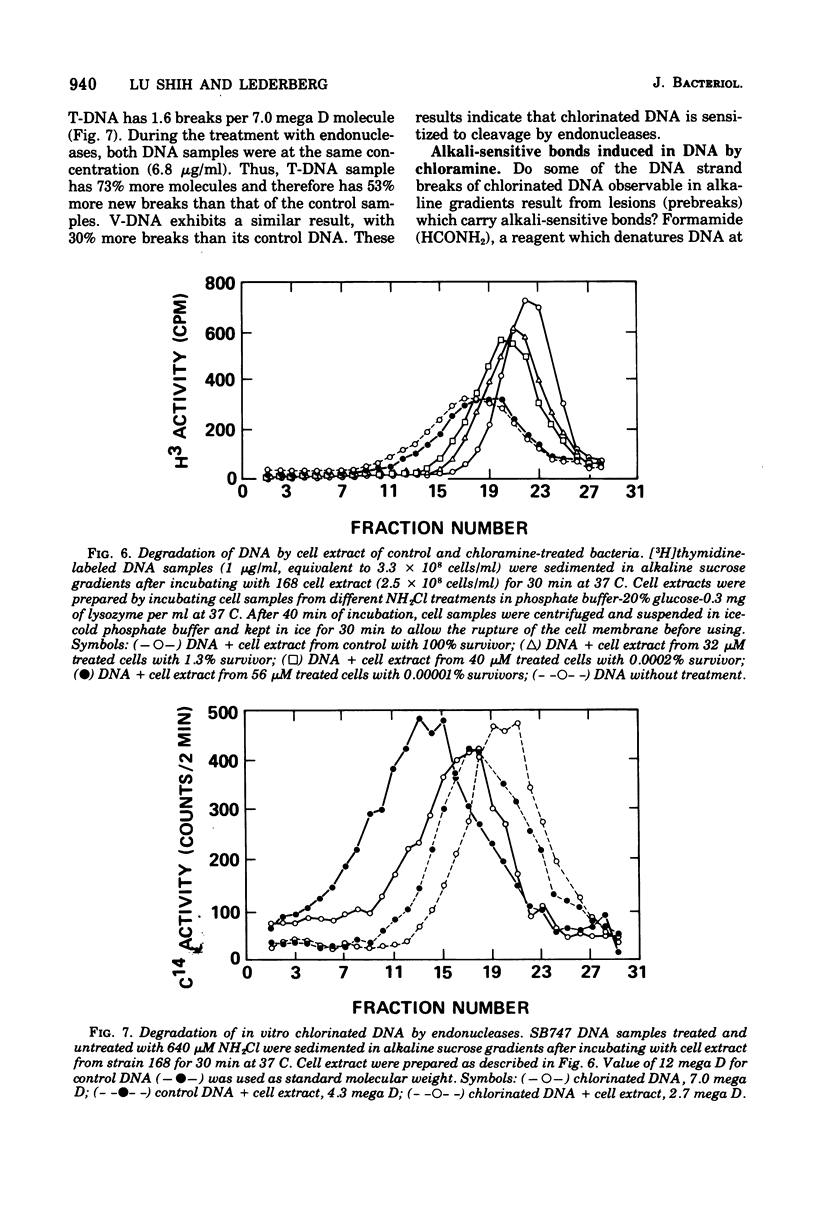
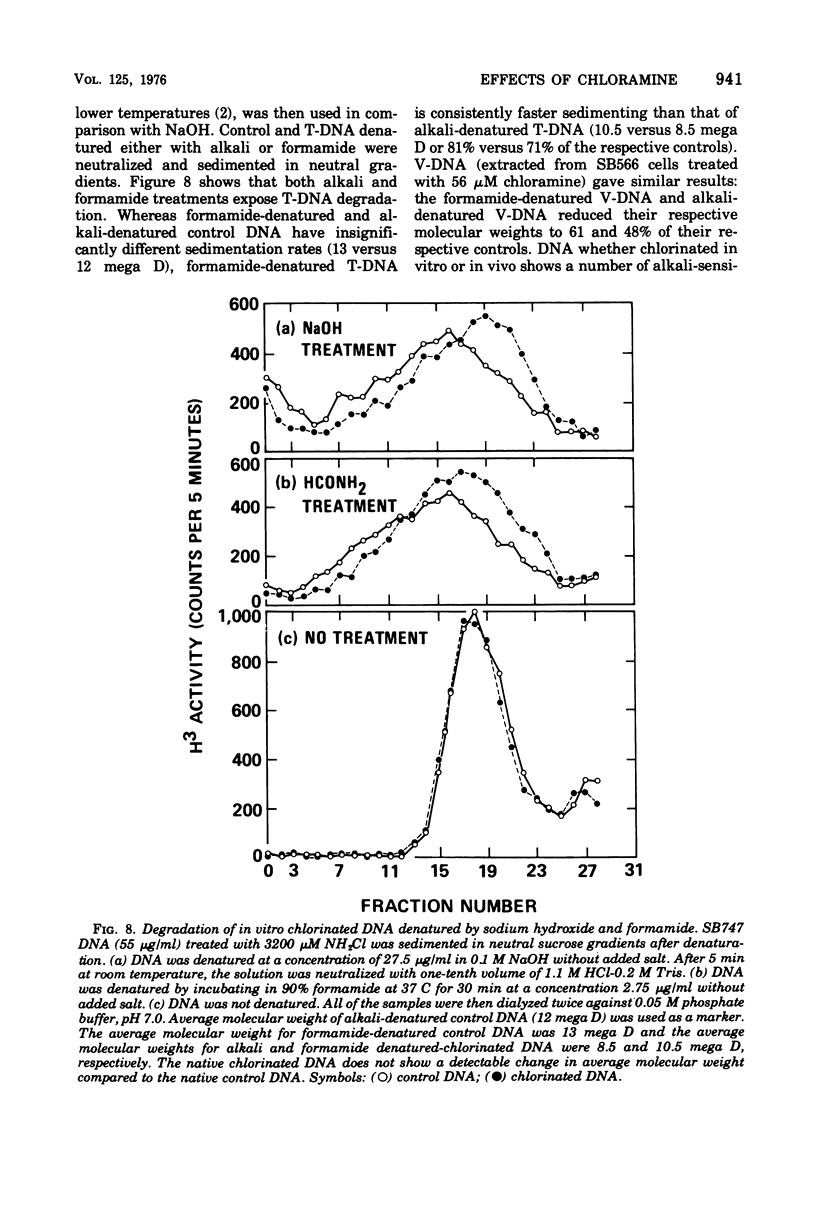
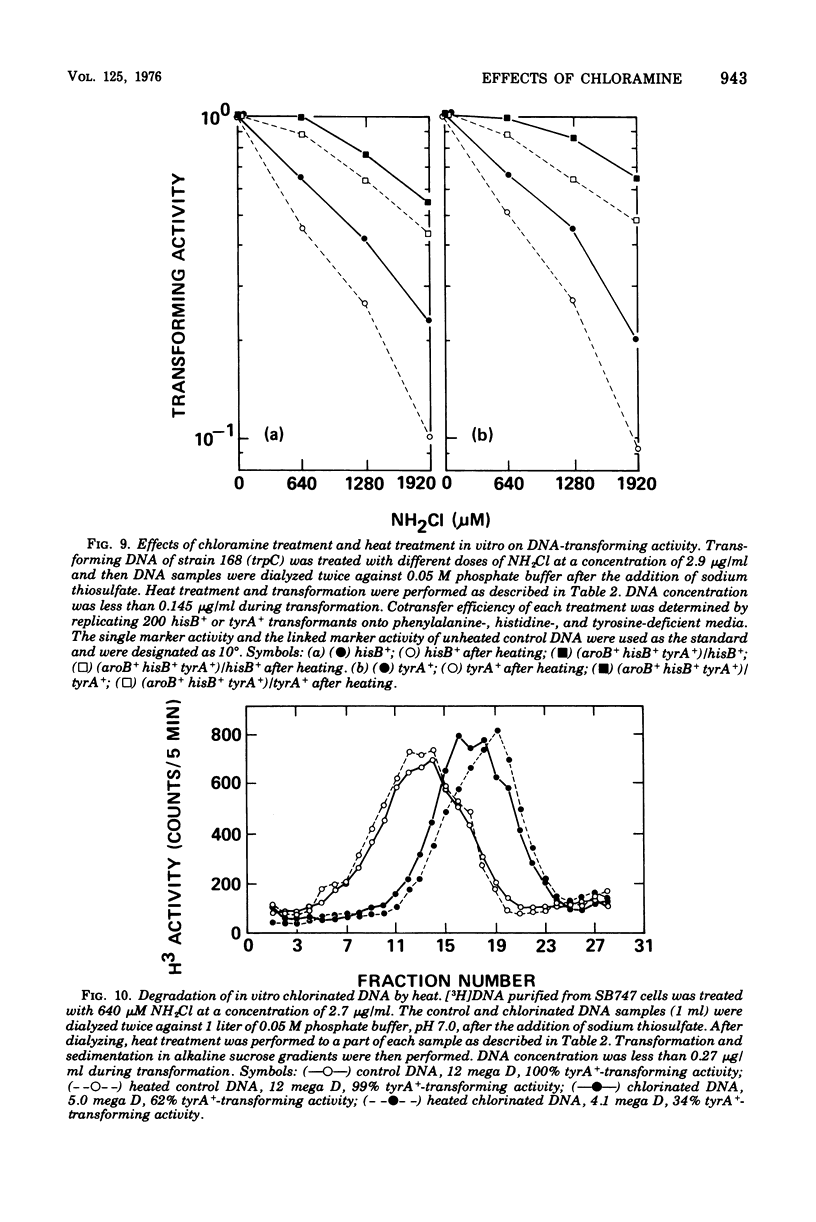
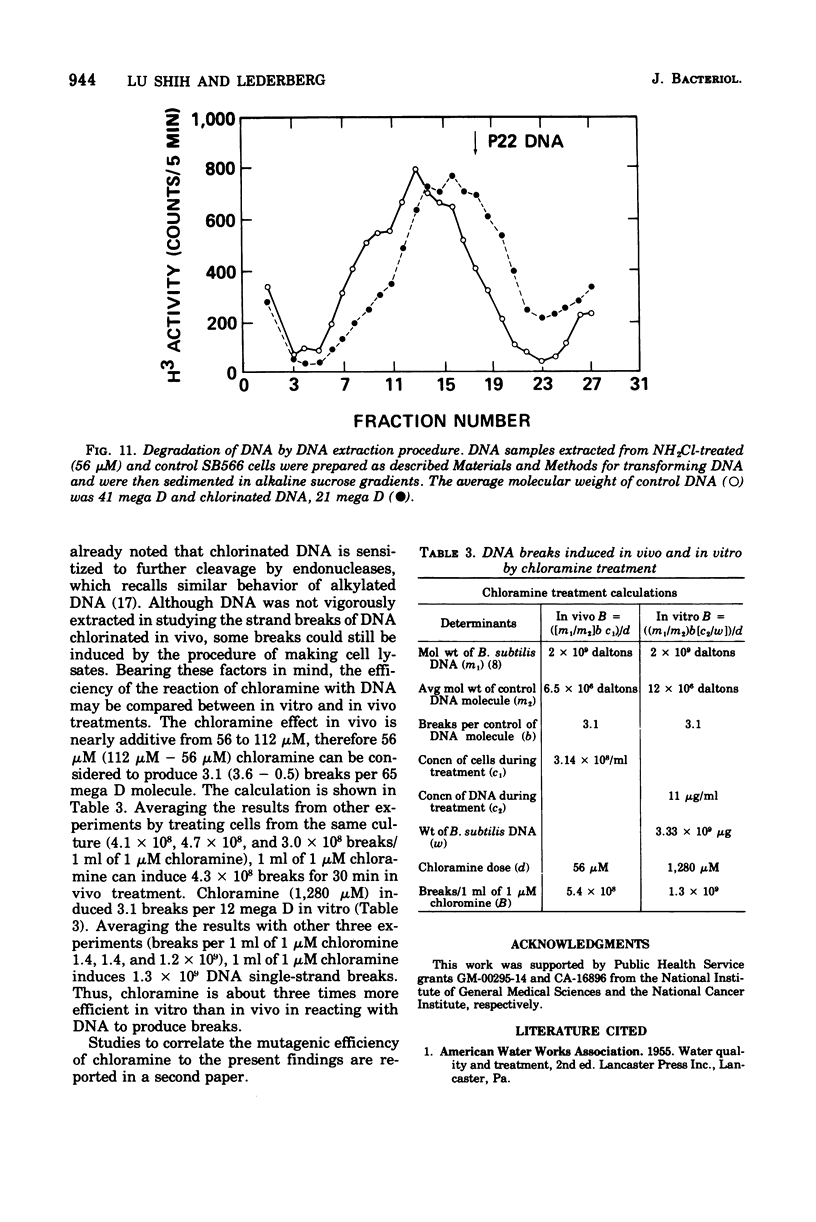
The lesions induced in Bacillus subtilis deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) after treating bacterial cells (in vivo) and bacterial DNA (in vitro) with chloramine were studied biologically and physically. Single-strand breaks and a few double-strand scissions (at higher chloramine doses) accompanied loss of DNA-transforming activity in both kinds of treatments. Chloramine was about three times more efficient in vitro than in vivo in inducing DNA single-strand breaks. DNA was slowly chlorinated; the subsequent efficiency of producing DNA breaks was high. Chlorination of cells also reduced activity of endonucleases in cells; however, chlorinated DNA of both treatments was sensitized to cleavage by endonucleases. The procedure of extracting DNA from cells treated with chloramine induced further DNA degradation. Both treatments introduced a small fraction of alkali-sensitive lesions in DNA. DNA chlorinated in vitro showed further reduction in transforming