Abstract
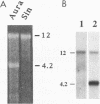
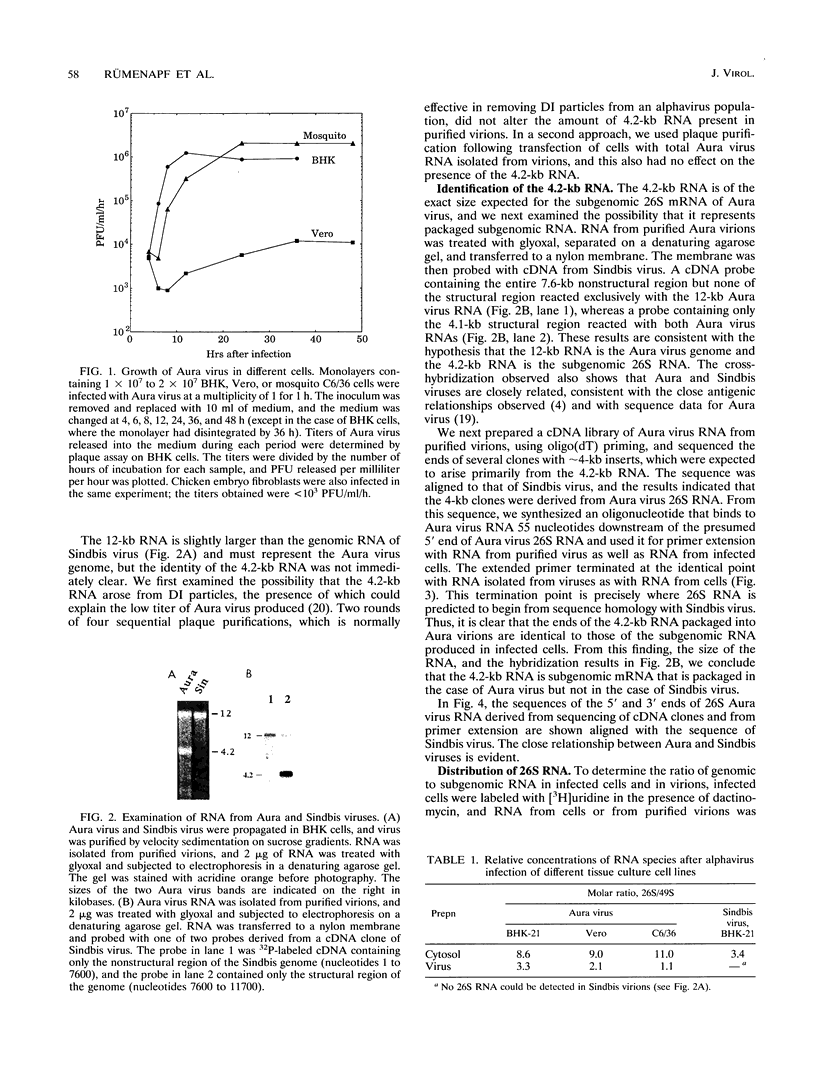
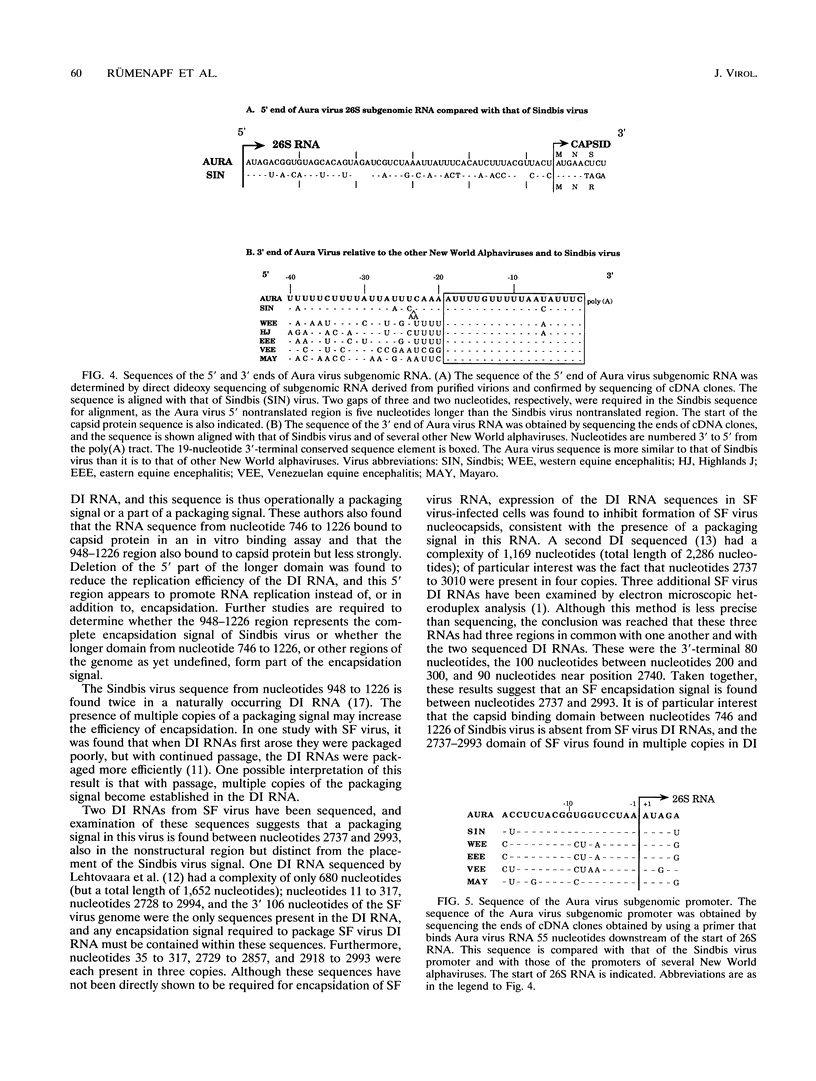
Purified virions of Aura virus, a South American alphavirus related to Sindbis virus, were found to contain two RNA species, one of 12 kb and the other of 4.2 kb. Northern (RNA) blot analysis, primer extension analysis, and limited sequencing showed that the 12-kb RNA was the viral genomic RNA, whereas the 4.2-kb RNA present in virus preparations was identical to the 26S subgenomic RNA present in infected cells. The subgenomic RNA is the messenger for translation of the viral structural proteins, and its synthesis is absolutely required for replication of the virus. Although 26S RNA is present in the cytosol of all cells infected by alphaviruses, this is the first report of incorporation of the subgenomic RNA into alphavirus particles. Packaging of the Aura virus subgenomic mRNA occurred following infection of mosquito (Aedes albopictus C6/36), hamster (BHK-21), or monkey (Vero) cells. Quantitation of the amounts of genomic and subgenomic RNA both in virions and in infected cells showed that the ratio of genomic to subgenomic RNA was 3- to 10-fold higher in Aura virions than in infected cells. Thus, although the subgenomic RNA is packaged efficiently, the genomic RNA has a selective advantage during packaging. In contrast, in parallel experiments with Sindbis virus, packaging of subgenomic RNA was not detectable. We also found that subgenomic RNA was present in about threefold-greater amounts relative to genomic RNA in cells infected by Aura virus than in cells infected by Sindbis virus. Packaging of the Aura virus subgenomic RNA, but not those of other alphaviruses, suggests that Aura virus 26S RNA contains a packaging signal for incorporation into virions. The importance of the packaging of this RNA into virions in the natural history of the virus remains to be determined.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alanen M., Wartiovaara J., Söderlund H. Sequences conserved in the defective interfering RNAs of Semliki Forest virus: an electron microscopic heteroduplex analysis. Hereditas. 1987;106(1):19–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1987.tb00232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAUSEY O. R., CASALS J., SHOPE R. E., UDOMSAKDI S. AURA AND UNA, TWO NEW GROUP A ARTHROPOD-BORNE VIRUSES. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 Sep;12:777–781. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1963.12.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calisher C. H., Karabatsos N., Lazuick J. S., Monath T. P., Wolff K. L. Reevaluation of the western equine encephalitis antigenic complex of alphaviruses (family Togaviridae) as determined by neutralization tests. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Mar;38(2):447–452. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy W. R., Hahn Y. S., de Groot R. J., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Synthesis and processing of the nonstructural polyproteins of several temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):199–208. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz J. M., Huang H. V. Utilization of heterologous alphavirus junction sequences as promoters by Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):857–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.857-864.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Pettersson R. F., Keränen S., Lehtovaara P., Söderlund H., Ukkonen P. Multiple structurally related defective-interfering RNAs formed during undiluted passages of Semliki forest virus. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):686–697. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtovaara P., Söderlund H., Keränen S., Pettersson R. F., Käriäinen L. 18S defective interfering RNA of Semliki Forest virus contains a triplicated linear repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5353–5357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtovaara P., Söderlund H., Keränen S., Pettersson R. F., Käriäinen L. Extreme ends of the genome are conserved and rearranged in the defective interfering RNAs of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):731–748. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemm J. A., Rice C. M. Assembly of functional Sindbis virus RNA replication complexes: requirement for coexpression of P123 and P34. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1905–1915. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1905-1915.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Schlesinger S., Huang H. V. Promoter for Sindbis virus RNA-dependent subgenomic RNA transcription. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1726–1733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1726-1733.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe S. S., Schlesinger S. Common and distinct regions of defective-interfering RNAs of Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):865–872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.865-872.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju R., Huang H. V. Analysis of Sindbis virus promoter recognition in vivo, using novel vectors with two subgenomic mRNA promoters. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2501–2510. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2501-2510.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Birdwell C. R., Lenches E. M., Staples S. E., Strauss J. H. Mutants of Sindbis virus. II. Characterization of a maturation-defective mutant, ts103. Virology. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):122–149. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., De Groot R. J., Levinson R., Strauss J. H. Identification of the active site residues in the nsP2 proteinase of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):932–940. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90268-T. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen M., Liljeström P., Garoff H. Spike protein-nucleocapsid interactions drive the budding of alphaviruses. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4737–4747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4737-4747.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Nitschko H., Ghattas I., Wright R., Schlesinger S. Evidence for specificity in the encapsidation of Sindbis virus RNAs. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5310–5318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5310-5318.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Boege U., Wengler G., Bischoff H., Wahn K. The core protein of the alphavirus Sindbis virus assembles into core-like nucleoproteins with the viral genome RNA and with other single-stranded nucleic acids in vitro. Virology. 1982 Apr 30;118(2):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G., Boege U., Wahn K. Establishment and analysis of a system which allows assembly and disassembly of alphavirus core-like particles under physiological conditions in vitro. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. J., Hardy W. R., Shirako Y., Strauss J. H. Cleavage-site preferences of Sindbis virus polyproteins containing the non-structural proteinase. Evidence for temporal regulation of polyprotein processing in vivo. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2631–2638. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. J., Rümenapf T., Kuhn R. J., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Sindbis virus RNA polymerase is degraded by the N-end rule pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8967–8971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steeg H., Kasperaitis M., Voorma H. O., Benne R. Infection of neuroblastoma cells by Semliki Forest virus. The interference of viral capsid protein with the binding of host messenger RNAs into initiation complexes is the cause of the shut-off of host protein synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 1;138(3):473–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]