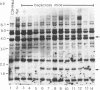
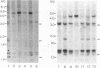
Abstract
Genetically determined resistance to flaviviruses in mice is a dominant trait conferred by alleles at a single autosomal locus designated Flv, but no gene products have been associated with this locus and the mechanism of resistance is not well understood. To further characterize this model of genetic resistance, we conducted mapping studies to determine the chromosomal location of Flv. Because of evidence suggesting that the Flv locus is on chromosome 5, three-point backcross linkage analyses were used to define the location of Flv relative to previously assigned chromosome 5 markers. The results confirm the chromosome 5 location of Flv and indicate a map position between the anchor loci rd and Gus-s. The chromosomal localization of Flv is the first step in the production of a detailed linkage map of the Flv region, which may open approaches to positional cloning of the resistance gene.
Full text
PDF

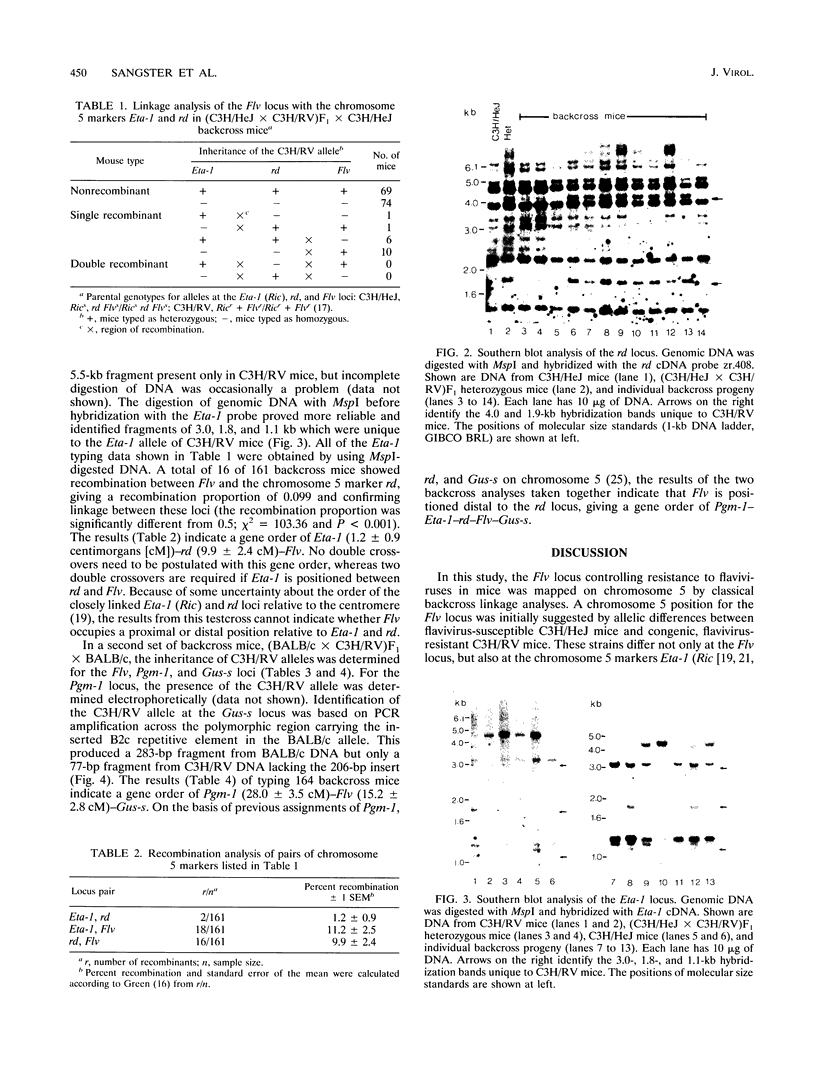

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Purification and properties of a host cell protein required for poliovirus replication in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12351–12358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes C., Danciger M., Kozak C. A., Farber D. B. Isolation of a candidate cDNA for the gene causing retinal degeneration in the rd mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9722–9726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes C., Li T., Danciger M., Baxter L. C., Applebury M. L., Farber D. B. Retinal degeneration in the rd mouse is caused by a defect in the beta subunit of rod cGMP-phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):677–680. doi: 10.1038/347677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton M. A., Arnheiter H., Haller O. Interferon independence of genetically controlled resistance to flaviviruses. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):284–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.284-288.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore M. A., Gallagher P. M., Korfhagen T. R., Ganschow R. E. Complete sequence and organization of the murine beta-glucuronidase gene. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7131–7140. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danciger M., Bowes C., Kozak C. A., LaVail M. M., Farber D. B. Fine mapping of a putative rd cDNA and its co-segregation with rd expression. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1990 Aug;31(8):1427–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell M. B., Koprowski H. Genetically determined resistance to infection with group B arboviruses. II. Increased production of interfering particles in cell cultures from resistant mice. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):248–256. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell M. B., Koprowski H., Lagerspetz K. Genetically determined resistance to infection with group B arboviruses. I. Distribution of the resistance gene among various mouse populations and characteristics of gene expression in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):240–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrieva T. M., Shcheglova M. V., Agol V. I. Inhibition of activity of encephalomyocarditis virus-induced RNA polymerase by antibodies against cellular components. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN G. T., KOPROWSKI H. Study of the mechanism of innate resistance to virus infection. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1962 Jun;59:333–373. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030590313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher P. M., D'Amore M. A., Lund S. D., Elliott R. W., Pazik J., Hohman C., Korfhagen T. R., Ganschow R. E. DNA sequence variation within the beta-glucuronidase gene complex among inbred strains of mice. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. G., Rosenstreich D. L., Taylor B. A., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: mapping the gene that controls natural resistance in mice. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1395–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gröschel D., Koprowski H. Development of a virus-resistant inbred mouse strain for the study of innate resistance to Arbo B viruses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;17(3):379–391. doi: 10.1007/BF01241192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby R. O., Bhatt P. N. Genetic resistance to lethal flavivirus encephalitis. I. Infection of congenic mice with Banzi virus. J Infect Dis. 1976 Aug;134(2):158–165. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.2.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: inflammatory response of congenic C3H mice differing at the Ric gene. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1014–1022. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1014-1022.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaVail M. M., Sidman R. L. C57BL-6J mice with inherited retinal degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 1974 May;91(5):394–400. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1974.03900060406015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liehne C. G., Leivers S., Stanley N. F., Alpers M. P., Paul S., Liehne P. F., Chan K. H. Ord River arboviruses--isolations from mosquitoes. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1976 Oct;54(5):499–504. doi: 10.1038/icb.1976.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Hughes T. P. The Inheritance of Susceptibility to Yellow Fever Encephalitis in Mice. Genetics. 1936 Mar;21(2):104–112. doi: 10.1093/genetics/21.2.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patarca R., Freeman G. J., Singh R. P., Wei F. Y., Durfee T., Blattner F., Regnier D. C., Kozak C. A., Mock B. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Structural and functional studies of the early T lymphocyte activation 1 (Eta-1) gene. Definition of a novel T cell-dependent response associated with genetic resistance to bacterial infection. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):145–161. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B. Genetic, hormonal and age factors in natural resistance to certain viruses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1952 Jul 10;54(6):936–944. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1952.tb39968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangster M. Y., Heliams D. B., MacKenzie J. S., Shellam G. R. Genetic studies of flavivirus resistance in inbred strains derived from wild mice: evidence for a new resistance allele at the flavivirus resistance locus (Flv). J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):340–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.340-347.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangster M. Y., Shellam G. R. Genetically controlled resistance to flaviviruses within the house mouse complex of species. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;127:313–318. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71304-0_37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal S. M., Malo D., Vogan K., Skamene E., Gros P. Natural resistance to infection with intracellular parasites: isolation of a candidate for Bcg. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):469–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90135-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicking C., Williamson B. From linked marker to gene. Trends Genet. 1991 Sep;7(9):288–293. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90310-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]