Abstract
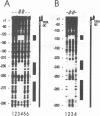
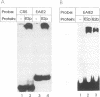
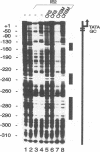
The 86-kDa IE2 protein (IE86) of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) can act as both an activator and a repressor of gene expression. The mechanisms for both of these functions are not well defined. It has recently been demonstrated that this protein has sequence-specific DNA binding properties: it interacts directly with a target sequence that is located between the TATA box and the cap site of its own promoter. This sequence, termed the CRS (cis repression signal) element, is required for negative autoregulation of the IE1/IE2 enhancer/promoter by IE2. We demonstrate now that binding of this protein to DNA is not confined to this site but occurs also within an early promoter of HCMV that has previously been shown to be strongly IE2 responsive. By DNase I protection analysis using a purified, procaryotically expressed IE2 protein, we could identify three binding sites within the region of -290 to -120 of the UL112 promoter of HCMV. Competition in DNase I protection experiments as well as gel retardation experiments showed that the identified binding sites are specific and have high affinity. Deletion of IE2 binding sites from this promoter reduced the level of transactivation; however, the remaining promoter could still be stimulated about 40-fold. Constructs in which IE2 binding sites were fused directly to the TATA box of the UL112 promoter did not reveal a significant contribution of these sequences to transactivation. However, if an IE2 binding site was reinserted upstream of nucleotide -117 of the UL112 promoter, an increase in transactivation by IE2 was obvious, whereas a mutated sequence could not mediate this effect. This finding suggests that DNA-bound IE2 can contribute to transactivation but seems to require the presence of additional transcription factors. Moreover, a comparison of the detected IE2 binding sites could not detect a strong homology, suggesting that this protein may be able to interact with a broad spectrum of different target sequences.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biegalke B. J., Geballe A. P. Sequence requirements for activation of the HIV-1 LTR by human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90151-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Khoury E. L., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie2 negatively regulates alpha gene expression via a short target sequence near the transcription start site. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):887–896. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.887-896.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou C. J., Zong J., Waheed I., Hayward G. S. Identification and mapping of dimerization and DNA-binding domains in the C terminus of the IE2 regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6201–6214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6201-6214.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Santomenna L. D., Harlow P. P., Benfield P. A., Tenney D. J. Human cytomegalovirus US3 and UL36-38 immediate-early proteins regulate gene expression. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):95–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.95-105.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDonato J. A., Muller M. T. DNA binding and gene regulation by the herpes simplex virus type 1 protein ICP4 and involvement of the TATA element. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3737–3747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3737-3747.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDonato J. A., Spitzner J. R., Muller M. T. A predictive model for DNA recognition by the herpes simplex virus protein ICP4. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jun 5;219(3):451–470. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90186-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furnari B. A., Poma E., Kowalik T. F., Huong S. M., Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene 2 protein interacts with itself and with several novel cellular proteins. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4981–4991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4981-4991.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Young J., Giulietti E., DeMattei C., Garcia J., Gaynor R., Stenberg R. M., Nelson J. A. A discrete cis element in the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat mediates synergistic trans activation by cytomegalovirus immediate-early proteins. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6735–6742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6735-6742.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grefte J. M., van der Gun B. T., Schmolke S., van der Giessen M., van Son W. J., Plachter B., Jahn G., The T. H. The lower matrix protein pp65 is the principal viral antigen present in peripheral blood leukocytes during an active cytomegalovirus infection. J Gen Virol. 1992 Nov;73(Pt 11):2923–2932. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-11-2923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeier C., Walker S., Caswell R., Kouzarides T., Sinclair J. The human cytomegalovirus 80-kilodalton but not the 72-kilodalton immediate-early protein transactivates heterologous promoters in a TATA box-dependent mechanism and interacts directly with TFIID. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4452–4456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4452-4456.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Malone C. L., Stinski M. F. Human cytomegalovirus immediate-early two protein region involved in negative regulation of the major immediate-early promoter. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3532–3536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3532-3536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Malone C. L., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Identification and characterization of the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 gene that stimulates gene expression from an inducible promoter. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3214–3221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3214-3221.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbalzano A. N., Coen D. M., DeLuca N. A. Herpes simplex virus transactivator ICP4 operationally substitutes for the cellular transcription factor Sp1 for efficient expression of the viral thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):565–574. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.565-574.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jupp R., Hoffmann S., Depto A., Stenberg R. M., Ghazal P., Nelson J. A. Direct interaction of the human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein with the cis repression signal does not preclude TBP from binding to the TATA box. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5595–5604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5595-5604.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jupp R., Hoffmann S., Stenberg R. M., Nelson J. A., Ghazal P. Human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein interacts with promoter-bound TATA-binding protein via a specific region distinct from the autorepression domain. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7539–7546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7539-7546.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klucher K. M., Sommer M., Kadonaga J. T., Spector D. H. In vivo and in vitro analysis of transcriptional activation mediated by the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1238–1250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D., Stamminger T. The 86-kilodalton IE-2 protein of human cytomegalovirus is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that interacts directly with the negative autoregulatory response element located near the cap site of the IE-1/2 enhancer-promoter. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):323–331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.323-331.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Hermiston T. W., Stinski M. F. A cis-acting element in the major immediate-early (IE) promoter of human cytomegalovirus is required for negative regulation by IE2. