Abstract
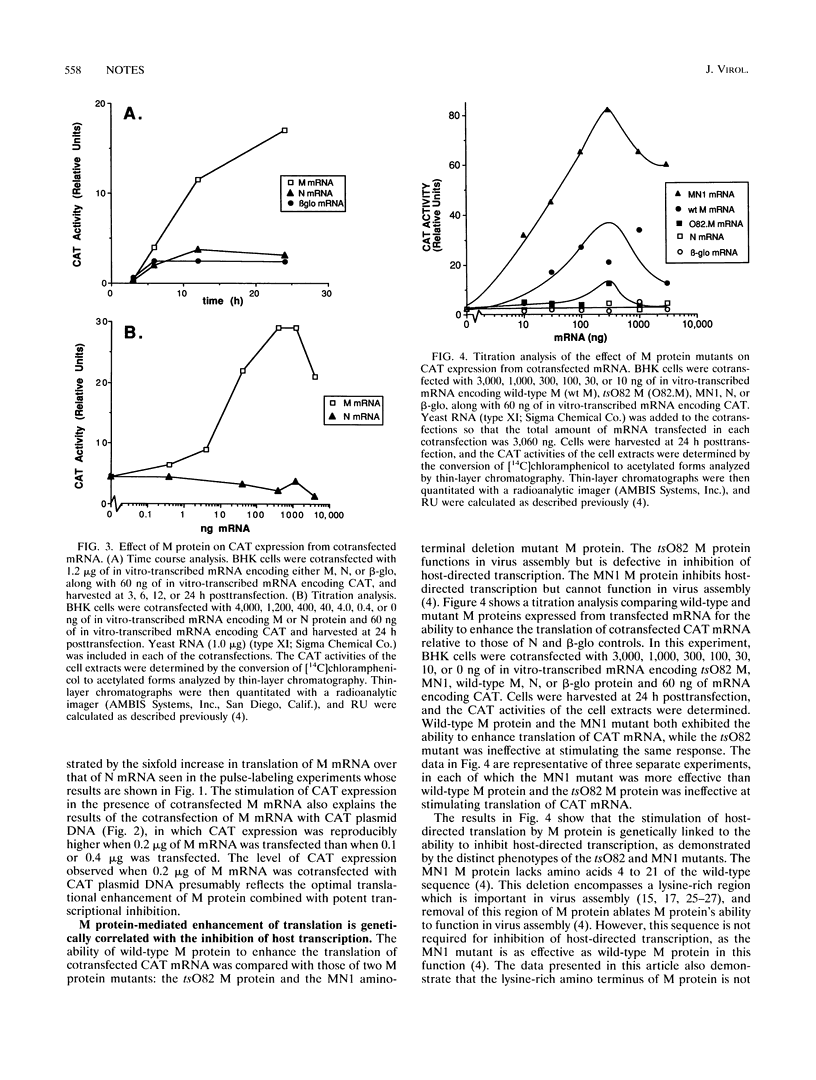
Vesicular stomatitis virus infection causes a rapid and potent inhibition of both host transcription and translation. Recently, the viral matrix (M) protein was shown to inhibit host-directed transcription in vivo in the absence of any other viral component (B. L. Black and D. S. Lyles, J. Virol. 66:4058-4064, 1992). The goal of this study was to determine the effect of M protein on host-directed translation. In vitro-transcribed mRNAs encoding M protein and chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) were cotransfected into BHK cells to determine the effect of M protein expression on translation of CAT mRNA. The results presented here show that M protein did not inhibit host-directed translation of CAT mRNA. On the contrary, this study gave the unexpected result that M protein actually stimulated host-directed translation under the same conditions in which it potently inhibited host-directed transcription. Under these conditions, the combined effect on host gene expression was a greater-than-20-fold inhibition. Furthermore, the enhancement of host translation mediated by M protein was genetically correlated with M protein's ability to inhibit host transcription. Thus, the results of this study establish that M protein does not inhibit host protein synthesis under the same conditions in which it potently inhibits host transcription and suggest that the inhibition of transcription and that of translation by vesicular stomatitis virus require separate viral gene products.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akusjärvi G., Svensson C., Nygård O. A mechanism by which adenovirus virus-associated RNAI controls translation in a transient expression assay. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):549–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt B., Bablanian R. Mechansims of vesicular stomatitis virus-induced cytopathic effects. II. Inhibition of macromolecular synthesis induced by infectious and defective-interfering particles. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black B. L., Lyles D. S. Vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein inhibits host cell-directed transcription of target genes in vivo. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4058–4064. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4058-4064.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black B. L., Rhodes R. B., McKenzie M., Lyles D. S. The role of vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein in inhibition of host-directed gene expression is genetically separable from its function in virus assembly. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4814–4821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4814-4821.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel D., Harmison G. G., Schubert M. Role of matrix protein in cytopathogenesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1716–1725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1716-1725.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callis J., Fromm M., Walbot V. Expression of mRNA electroporated into plant and animal cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5823–5831. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centrella M., Lucas-Lenard J. Regulation of protein synthesis in vesicular stomatitis virus-infected mouse L-929 cells by decreased protein synthesis initiation factor 2 activity. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):781–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.781-791.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulon P., Deutsch V., Lafay F., Martinet-Edelist C., Wyers F., Herman R. C., Flamand A. Genetic evidence for multiple functions of the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):991–996. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. V., Elroy-Stein O., Jagus R., Moss B., Kaufman R. J. The vaccinia virus K3L gene product potentiates translation by inhibiting double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase and phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1943–1950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1943-1950.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dratewka-Kos E., Kiss I., Lucas-Lenard J., Mehta H. B., Woodley C. L., Wahba A. J. Catalytic utilization of eIF-2 and mRNA binding proteins are limiting in lysates from vesicular stomatitis virus infected L cells. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):6184–6190. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunigan D. D., Baird S., Lucas-Lenard J. Lack of correlation between the accumulation of plus-strand leader RNA and the inhibition of protein and RNA synthesis in vesicular stomatitis virus infected mouse L cells. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):231–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giantini M., Shatkin A. J. Stimulation of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase mRNA translation by reovirus capsid polypeptide sigma 3 in cotransfected COS cells. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2415–2421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2415-2421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M. C., Godchaux W., 3rd, Lucas-Lenard J. Further studies on the inhibition of cellular protein synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):148–162. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90410-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaptur P. E., Rhodes R. B., Lyles D. S. Sequences of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein involved in binding to nucleocapsids. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1057–1065. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1057-1065.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancios L., Lyles D. S. The interactionof antiody with the major surface glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Analysis of neutralizing epitopes with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1982 Aug;121(1):157–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Vanderoef R. Localization of the membrane-associated region of vesicular stomatitis virus M protein at the N terminus, using the hydrophobic, photoreactive probe 125I-TID. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3486–3491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3486-3491.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Luo L. Z., Snyder R. M., Wagner R. R. Expression of the M gene of vesicular stomatitis virus cloned in various vaccinia virus vectors. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):776–782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.776-782.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles D. S., Puddington L., McCreedy B. J., Jr Vesicular stomatitis virus M protein in the nuclei of infected cells. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4387–4392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4387-4392.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone R. W., Felgner P. L., Verma I. M. Cationic liposome-mediated RNA transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6077–6081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvaldi J., Sekellick M. J., Marcus P. I., Lucas-Lenard J. Inhibition of mouse L cell protein synthesis by ultraviolet-irradiated vesicular stomatitis virus requires viral transcription. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. J., Wagner R. R. Inhibition of cellular DNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):356–367. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.356-367.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden J. R., Pal R., Wagner R. R. Mapping regions of the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus which bind to ribonucleocapsids, liposomes, and monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):860–868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.860-868.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Grinnell B. W., Snyder R. M., Wagner R. R. Regulation of viral transcription by the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus probed by monoclonal antibodies and temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):386–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.386-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley J. B., Pal R., Wagner R. R. Antigenicity, function, and conformation of synthetic oligopeptides corresponding to amino-terminal sequences of wild-type and mutant matrix proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2569–2577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2569-2577.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R., Wagner R. R. Inhibition of translation in lysates of mouse L cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus: presence of a defective ribosome-associated factor. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1540–1546. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Wagner R. R. Transcription of vesicular stomatitis virus is required to shut off cellular RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):410–413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.410-413.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Youngner J. S. Inhibition of protein synthesis in L cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):85–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.85-89.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Youngner J. S. Interferon production and inhibition of host synthesis in cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):476–484. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.476-484.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S. Alteration of vesicular stomatitis virus L and NS proteins by uv irradiation: implications for the mechanism of host cell shut-off. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90633-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]