Abstract
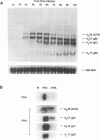
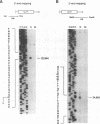
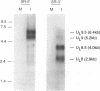
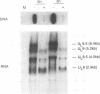
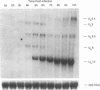
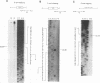
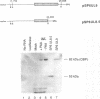
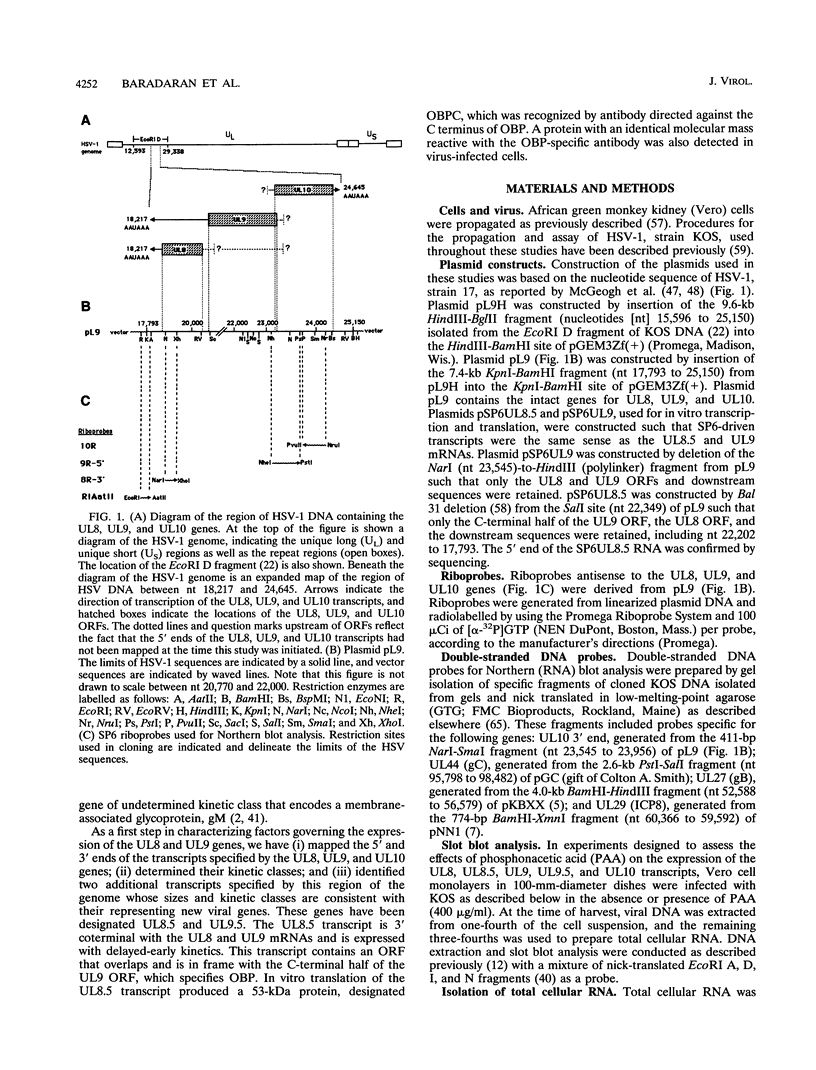
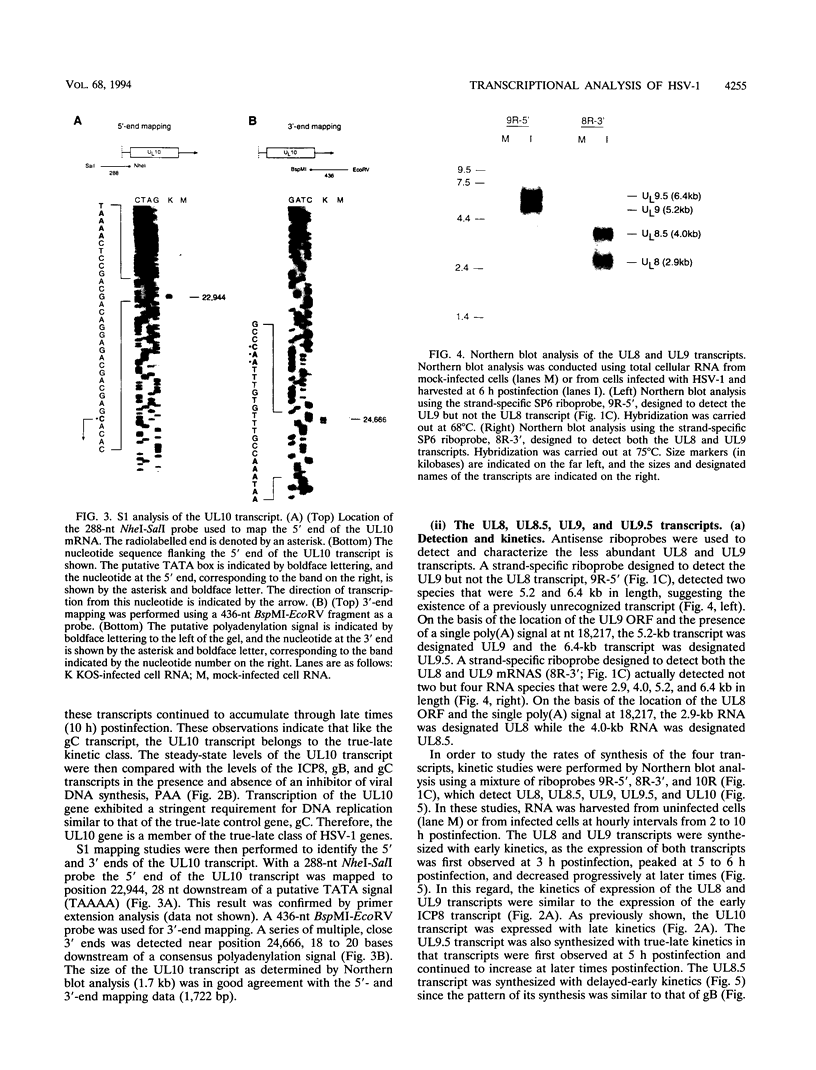
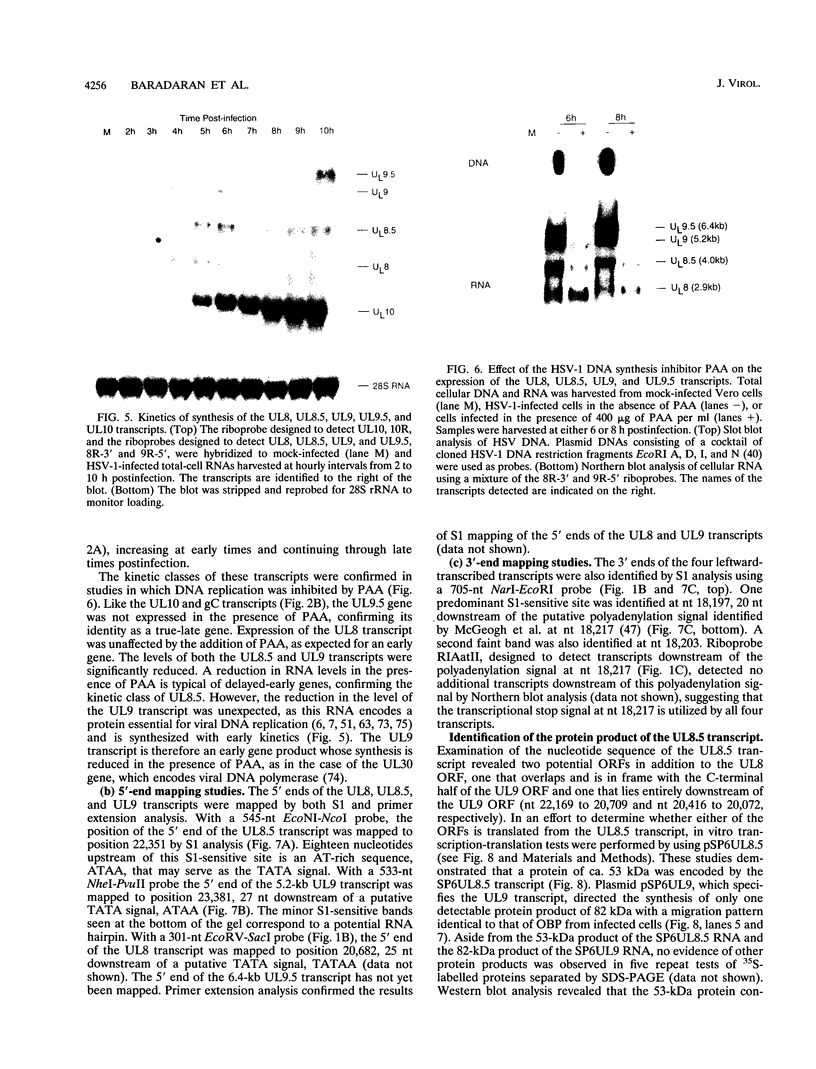
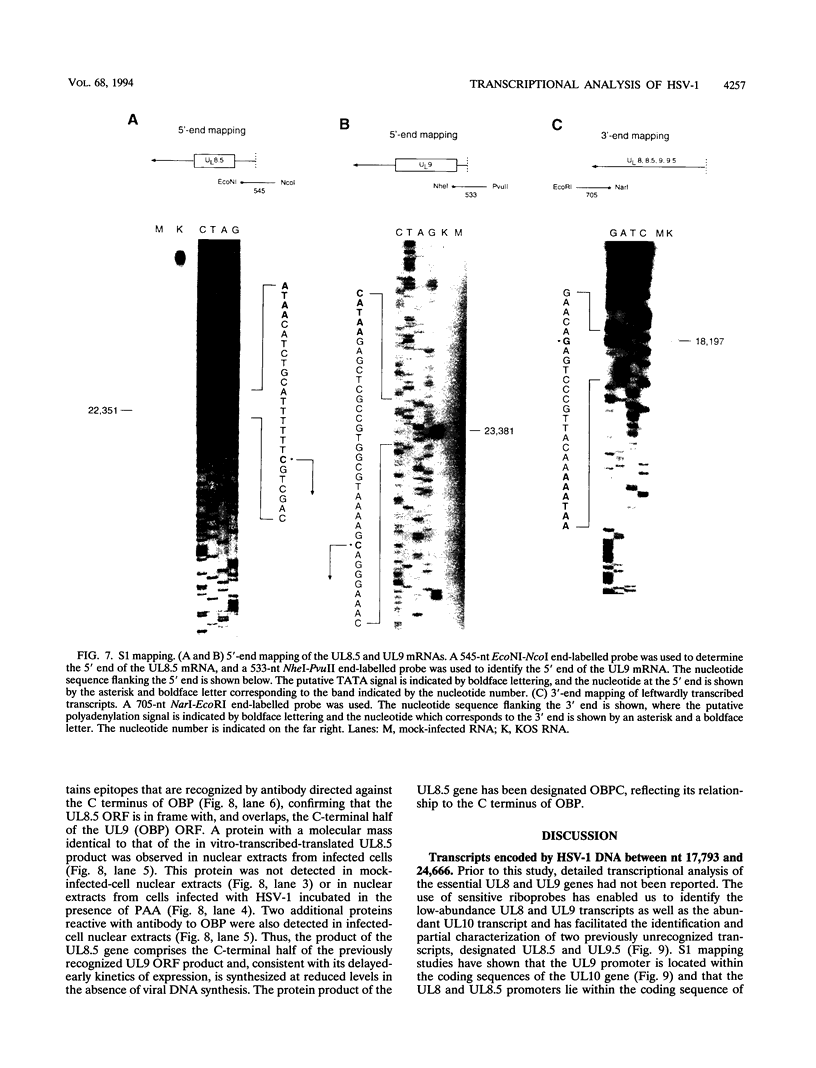
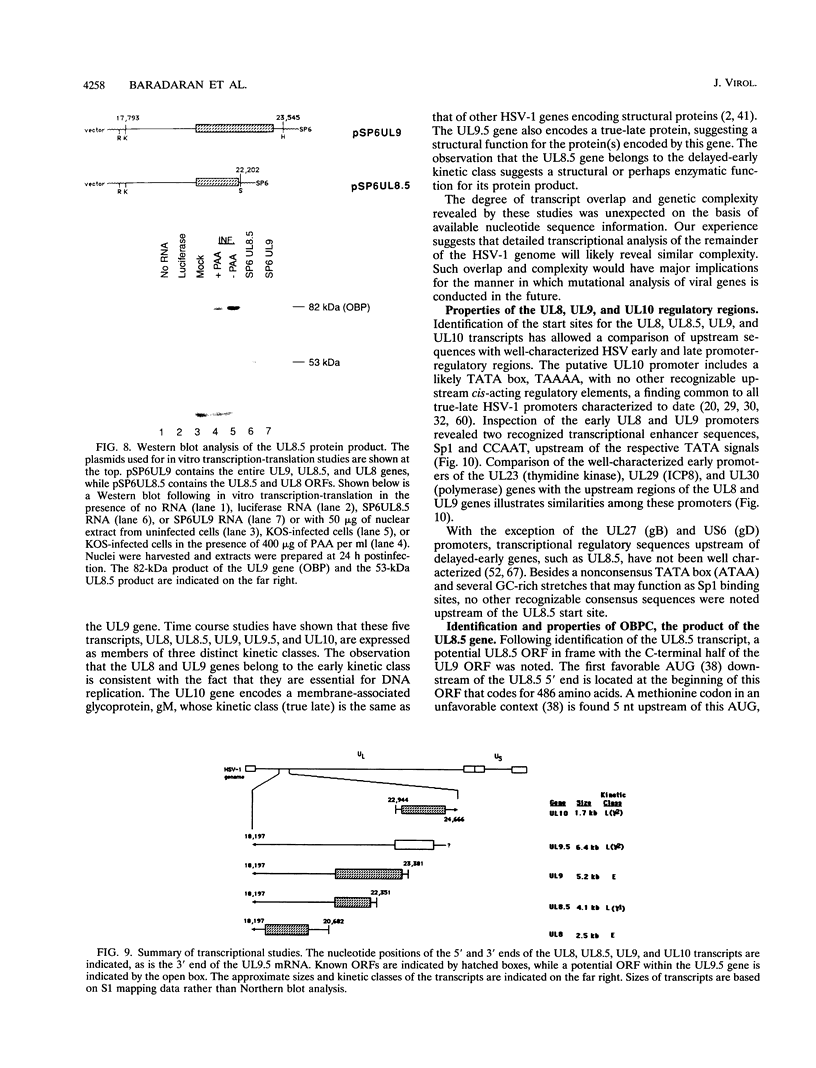
The region of the UL component of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome between nucleotides 17,793 and 25,150 includes three open reading frames that code for the protein products of the UL8, UL9, and UL10 genes (D.J. McGeogh, M.A. Dalrymple, A.J. Davison, A. Dolan, M.C. Frame, D. McNab, L.J. Perry, J.E. Scott, and P. Taylor, J. Gen. Virol. 69:1531-1574, 1988). We have mapped and characterized the overlapping transcripts in this region and have found that, in addition to the low-abundance UL8 and UL9 transcripts and the abundant UL10 transcript, at least two additional transcription units, designated UL8.5 and UL9.5, are specified by this region of the genome. The 5' ends of the UL8, UL8.5, and UL9 transcripts were mapped to nucleotides 20,682, 22,351, and 23,381, respectively. The 5' terminus of the UL9.5 transcript has not yet been mapped. The 3' ends of the UL8, UL8.5, UL9, and UL9.5 transcripts are coterminal at nucleotide 18,197. The 5' end of the UL10 mRNA, which is transcribed from the strand opposite that specifying the UL8, UL8.5, UL9, and UL9.5 transcripts, lies within the UL9 open reading frame at nucleotide 22,944, while the 3' terminus was mapped to nucleotide 24,666. Time course studies demonstrated that the UL8 and UL9 transcripts are members of the early kinetic class, the UL8.5 mRNA is a delayed-early transcript, and the UL9.5 and UL10 transcripts belong to the true-late kinetic class. Examination of the nucleotide sequence of the UL8.5 transcript revealed a potential open reading frame that overlaps and is in frame with the C-terminal half of the open reading frame encoding the origin-binding protein (OBP), the product of the UL9 gene. In vitro translation of the UL8.5 transcript demonstrated that it encodes a protein with an apparent molecular mass of 53 kDa. This protein was recognized by antibody directed against the C-terminal region of OBP and has thus been designated OBPC. A protein with an identical apparent molecular mass was also recognized by this antibody in infected-cell lysates, indicating that OBPC is synthesized during viral infection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuckle M. I., Stow N. D. A mutational analysis of the DNA-binding domain of the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL9 protein. J Gen Virol. 1993 Jul;74(Pt 7):1349–1355. