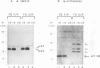
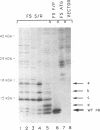
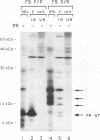
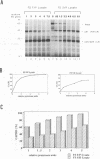
Abstract
The mature human immunodeficiency virus type 1 proteinase (PR; 11 kDa) can cleave all interdomain junctions in the Gag and Gag-Pol polyprotein precursors. To determine the activity of the enzyme in its precursor form, we blocked release of mature PR from a truncated Gag-Pol polyprotein by introducing mutations into the N-terminal Phe-Pro cleavage site of the PR domain. The mutant precursor autoprocessed efficiently upon expression in Escherichia coli. No detectable mature PR was released; however, several PR-related products ranging in size from approximately 14 to 18 kDa accumulated. Products of the same size were generated when mutant precursors were digested with wild-type PR. Thus, PR can utilize cleavage sites in the region upstream of the PR domain, resulting in the formation of extended PR species. On the basis of active-site titration, the PR species generated from mutated precursor exhibited wild-type activity on peptide substrates. However, the proteolytic activity of these extended enzymes on polyprotein substrates provided exogenously was low when equimolar amounts of extended and wild-type PR proteins were compared. Mammalian cells expressing the mutated precursor produced predominantly precursor and considerably reduced amounts of mature products. Released particles consisted mostly of uncleaved or partially cleaved polyproteins. Our results suggest that precursor forms of PR can autoprocess but are less efficient in processing of the Gag precursor for formation of mature virus particles.
Full text
PDF



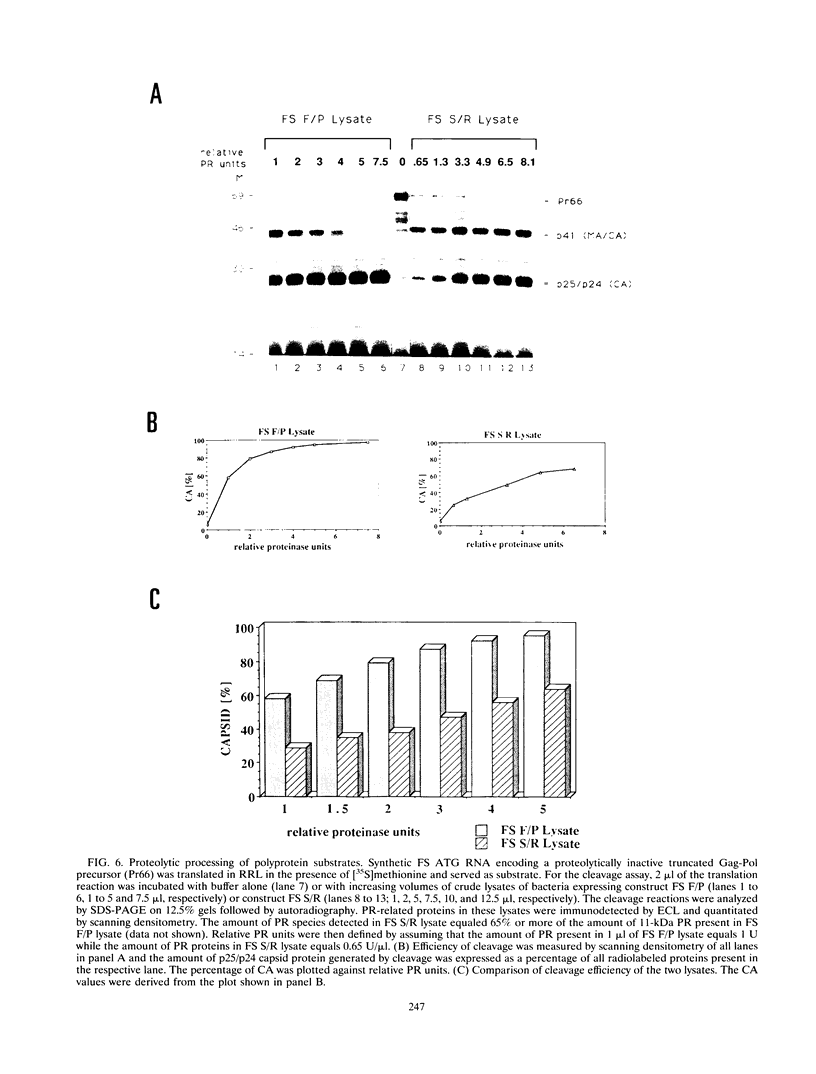



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burstein H., Bizub D., Kotler M., Schatz G., Vogt V. M., Skalka A. M. Processing of avian retroviral gag polyprotein precursors is blocked by a mutation at the NC-PR cleavage site. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1781–1785. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1781-1785.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darke P. L., Leu C. T., Davis L. J., Heimbach J. C., Diehl R. E., Hill W. S., Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S. Human immunodeficiency virus protease. Bacterial expression and characterization of the purified aspartic protease. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2307–2312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debouck C. The HIV-1 protease as a therapeutic target for AIDS. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Feb;8(2):153–164. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. M., Valler M. J., Rolph C. E., Foundling S. I., Jimenez M., Kay J. The pH dependence of the hydrolysis of chromogenic substrates of the type, Lys-Pro-Xaa-Yaa-Phe-(NO2)Phe-Arg-Leu, by selected aspartic proteinases: evidence for specific interactions in subsites S3 and S2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 17;913(2):122–130. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich L. S., Krausslich H. G., Wimmer E., Carter C. A. Expression in Escherichia coli and purification of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 capsid protein (p24). AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Oct;6(10):1169–1175. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald P. M., Springer J. P. Structure and function of retroviral proteases. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:299–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C., Lim J. J., Heimer E. P., Kramer R. A. An 11-kDa form of human immunodeficiency virus protease expressed in Escherichia coli is sufficient for enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2449–2453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. M., Berg J. M. A retroviral Cys-Xaa2-Cys-Xaa4-His-Xaa4-Cys peptide binds metal ions: spectroscopic studies and a proposed three-dimensional structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4047–4051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlinger H. G., Dorfman T., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Effect of mutations affecting the p6 gag protein on human immunodeficiency virus particle release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3195–3199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlinger H. G., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Role of capsid precursor processing and myristoylation in morphogenesis and infectivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5781–5785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Bowers M. A., Sowder R. C., 2nd, Serabyn S. A., Johnson D. G., Bess J. W., Jr, Arthur L. O., Bryant D. K., Fenselau C. Gag proteins of the highly replicative MN strain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: posttranslational modifications, proteolytic processings, and complete amino acid sequences. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1856–1865. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1856-1865.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Power M. D., Masiarz F. R., Luciw P. A., Barr P. J., Varmus H. E. Characterization of ribosomal frameshifting in HIV-1 gag-pol expression. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):280–283. doi: 10.1038/331280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. H., Swanstrom R. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag proteins are processed in two cellular compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4528–4532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh I., Yasunaga T., Ikawa Y., Yoshinaka Y. Inhibition of retroviral protease activity by an aspartyl proteinase inhibitor. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):654–656. doi: 10.1038/329654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Emini E. A., Schleif W. A., Davis L. J., Heimbach J. C., Dixon R. A., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S. Active human immunodeficiency virus protease is required for viral infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4686–4690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler M., Arad G., Hughes S. H. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gag-protease fusion proteins are enzymatically active. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6781–6783. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6781-6783.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Ingraham R. H., Skoog M. T., Wimmer E., Pallai P. V., Carter C. A. Activity of purified biosynthetic proteinase of human immunodeficiency virus on natural substrates and synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):807–811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Schneider H., Zybarth G., Carter C. A., Wimmer E. Processing of in vitro-synthesized gag precursor proteins of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 by HIV proteinase generated in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4393–4397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4393-4397.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis J. M., McDonald R. A., Nashed N. T., Wondrak E. M., Jerina D. M., Oroszlan S., Mora P. T. Autoprocessing of the HIV-1 protease using purified wild-type and mutated fusion proteins expressed at high levels in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):361–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuade T. J., Tomasselli A. G., Liu L., Karacostas V., Moss B., Sawyer T. K., Heinrikson R. L., Tarpley W. G. A synthetic HIV-1 protease inhibitor with antiviral activity arrests HIV-like particle maturation. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):454–456. doi: 10.1126/science.2405486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek T. D., Dayton B. D., Metcalf B. W., Dreyer G. B., Strickler J. E., Gorniak J. G., Rosenberg M., Moore M. L., Magaard V. W., Debouck C. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 protease expressed in Escherichia coli behaves as a dimeric aspartic protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1841–1845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek T. D., Lambert D. M., Dreyer G. B., Carr T. J., Tomaszek T. A., Jr, Moore M. L., Strickler J. E., Debouck C., Hyland L. J., Matthews T. J. Inhibition of HIV-1 protease in infected T-lymphocytes by synthetic peptide analogues. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):90–92. doi: 10.1038/343090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergener K., Fäcke M., Welker R., Brinkmann V., Gelderblom H. R., Kräusslich H. G. Analysis of HIV particle formation using transient expression of subviral constructs in mammalian cells. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):25–39. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90058-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partin K., Kräusslich H. G., Ehrlich L., Wimmer E., Carter C. Mutational analysis of a native substrate of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 proteinase. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3938–3947. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3938-3947.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partin K., Zybarth G., Ehrlich L., DeCrombrugghe M., Wimmer E., Carter C. Deletion of sequences upstream of the proteinase improves the proteolytic processing of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4776–4780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl L. H., Taylor W. R. A structural model for the retroviral proteases. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):351–354. doi: 10.1038/329351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit S. C., Simsic J., Loeb D. D., Everitt L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Swanstrom R. Analysis of retroviral protease cleavage sites reveals two types of cleavage sites and the structural requirements of the P1 amino acid. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14539–14547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phylip L. H., Mills J. S., Parten B. F., Dunn B. M., Kay J. Intrinsic activity of precursor forms of HIV-1 proteinase. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81524-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A. D., Phylip L. H., Farmerie W. G., Scarborough P. E., Alvarez A., Dunn B. M., Hirel P. H., Konvalinka J., Strop P., Pavlickova L. Sensitive, soluble chromogenic substrates for HIV-1 proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7733–7736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer W. E., Jr, Love W. E., Fenderson F. F. Cooperative dimeric and tetrameric clam haemoglobins are novel assemblages of myoglobin folds. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):277–280. doi: 10.1038/316277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm H. J., Nakashima H., Schramm W., Wakayama H., Yamamoto N. HIV-1 reproduction is inhibited by peptides derived frm the N- and C-termini of HIV-1 protease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 16;179(2):847–851. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91895-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Cho M. I., Hammarskjöld M. L., Rekosh D. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Pr55gag and Pr160gag-pol expressed from a simian virus 40 late replacement vector are efficiently processed and assembled into viruslike particles. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2743–2750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2743-2750.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickler J. E., Gorniak J., Dayton B., Meek T., Moore M., Magaard V., Malinowski J., Debouck C. Characterization and autoprocessing of precursor and mature forms of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV 1) protease purified from Escherichia coli. Proteins. 1989;6(2):139–154. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tözsér J., Bláha I., Copeland T. D., Wondrak E. M., Oroszlan S. Comparison of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 proteinases using oligopeptide substrates representing cleavage sites in Gag and Gag-Pol polyproteins. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer A., Miller M., Jaskólski M., Sathyanarayana B. K., Baldwin E., Weber I. T., Selk L. M., Clawson L., Schneider J., Kent S. B. Conserved folding in retroviral proteases: crystal structure of a synthetic HIV-1 protease. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):616–621. doi: 10.1126/science.2548279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. Y., Poorman R. A., Maggiora L. L., Heinrikson R. L., Kézdy F. J. Dissociative inhibition of dimeric enzymes. Kinetic characterization of the inhibition of HIV-1 protease by its COOH-terminal tetrapeptide. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15591–15594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]