activity as well as further degradation after incubation at 50 C for 5 h whereas DNA extracted from chloramine-treated cells did not show such a heat sensitivity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGI E., HERSHEY A. D. Sedimentation rate as a measure of molecular weight of DNA. Biophys J. 1963 Jul;3:309–321. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(63)86823-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blüthmann H., Brück D., Hübner L., Schöffski A. Reassociation of nucleic acids in solutions containing formamide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 4;50(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F. Integration of deoxyribonuclease-treated DNA in bacillus subtilis transformation. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):233–258. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.6.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayatsu H., Pan S., Ukita T. Reaction of sodium hypochlorite with nucleic acids and their constituents. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1971 Oct;19(10):2189–2192. doi: 10.1248/cpb.19.2189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz L. C., Zimm B. H. Size of DNA determined by viscoelastic measurements: results on bacteriophages, Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):779–800. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN L. S., TOLMACH L. J. Genetic transformation. I. Cellular incorporation of DNA accompanying transformation in Pneumococcus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):68–82. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN L. S., TOLMACH L. J. Genetic transformation. II. The significance of damage to the DNA molecule. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jun;33(2):371–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton W., Bacon V., Duffield A. M., Halpern B., Hoyano Y., Pereira W., Lederberg J. Chlorination studies. I. The reaction of aqueous hypochlorous acid with cytosine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 21;48(4):880–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90690-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat R., Nofre C., Cier A. Effet de l'hypochlorite de sodium sur les constituants pyrimidiques des bactéries. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1965 May 3;260(18):4859–4861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat R., Nofre C., Cier A. Effets de l'hypochlorite de sodium, de l'ozone et des radiations ionisantes sur les constituants pyrimidiques d'Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1968 May;114(5):595–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS B. S. Recovery of deoxyribonucleic acid from the effects of alkylation. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:89–103. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. R. Physical heterogeneity among Bacillus subtilis deoxyribonucleic acid molecules carrying particular genetic markers. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1239–1247. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1239-1247.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss B. S., Robbins M. DNA methylated in vitro by a monofunctional alkylating agent as a substrate for a specific nuclease from Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 18;161(1):68–75. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



