Abstract
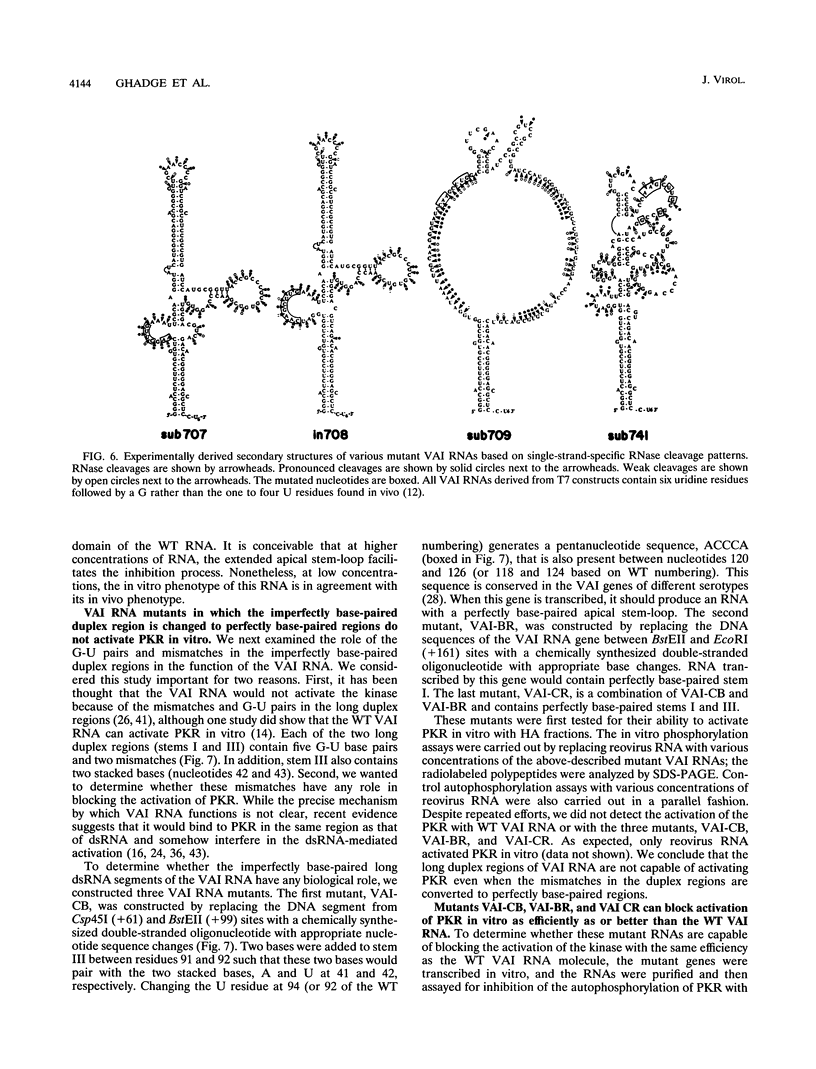
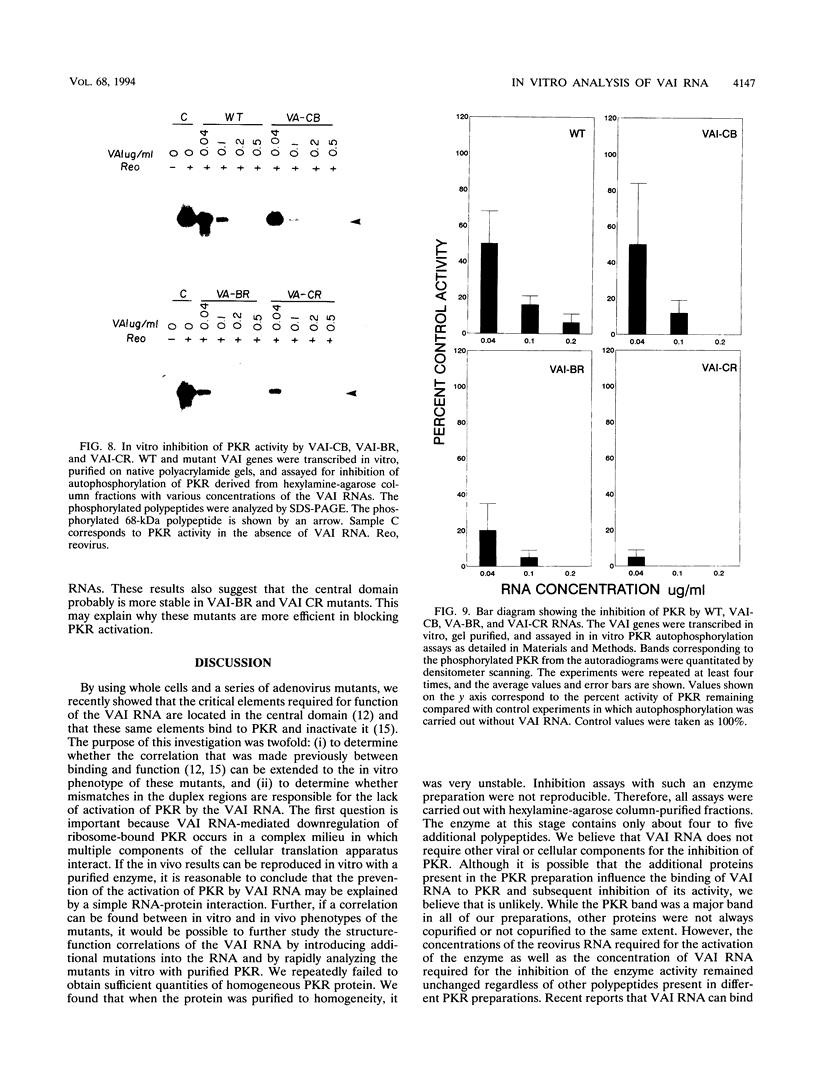
Adenoviruses use the virus-encoded virus-associated RNA (VAI RNA) as a defense against cellular antiviral response by blocking the activation of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase PKR. The structure of VAI RNA consists of two long, imperfectly base-paired duplex regions connected by a complex short stem-loop at the center, referred to as the central domain. By using a series of adenovirus mutants with linker-scan mutations in the VAI RNA gene, we recently showed that the critical elements required for function in the VAI RNA molecule are in the central domain and that these same elements of the central domain are also involved in binding to PKR. In virus-infected cells, VAI RNA interacts with latent kinase, which is bound to ribosomes; this interaction takes place in a complex milieu. To more fully understand the relationship between structure and function and to determine whether the in vivo phenotype of these mutants can be reproduced in vitro, we have now analyzed these mutant VAI alleles for their ability to block the activation of a partially purified PKR from HeLa cells. We have also derived the structure of these mutants experimentally and correlated the structure with function. Without exception, when the structure of the short stem-loop of the central domain was perturbed, the mutants failed to inhibit PKR. Structural disruptions elsewhere in the central domain or in the long duplex regions of the molecule were not deleterious for in vitro function. Thus, these results support our previous findings and underscore the importance of the elements present in the central domain of the VAI RNA for its function. Our results also suggest that the interaction between PKR and VAI RNA involves a precise secondary (and tertiary) structure in the central domain. It has been suggested that VAI RNA does not activate PKR in virus-infected cells because of mismatches in the imperfectly base-paired long duplex regions. We constructed mutant VAI genes in which the imperfectly base-paired duplex regions were converted to perfectly base-paired regions and assayed in vitro for the activation of PKR. As with the wild-type VAI RNA, these mutants failed to activate PKR in vitro, while they were able to block the activation of PKR better than did the wild type. These results suggest that the failure of VAI RNA to activate PKR is not the result of mismatches in the long duplex regions.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akusjärvi G., Svensson C., Nygård O. A mechanism by which adenovirus virus-associated RNAI controls translation in a transient expression assay. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):549–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Knutson G. S., Lasky S. R., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Purification and substrate specificities of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase from untreated and interferon-treated mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11240–11247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R. A., Domer P. H., Thimmappaya B. Structural requirements of adenovirus VAI RNA for its translation enhancement function. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):187–196. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R. A., Thimmappaya B. Adenovirus mutants with DNA sequence perturbations in the intragenic promoter of VAI RNA gene allow the enhanced transcription of VAII RNA gene in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7377–7388. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R. A., Thimmappaya B. Construction and analysis of additional adenovirus substitution mutants confirm the complementation of VAI RNA function by two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):750–756. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.750-756.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnan B. J., Biancalana S., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. Analysis of arginine-rich peptides from the HIV Tat protein reveals unusual features of RNA-protein recognition. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):201–210. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. A., Schwemmle M., Schickinger J., Hilse K., Clemens M. J. Binding of Epstein-Barr virus small RNA EBER-1 to the double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase DAI. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):243–248. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. A., Sharp N. A., Clemens M. J. Translational control by the Epstein-Barr virus small RNA EBER-1. Reversal of the double-stranded RNA-induced inhibition of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):635–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furtado M. R., Subramanian S., Bhat R. A., Fowlkes D. M., Safer B., Thimmappaya B. Functional dissection of adenovirus VAI RNA. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3423–3434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3423-3434.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Hovanessian A. Autophosphorylation of the protein kinase dependent on double-stranded RNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15538–15544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadge G. D., Swaminathan S., Katze M. G., Thimmapaya B. Binding of the adenovirus VAI RNA to the interferon-induced 68-kDa protein kinase correlates with function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7140–7144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. R., Mathews M. B. Two RNA-binding motifs in the double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase, DAI. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2478–2490. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnery S., Green S. R., Mathews M. B. Tat-responsive region RNA of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 stimulates protein synthesis in vivo and in vitro: relationship between structure and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11557–11561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnery S., Rice A. P., Robertson H. D., Mathews M. B. Tat-responsive region RNA of human immunodeficiency virus 1 can prevent activation of the double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8687–8691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G. The double stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon: dsRNA-PK. J Interferon Res. 1989 Dec;9(6):641–647. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Robertson H. D. The characteristics of inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded ribonucleic acid in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K. Procedures for studying transcription and translation of viral and host nucleic acids in interferon-treated cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):307–330. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., DeCorato D., Safer B., Galabru J., Hovanessian A. G. Adenovirus VAI RNA complexes with the 68 000 Mr protein kinase to regulate its autophosphorylation and activity. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):689–697. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Wambach M., Wong M. L., Garfinkel M., Meurs E., Chong K., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G., Barber G. N. Functional expression and RNA binding analysis of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated, 68,000-Mr protein kinase in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5497–5505. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y., Mathews M. B. Comparative analysis of the structure and function of adenovirus virus-associated RNAs. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6605–6617. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6605-6617.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manche L., Green S. R., Schmedt C., Mathews M. B. Interactions between double-stranded RNA regulators and the protein kinase DAI. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5238–5248. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B. Binding of adenovirus VA RNA to mRNA: a possible role in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):575–577. doi: 10.1038/285575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Shenk T. Adenovirus virus-associated RNA and translation control. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5657–5662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5657-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. A selective review of RNA-protein interactions in eukaryotes. Mol Biol Rep. 1990;14(2-3):151–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00360454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. RNA recognition: a family matter? Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):837–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90265-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack S. J., Thomis D. C., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: identification of a RNA binding domain within the N-terminal region of the human RNA-dependent P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Kostura M., Mathews M. B. Interaction of adenovirus VA RNAl with the protein kinase DAI: nonequivalence of binding and function. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):843–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90194-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Mathews M. B. Effects of mutations in stem and loop regions on the structure and function of adenovirus VA RNAI. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2849–2859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Pe'ery T., Mathews M. B. Role of the apical stem in maintaining the structure and function of adenovirus virus-associated RNA. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2369–2377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2369-2377.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minks M. A., West D. K., Benvin S., Baglioni C. Structural requirements of double-stranded RNA for the activation of 2',5'-oligo(A) polymerase and protein kinase of interferon-treated HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10180–10183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Mariano T. M., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. A mechanism for the control of protein synthesis by adenovirus VA RNAI. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. C., Sen G. C. Identification of the double-stranded RNA-binding domain of the human interferon-inducible protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7671–7676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pe'ery T., Mellits K. H., Mathews M. B. Mutational analysis of the central domain of adenovirus virus-associated RNA mandates a revision of the proposed secondary structure. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3534–3543. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3534-3543.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A. Regulation of HIV gene expression by RNA-protein interactions. Trends Genet. 1991 Jan;7(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90015-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Knutson G. S., Berry M. J., Atwater J. A., Lasky S. R. Purification of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase from mouse fibroblasts. Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:499–516. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. The eIF-2 alpha protein kinases, regulators of translation in eukaryotes from yeasts to humans. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7603–7606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA prevents phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit subsequent to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Impact of virus infection on host cell protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:317–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Weinberger C., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA facilitates the initiation of translation in virus-infected cells. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Mariano T. M., Reichel P. A., Mathews M. B. Translational control by adenovirus: lack of virus-associated RNAI during adenovirus infection results in phosphorylation of initiation factor eIF-2 and inhibition of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. A novel effect of adenovirus VA RNA1 on cytoplasmic mRNA abundance. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):613–617. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Adenovirus VA RNAI mediates a translational stimulation which is not restricted to the viral mRNAs. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):957–964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Weinberger C., Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA is required for efficient translation of viral mRNAs at late times after infection. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







