Abstract
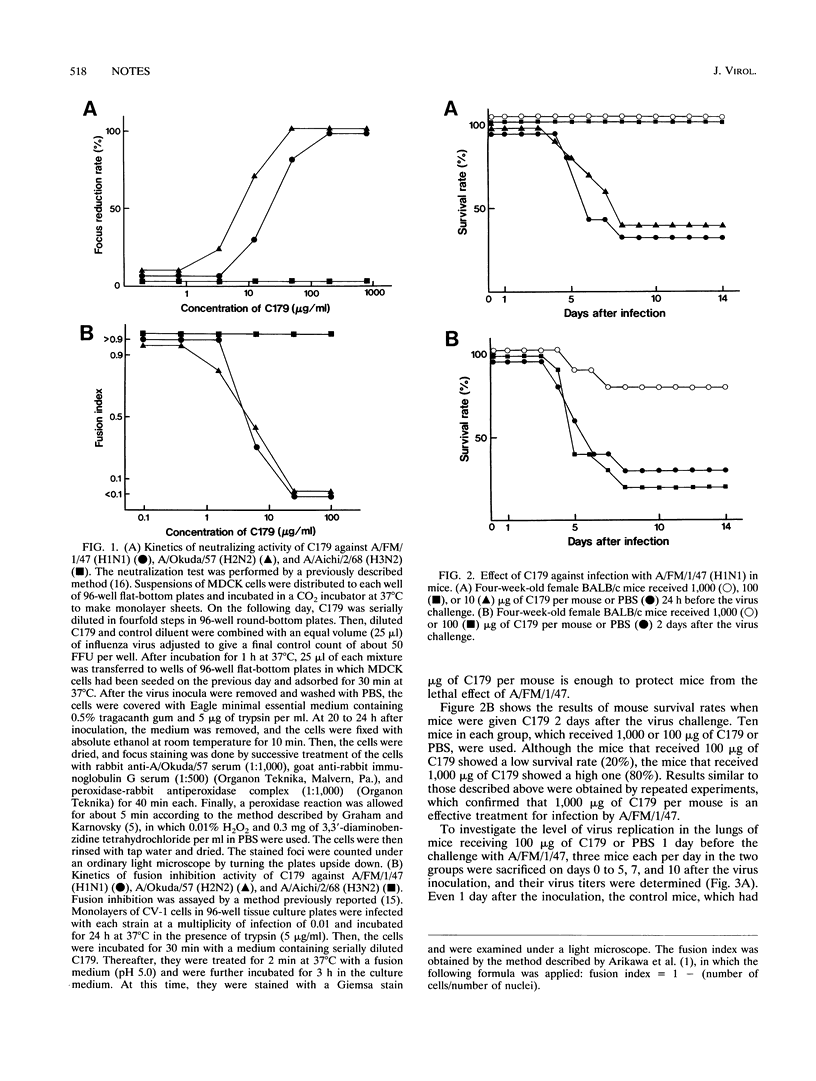
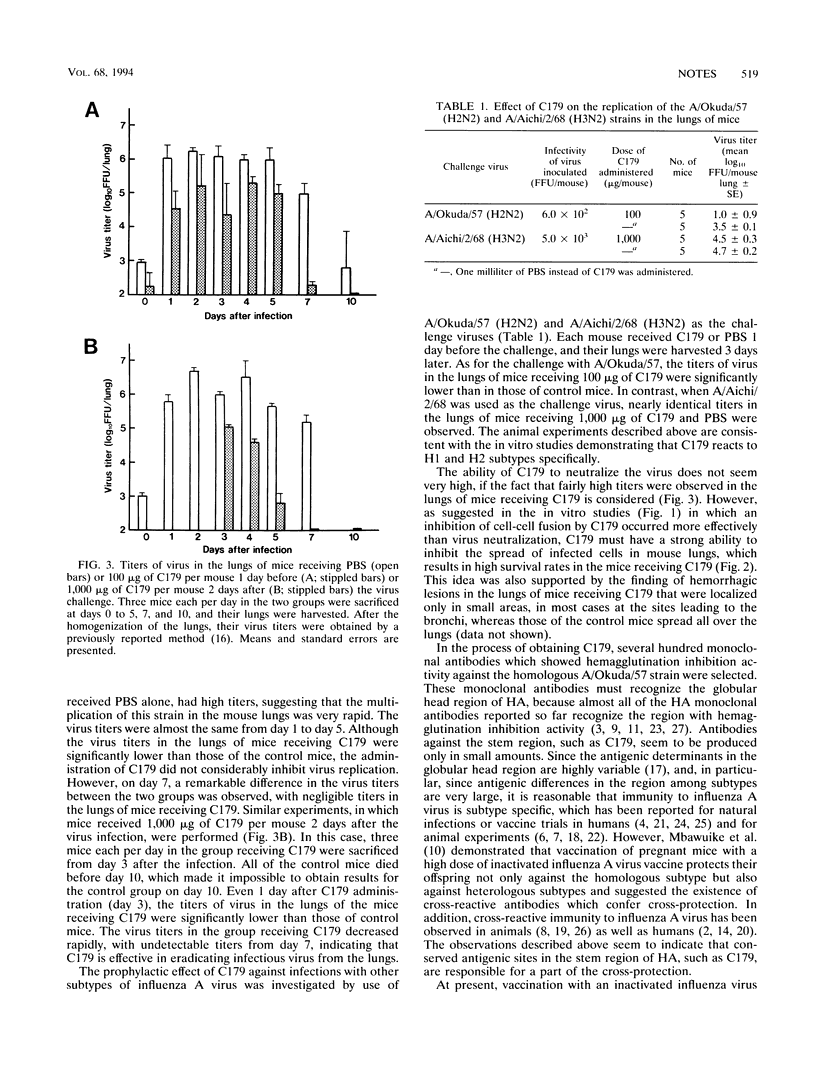
The monoclonal antibody designated C179 was found to neutralize all of the H1 and H2 strains of influenza A virus studied (Y. Okuno, Y. Isegawa, F. Sasao, and S. Ueda, J. Virol. 67:2552-2558, 1993). In the present study, the ability of C179 to protect mice from the lethal effect of the A/FM/1/47 (H1N1) strain was examined. When the mice were injected intraperitoneally with 100 micrograms of C179 per mouse a day before the virus challenge (2.0 x 10(3) focus-forming units per mouse), all of the mice survived. Moreover, significantly higher survival rates were observed in mice receiving 1,000 micrograms of C179 per mouse 2 days after the virus challenge than in those receiving phosphate-buffered saline alone. These results indicate that C179 is effective not only for prevention but also for treatment of mice infected with H1 and H2 strains. The possibility that C179 can be used for passive immunization in humans is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arikawa J., Takashima I., Hashimoto N. Cell fusion by haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) viruses and its application for titration of virus infectivity and neutralizing antibody. Arch Virol. 1985;86(3-4):303–313. doi: 10.1007/BF01309834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlington D. B., Wright P. F., van Wyke K. L., Phelan M. A., Mayner R. E., Murphy B. R. Development of subtype-specific and heterosubtypic antibodies to the influenza A virus hemagglutinin after primary infection in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):847–849. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.847-849.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels P. S., Jeffries S., Yates P., Schild G. C., Rogers G. N., Paulson J. C., Wharton S. A., Douglas A. R., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. The receptor-binding and membrane-fusion properties of influenza virus variants selected using anti-haemagglutinin monoclonal antibodies. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1459–1465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank A. L., Taber L. H., Wells J. M. Individuals infected with two subtypes of influenza A virus in the same season. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):120–124. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husseini R. H., Sweet C., Overton H., Smith H. Role of maternal immunity in the protection of newborn ferrets against infection with a virulent influenza virus. Immunology. 1984 Jul;52(3):389–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakeman K. J., Smith H., Sweet C. Mechanism of immunity to influenza: maternal and passive neonatal protection following immunization of adult ferrets with a live vaccinia-influenza virus haemagglutinin recombinant but not with recombinants containing other influenza virus proteins. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jun;70(Pt 6):1523–1531. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-6-1523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurimura T., Hirano A., Okuno Y. The nature of the immunity evoked by infection of mice with avirulent influenza virus. Biken J. 1972 Mar;15(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G., Gerhard W., Ward C. W., Dopheide T. A. Antigenic drift in type A influenza virus: sequence differences in the hemagglutinin of Hong Kong (H3N2) variants selected with monoclonal hybridoma antibodies. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):226–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90540-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mbawuike I. N., Six H. R., Cate T. R., Couch R. B. Vaccination with inactivated influenza A virus during pregnancy protects neonatal mice against lethal challenge by influenza A viruses representing three subtypes. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1370–1374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1370-1374.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Nakajima K., Kendal A. P. Identification of the binding sites to monoclonal antibodies on A/USSR/90/77 (H1N1) hemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic drift in H1N1 influenza viruses. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):116–127. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90538-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of various strains of influenza virus for mice. Biken J. 1965 Sep;8(3):155–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble G. R., Kaye H. S., Kendal A. P., Dowdle W. R. Age-related heterologous antibody responses to influenza virus vaccination. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136 (Suppl):S686–S692. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_3.s686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno Y., Isegawa Y., Sasao F., Ueda S. A common neutralizing epitope conserved between the hemagglutinins of influenza A virus H1 and H2 strains. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2552–2558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2552-2558.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno Y., Tanaka K., Baba K., Maeda A., Kunita N., Ueda S. Rapid focus reduction neutralization test of influenza A and B viruses in microtiter system. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1308–1313. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1308-1313.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R. R., Teillaud J. L., Scharff M. D. Monoclonal antibodies: a powerful tool for selecting and analyzing mutations in antigens and antibodies. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:389–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuman P. D., Paganini C. M., Ayoub E. M., Small P. A., Jr Maternal-infant transfer of influenza-specific immunity in the mouse. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):932–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULMAN J. L., KILBOURNE E. D. INDUCTION OF PARTIAL SPECIFIC HETEROTYPIC IMMUNITY IN MICE BY A SINGLE INFECTION WITH INFLUENZA A VIRUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:170–174. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.170-174.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoguchi T., Naito H., Hara M., Takeuchi Y., Fukumi H. Cross-subtype protection in humans during sequential, overlapping, and/or concurrent epidemics caused by H3N2 and H1N1 influenza viruses. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):81–88. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff M. C., Fries L. F., Karron R. A., Clements M. L., Murphy B. R. Effect of heterosubtypic immunity on infection with attenuated influenza A virus vaccines in young children. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Apr;31(4):836–838. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.4.836-838.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet C., Bird R. A., Jakeman K., Coates D. M., Smith H. Production of passive immunity in neonatal ferrets following maternal vaccination with killed influenza A virus vaccines. Immunology. 1987 Jan;60(1):83–89. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):373–378. doi: 10.1038/289373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. F., Thompson J., Karzon D. T. Differing virulence of H1N1 and H3N2 influenza strains. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Dec;112(6):814–819. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane N., Arikawa J., Odagiri T., Sukeno N., Ishida N. Isolation of three different influenza A viruses from an individual after probable double infection with H3N2 and H1N1 viruses. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1978 Oct-Dec;31(5-6):431–434. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.31.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yetter R. A., Barber W. H., Small P. A., Jr Heterotypic immunity to influenza in ferrets. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):650–653. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.650-653.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Caton A. J., Gerhard W. Selection of influenza A virus adsorptive mutants by growth in the presence of a mixture of monoclonal antihemagglutinin antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):623–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.623-628.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