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):897–903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.897-903.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Stinski M. F. Human cytomegalovirus contains a tegument protein that enhances transcription from promoters with upstream ATF and AP-1 cis-acting elements. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4434–4444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4434-4444.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macias M. P., Stinski M. F. An in vitro system for human cytomegalovirus immediate early 2 protein (IE2)-mediated site-dependent repression of transcription and direct binding of IE2 to the major immediate early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):707–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone C. L., Vesole D. H., Stinski M. F. Transactivation of a human cytomegalovirus early promoter by gene products from the immediate-early gene IE2 and augmentation by IE1: mutational analysis of the viral proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1498-1506.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael N., Spector D., Mavromara-Nazos P., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. The DNA-binding properties of the major regulatory protein alpha 4 of herpes simplex viruses. Science. 1988 Mar 25;239(4847):1531–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.2832940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., Hayward G. S. The IE2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus specifically down-regulate expression from the major immediate-early promoter through a target sequence located near the cap site. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6154–6165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6154-6165.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., Mullen M. A., Chang Y. N., Hayward G. S. The functionally active IE2 immediate-early regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus is an 80-kilodalton polypeptide that contains two distinct activator domains and a duplicated nuclear localization signal. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3839–3852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3839-3852.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., O'Hare P., Sha L., LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. trans-activation and autoregulation of gene expression by the immediate-early region 2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1167–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1167-1179.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plachter B., Britt W., Vornhagen R., Stamminger T., Jahn G. Analysis of proteins encoded by IE regions 1 and 2 of human cytomegalovirus using monoclonal antibodies generated against recombinant antigens. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):642–652. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plachter B., Traupe B., Albrecht J., Jahn G. Abundant 5 kb RNA of human cytomegalovirus without a major translational reading frame. J Gen Virol. 1988 Sep;69(Pt 9):2251–2266. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-9-2251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchtler E., Stamminger T. An inducible promoter mediates abundant expression from the immediate-early 2 gene region of human cytomegalovirus at late times after infection. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6301–6306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6301-6306.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. S., Boundy A., O'Hare P., Pizzorno M. C., Ciufo D. M., Hayward G. S. Direct correlation between a negative autoregulatory response element at the cap site of the herpes simplex virus type 1 IE175 (alpha 4) promoter and a specific binding site for the IE175 (ICP4) protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4307–4320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4307-4320.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Johnson D. C., Pizer L. I., Everett R. D. The ICP4 binding sites in the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D (gD) promoter are not essential for efficient gD transcription during virus infection. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):623–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.623-631.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Bates P., Rivera-Gonzalez R., Gu B., DeLuca N. A. ICP4, the major transcriptional regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus type 1, forms a tripartite complex with TATA-binding protein and TFIIB. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4676–4687. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4676-4687.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J., Tevethia M. J. Identification of a human cytomegalovirus virus DNA segment that complements an adenovirus 5 immediate early mutant. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamminger T., Puchtler E., Fleckenstein B. Discordant expression of the immediate-early 1 and 2 gene regions of human cytomegalovirus at early times after infection involves posttranscriptional processing events. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2273–2282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2273-2282.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Rabert D. K., Spector D. H. Identification of sequence requirements and trans-acting functions necessary for regulated expression of a human cytomegalovirus early gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3463–3473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3463-3473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Spector D. H. 2.2-kilobase class of early transcripts encoded by cell-related sequences in human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):591–602. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.591-602.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasiak P. C., Mocarski E. S. Transactivation of the cytomegalovirus ICP36 gene promoter requires the alpha gene product TRS1 in addition to IE1 and IE2. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1050–1058. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1050-1058.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Depto A. S., Fortney J., Nelson J. A. Regulated expression of early and late RNAs and proteins from the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene region. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2699–2708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2699-2708.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Fortney J., Barlow S. W., Magrane B. P., Nelson J. A., Ghazal P. Promoter-specific trans activation and repression by human cytomegalovirus immediate-early proteins involves common and unique protein domains. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1556–1565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1556-1565.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Multiple spliced and unspliced transcripts from human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 and evidence for a common initiation site within immediate-early region 1. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.665-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder D. G., Pizer L. I. Role for DNA-protein interaction in activation of the herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D gene. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4661–4672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4661-4672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Spector D. J., Leisure K. M., Stinski M. F. Participation of two human cytomegalovirus immediate early gene regions in transcriptional activation of adenovirus promoters. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade E. J., Klucher K. M., Spector D. H. An AP-1 binding site is the predominant cis-acting regulatory element in the 1.2-kilobase early RNA promoter of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2407–2417. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2407-2417.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade M., Kowalik T. F., Mudryj M., Huang E. S., Azizkhan J. C. E2F mediates dihydrofolate reductase promoter activation and multiprotein complex formation in human cytomegalovirus infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4364–4374. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]