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-7-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines J. D., Roizman B. The UL10 gene of herpes simplex virus 1 encodes a novel viral glycoprotein, gM, which is present in the virion and in the plasma membrane of infected cells. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1441–1452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1441-1452.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehmer P. E., Lehman I. R. Physical interaction between the herpes simplex virus 1 origin-binding protein and single-stranded DNA-binding protein ICP8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8444–8448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. Z., Person S., Warner S. C., Zhou J. H., DeLuca N. A. Linker-insertion nonsense and restriction-site deletion mutations of the gB glycoprotein gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):714–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.714-721.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D. A method for identifying the viral genes required for herpesvirus DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9094–9098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. A genetic approach to promoter recognition during trans induction of viral gene expression. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3018926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowski C. E., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-specific binding protein: oriS-binding properties and effects of cellular proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3140–3150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3140-3150.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowski C., Alwine J. C. Translational control of synthesis of simian virus 40 late proteins from polycistronic 19S late mRNA. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3182–3192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3182-3192.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Deb S. P. A 269-amino-acid segment with a pseudo-leucine zipper and a helix-turn-helix motif codes for the sequence-specific DNA-binding domain of herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2829–2838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2829-2838.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Coen D. M., McKnight S. L. Promoter domains required for expression of plasmid-borne copies of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene in virus-infected mouse fibroblasts and microinjected frog oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1940–1947. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Gustafsson C. M., Hammarsten O., Stow N. D. Structural elements required for the cooperative binding of the herpes simplex virus origin binding protein to oriS reside in the N-terminal part of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17424–17429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Gustafsson C. M., Hammarsten O. The origin binding protein of herpes simplex virus 1 binds cooperatively to the viral origin of replication oris. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17167–17173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Lehman I. R. Interaction of origin binding protein with an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., O'Donnell M. E., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA binding protein specific for an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierer D. S., Challberg M. D. Purification and characterization of UL9, the herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):3986–3995. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.3986-3995.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Papavassiliou A. G., Rice M., Hecht L. B., Silverstein S., Wagner E. K. Analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter controlling the expression of UL38, a true late gene involved in capsid assembly. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):769–786. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.769-786.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. Staining and radiolabeling properties of B capsid and virion proteins in polyacrylamide gels. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):155–165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.155-165.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Cloning of herpes simplex virus type 1 sequences representing the whole genome. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.50-58.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich L. D., Rixon F. J., Parris D. S. Kinetics of expression of the gene encoding the 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):137–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.137-147.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. Two related superfamilies of putative helicases involved in replication, recombination, repair and expression of DNA and RNA genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4713–4730. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazuda D. J., Perry H. C., McClements W. L. Cooperative interactions between replication origin-bound molecules of herpes simplex virus origin-binding protein are mediated via the amino terminus of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14309–14315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazuda D. J., Perry H. C., Naylor A. M., McClements W. L. Characterization of the herpes simplex virus origin binding protein interaction with OriS. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24621–24626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. A specific 15-bp TATA box promoter element is required for expression of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):40–53. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Otal T. M., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Transcriptional control signals of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) gene lie within bases -34 to +124 relative to the 5' terminus of the mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3652–3666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., Everett R. D. DNA replication is required for abundant expression of a plasmid-borne late US11 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3609–3625. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., Everett R. D. The control of herpes simplex virus type-1 late gene transcription: a 'TATA-box'/cap site region is sufficient for fully efficient regulated activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8247–8264. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibler P. K., Duncan J., Keith B. D., Hupel T., Smiley J. R. Regulation of herpes simplex virus true late gene expression: sequences downstream from the US11 TATA box inhibit expression from an unreplicated template. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6749–6760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6749-6760.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Tegtmeyer P. Characterization of major recognition sequences for a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4096–4103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4096-4103.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leib D. A., Coen D. M., Bogard C. L., Hicks K. A., Yager D. R., Knipe D. M., Tyler K. L., Schaffer P. A. Immediate-early regulatory gene mutants define different stages in the establishment and reactivation of herpes simplex virus latency. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):759–768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.759-768.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean C. A., Efstathiou S., Elliott M. L., Jamieson F. E., McGeoch D. J. Investigation of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes encoding multiply inserted membrane proteins. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):897–906. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. K., Martinez R., Muncy L., Carmichael E. P., Weller S. K. Genetic analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL9 gene: isolation of a LacZ insertion mutant and expression in eukaryotic cells. Virology. 1992 Oct;190(2):702–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90908-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. W., Deb S. P., Klauer J. S., Deb S. Analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 OriS sequence: mapping of functional domains. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4359–4369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4359-4369.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. W., Muñoz R. M., Oliver D., Subler M. A., Deb S. Analysis of the DNA-binding domain of the HSV-1 origin-binding protein. Virology. 1994 Jan;198(1):71–80. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R., Shao L., Weller S. K. The conserved helicase motifs of the herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein UL9 are important for function. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6735–6746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6735-6746.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Roizman B. Activation of herpes simplex virus 1 gamma 2 genes by viral DNA replication. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):593–598. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products required for DNA replication: identification and overexpression. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):196–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.196-204.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson N. E., Person S., Homa F. L. Analysis of the gB promoter of herpes simplex virus type 1: high-level expression requires both an 89-base-pair promoter fragment and a nontranslated leader sequence. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6226–6232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6226-6232.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry H. C., Hazuda D. J., McClements W. L. The DNA binding domain of herpes simplex virus type 1 origin binding protein is a transdominant inhibitor of virus replication. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):73–79. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin S. D., Hanlon B. Nucleoprotein complex formed between herpes simplex virus UL9 protein and the origin of DNA replication: inter- and intramolecular interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10946–10950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Greene C. C., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.796-805.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Carter V. C., Timbury M. C. Collaborative complementation study of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):490–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.490-504.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Regulation of the herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) glycoprotein C gene: sequences between base pairs -34 to +29 control transient expression and responsiveness to transactivation by the products of the immediate early (alpha) 4 and 0 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3097–3111. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabell E. C., Olivo P. D. A truncated herpes simplex virus origin binding protein which contains the carboxyl terminal origin binding domain binds to the origin of replication but does not alter its conformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5203–5211. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Hammarsten O., Arbuckle M. I., Elias P. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA replication by mutant forms of the origin-binding protein. Virology. 1993 Oct;196(2):413–418. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-dependent DNA replication in insect cells using recombinant baculoviruses. J Gen Virol. 1992 Feb;73(Pt 2):313–321. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L., Knipe D. M. Mapping of the transcriptional initiation site of the herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP8 gene in infected and transfected cells. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):615–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.615-620.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder D. G., Everett R. D., Wilcox K. W., Beard P., Pizer L. I. ICP4-binding sites in the promoter and coding regions of the herpes simplex virus gD gene contribute to activation of in vitro transcription by ICP4. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2510–2520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2510-2520.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls establish the cascade of herpes simplex virus protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):819–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Calder J. M., Stow N. D. Binding of the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL9 gene product to an origin of viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1409–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Stow N. D. Two binding sites for the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL9 protein are required for efficient activity of the oriS replication origin. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jun;71(Pt 6):1379–1385. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-6-1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe K. K., Digard P., Staknis D., Coen D. M. Unusual regulation of expression of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5419–5425. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5419-5425.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager D. R., Coen D. M. Analysis of the transcript of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene provides evidence that polymerase expression is inefficient at the level of translation. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2007–2015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2007-2015.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]