Abstract
The reovirus group C temperature-sensitive mutant tsC447, whose defect maps to the S2 gene, which encodes the major core protein sigma 2, fails to assemble core particles at the nonpermissive temperature. To identify other proteins that may interact with sigma 2 during assembly, we generated and examined 10 independent revertants of the mutant. To determine which gene(s) carried a compensatory suppressor mutation(s), we generated intertypic reassortants between wild-type reovirus serotype 1 Lang and each revertant and determined the temperature sensitivities of the reassortants by efficiency-of-plating assays. Results of the efficiency-of-plating analyses indicated that reversion of the tsC447 defect was an intragenic process in all revertants. To identify the region(s) of sigma 2 that had reverted, we determined the nucleotide sequences of the S2 genes. In all revertant sequences examined, the G at nucleotide position 1166 in tsC447 had reverted to the A present in the wild-type sequence. This reversion leads to the restoration of a wild-type asparagine (in place of a mutant aspartic acid) at amino acid 383 in the sigma 2 sequence. These results collectively indicate that the functional lesion in tsC447 is Asp-383 and that this lesion cannot be corrected by alterations in other core proteins. These observations suggest that this region of sigma 2, which may be important in mediating assembly of the core particle, does not interact significantly with other reovirus proteins.
Full text
PDF

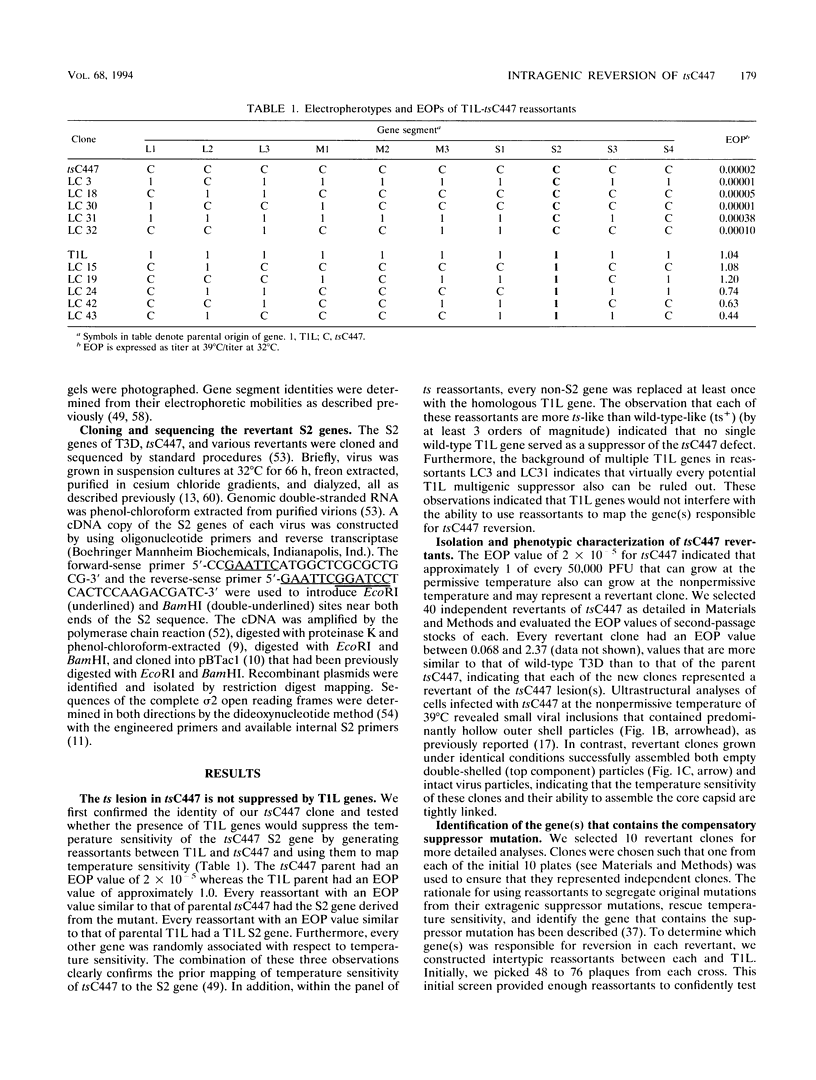
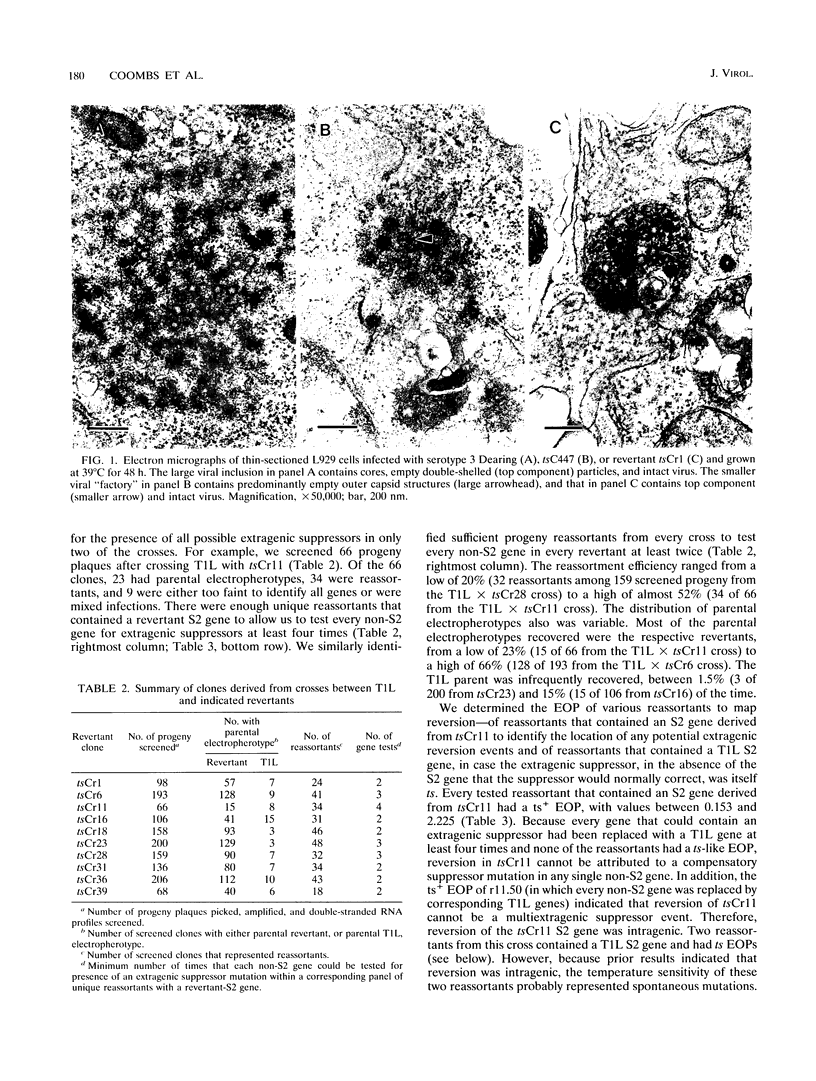
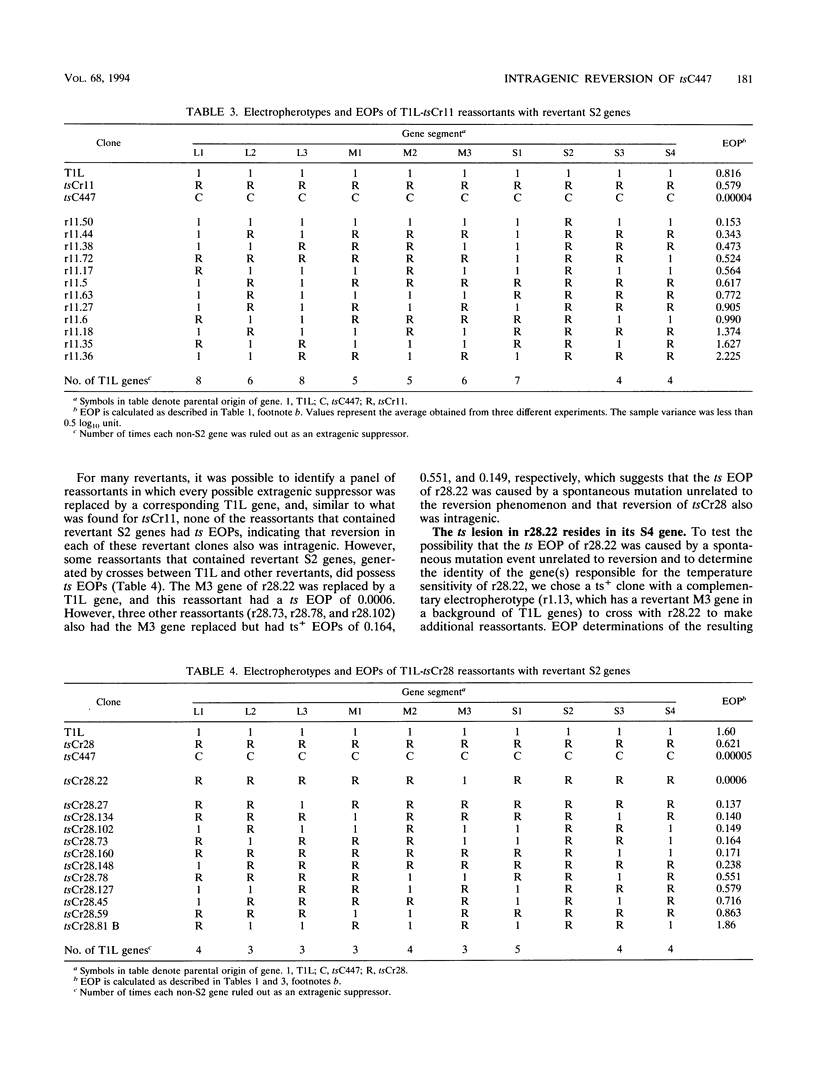




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. A., Joklik W. K. The sequence of the reovirus serotype 3 L3 genome segment which encodes the major core protein lambda 1. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J. The current picture of the structure and assembly of tobacco mosaic virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Feb;65(Pt 2):253–279. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. T., Zweerink H. J. Fate of parental reovirus in infected cell. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):544–555. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. R., Zarbl H., Millward S. Reovirus guanylyltransferase is L2 gene product lambda 2. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):307–311. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.307-311.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs K. M., Fields B. N., Harrison S. C. Crystallization of the reovirus type 3 Dearing core. Crystal packing is determined by the lambda 2 protein. J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 5;215(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80089-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Protein folding. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):1–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2700001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe J. S., Cooper H. J., Smith M. A., Sims M. J., Parker D., Gewert D. Improved cloning efficiency of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products after proteinase K digestion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):184–184. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermody T. S., Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Coombs K. M., Fields B. N. The S2 gene nucleotide sequences of prototype strains of the three reovirus serotypes: characterization of reovirus core protein sigma 2. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5721–5731. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5721-5731.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Fields B. N. Activation and characterization of the reovirus transcriptase: genetic analysis. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):110–118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.110-118.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryden K. A., Wang G., Yeager M., Nibert M. L., Coombs K. M., Furlong D. B., Fields B. N., Baker T. S. Early steps in reovirus infection are associated with dramatic changes in supramolecular structure and protein conformation: analysis of virions and subviral particles by cryoelectron microscopy and image reconstruction. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1023–1041. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fane B. A., Hayashi M. Second-site suppressors of a cold-sensitive prohead accessory protein of bacteriophage phi X174. Genetics. 1991 Aug;128(4):663–671. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.4.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fane B., King J. Intragenic suppressors of folding defects in the P22 tailspike protein. Genetics. 1991 Feb;127(2):263–277. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.2.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. N., Joklik W. K. Isolation and preliminary genetic and biochemical characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. N., Raine C. S., Baum S. G. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus type 3: defects in viral maturation as studied by immunofluorescence and electron microscopy. Virology. 1971 Mar;43(3):569–578. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French T. J., Roy P. Synthesis of bluetongue virus (BTV) corelike particles by a recombinant baculovirus expressing the two major structural core proteins of BTV. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1530–1536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1530-1536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Morgan M., Muthukrishnan S., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus messenger RNA contains a methylated, blocked 5'-terminal structure: m-7G(5')ppp(5')G-MpCp-. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):362–366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghendon Y., Markushin S., Lisovskaya K., Penn C. R., Mahy B. W. Extragenic suppression of a ts phenotype during recombination between ts mutants of two fowl plague virus strains with a ts mutation in gene 1. J Gen Virol. 1982 Oct;62(Pt 2):239–248. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-2-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. P. Genetic studies of protein stability and mechanisms of folding. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:481–507. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P. E., Roth J. R. Mechanisms of suppression. Adv Genet. 1973;17:1–105. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J. D., Bellamy A. R., Earnshaw W. C., Schutt C. Biophysical studies of reovirus type 3. IV. Low-angle x-ray diffraction studies. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):240–249. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90629-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvik J., Botstein D. Conditional-lethal mutations that suppress genetic defects in morphogenesis by altering structural proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2738–2742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Slade W. R., Newman J. W., McCahon D. Temperature-sensitive mutants of foot-and-mouth disease virus with altered structural polypeptides. II. Comparison of recombination and biochemical maps. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):67–72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.67-72.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Hayes E. C., Joklik W. K. Characterization of anti-reovirus immunoglobulins secreted by cloned hybridoma cell lines. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):134–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Hayes E. C., Joklik W. K. Protein sigma 1 is the reovirus cell attachment protein. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):156–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90535-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., Baltimore D. An intragenic revertant of a poliovirus 2C mutant has an uncoating defect. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1102–1107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1102-1107.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luftig R. B., Kilham S. S., Hay A. J., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. An ultrastructural study of virions and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):170–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matoba Y., Sherry B., Fields B. N., Smith T. W. Identification of the viral genes responsible for growth of strains of reovirus in cultured mouse heart cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1628–1633. doi: 10.1172/JCI115177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurides P. A., Schwarz J. J., Berget P. B. Intragenic suppression of a capsid assembly-defective P22 tailspike mutation. Genetics. 1990 Aug;125(4):673–681. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.4.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden G., Essani K., Dales S. A new endonuclease restriction site which is at the locus of a temperature-sensitive mutation in vaccinia virus is associated with true and pseudoreversion. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90503-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhillips T. H., Ramig R. F. Extragenic suppression of temperature-sensitive phenotype in reovirus: mapping suppressor mutations. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):428–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf P., Cyrklaff M., Adrian M. The three-dimensional structure of reovirus obtained by cryo-electron microscopy. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3129–3136. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. M., Kingsbury D. W. Pyridoxal phosphate as a probe of reovirus transcriptase. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):484–489. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozov S. Y. A possible relationship of reovirus putative RNA polymerase to polymerases of positive-strand RNA viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5394–5394. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustoe T. A., Ramig R. F., Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. A genetic map of reovirus. III. Assignment of the double-stranded RNA-positive mutant groups A, B, and G to genome segments. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nibert M. L., Furlong D. B., Fields B. N. Mechanisms of viral pathogenesis. Distinct forms of reoviruses and their roles during replication in cells and host. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):727–734. doi: 10.1172/JCI115369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevelige P. E., Jr, King J. Assembly of bacteriophage P22: a model for ds-DNA virus assembly. Prog Med Virol. 1993;40:206–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph S. J., Harvey J. D., Bellamy A. R. Subunit structure of the reovirus spike. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):894–896. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.894-896.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Ahmed R., Fields B. N. A genetic map of reovirus: assignment of the newly defined mutant groups H, I, and J to genome segments. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):299–313. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90203-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Fields B. N. Revertants of temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus: evidence for frequent extragenic suppression. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Mustoe T. A., Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. A genetic map of reovirus. II. Assignment of the double-stranded RNA-negative mutant groups C, D, and E to genome segments. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):531–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Ward R. L. Genomic segment reassortment in rotaviruses and other reoviridae. Adv Virus Res. 1991;39:163–207. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60795-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott R., Orlich M., Scholtissek C. Attenuation of pathogenicity of fowl plague virus by recombination with other influenza A viruses nonpathogenic for fowl: nonexculsive dependence of pathogenicity on hemagglutinin and neuraminidase of the virus. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):54–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.54-60.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEMPAK J. G., WARD R. T. AN IMPROVED STAINING METHOD FOR ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Sep;22:697–701. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Co M. S., Brown E. G., Fields B. N. Distinct binding sites for zinc and double-stranded RNA in the reovirus outer capsid protein sigma 3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):273–283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Spring S. B. Extragenic suppression of temperature-sensitive mutations in RNA segment 8 by replacement of different rna segments with those of other influenza A virus prototype strains. Virology. 1982 Apr 15;118(1):28–34. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seliger L. S., Zheng K., Shatkin A. J. Complete nucleotide sequence of reovirus L2 gene and deduced amino acid sequence of viral mRNA guanylyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16289–16293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Ramig R. F., Mustoe T. A., Fields B. N. A genetic map of reovirus. 1. Correlation of genome RNAs between serotypes 1, 2, and 3. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Fields B. N. The reovirus M1 gene, encoding a viral core protein, is associated with the myocarditic phenotype of a reovirus variant. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4850–4856. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4850-4856.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbarao E. K., Perkins M., Treanor J. J., Murphy B. R. The attenuation phenotype conferred by the M gene of the influenza A/Ann Arbor/6/60 cold-adapted virus (H2N2) on the A/Korea/82 (H3N2) reassortant virus results from a gene constellation effect. Virus Res. 1992 Sep 1;25(1-2):37–50. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90098-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolpin M. D., Massicot J. G., Mullinix M. G., Kim H. W., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M., Murphy B. R. Genetic factors associated with loss of the temperature-sensitive phenotype of the influenza A/Alaska/77-ts-1A2 recombinant during growth in vivo. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):505–517. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosser G., Labbé M., Brémont M., Cohen J. Expression of the major capsid protein VP6 of group C rotavirus and synthesis of chimeric single-shelled particles by using recombinant baculoviruses. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5825–5831. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5825-5831.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treanor J. J., Buja R., Murphy B. R. Intragenic suppression of a deletion mutation of the nonstructural gene of an influenza A virus. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4204–4210. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4204-4210.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Powers M. L., Fields B. N. Absolute linkage of virulence and central nervous system cell tropism of reoviruses to viral hemagglutinin. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):609–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. K., Zweerink H. J. Studies on the structure of reovirus cores: selective removal of polypeptide lambda 2. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., McLaughlin T., Joklik W. K. The sequences of the S2 genome segments of reovirus serotype 3 and of the dsRNA-negative mutant ts447. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):340–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90392-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L. C., Gulyas B. J. An improved method for processing single cells for electron microscopy utilizing agarose. Anat Rec. 1981 Oct;201(2):273–281. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092010207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Comstock L. J., Vasser M. The tac promoter: a functional hybrid derived from the trp and lac promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]