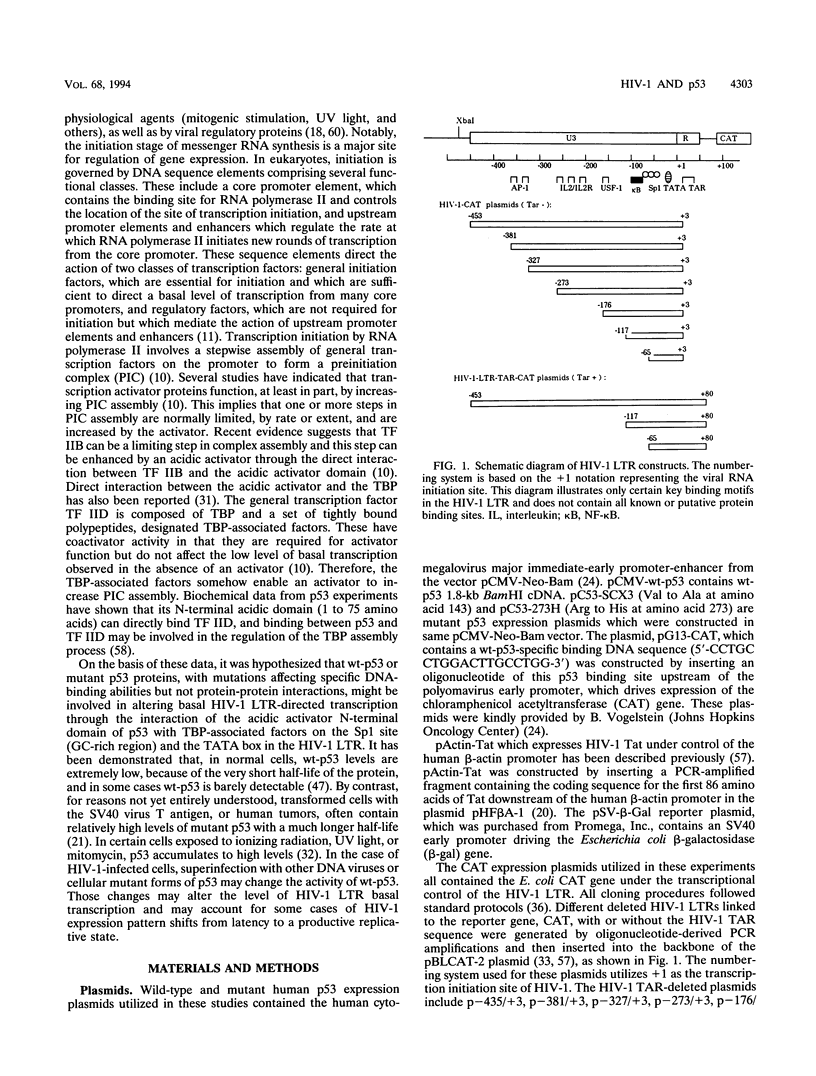
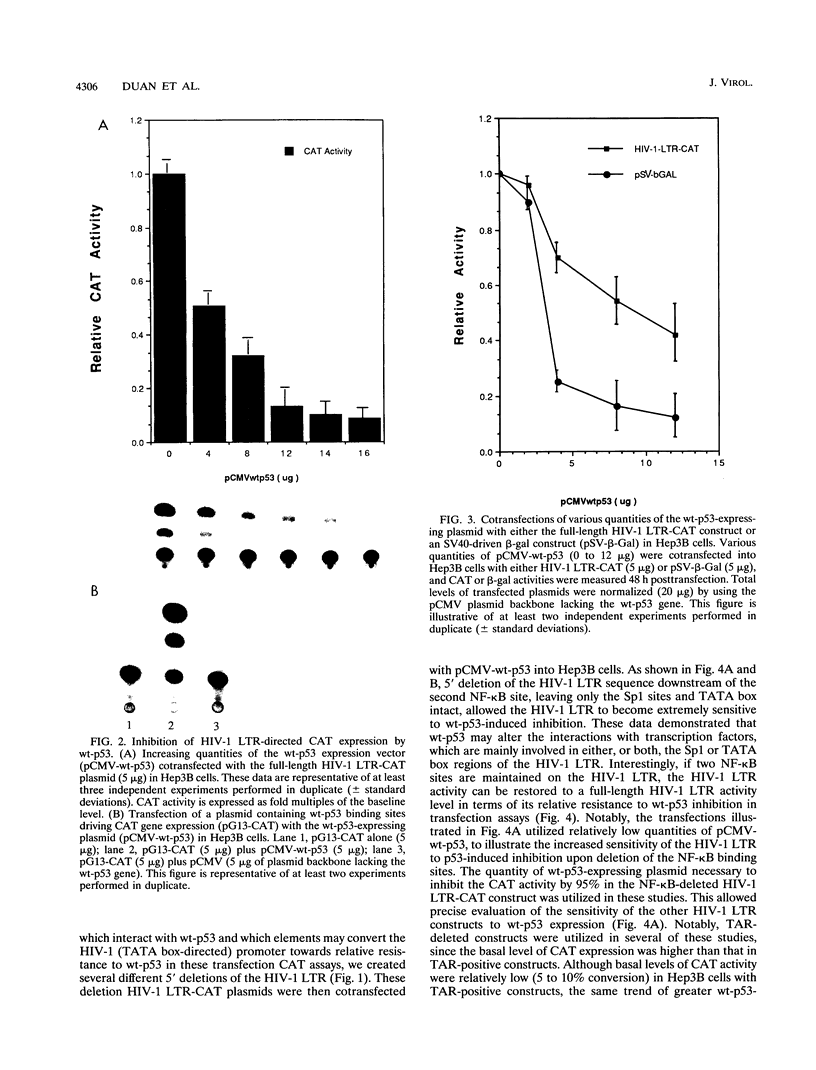
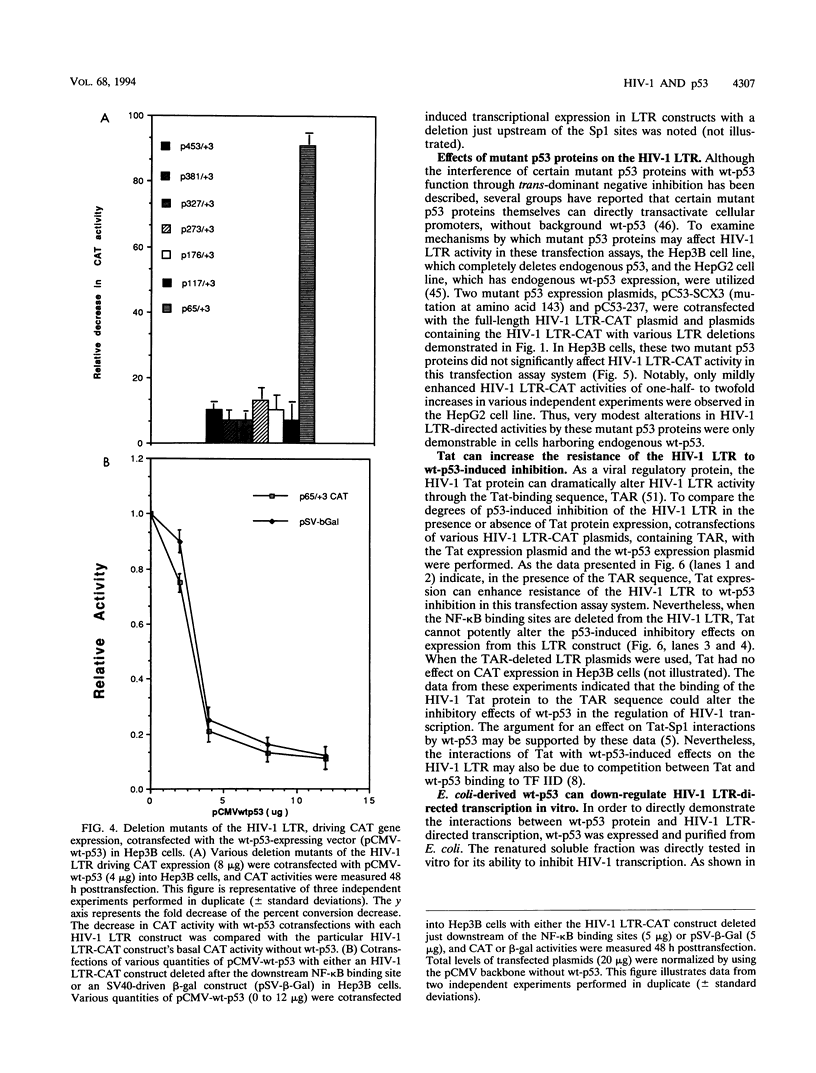
Abstract
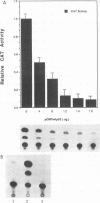
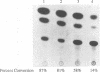
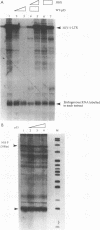
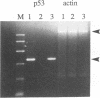
The p53 tumor suppressor gene product, a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein, has been shown to act as a transcriptional activator and repressor both in vitro and in vivo. Consistent with its role in regulating transcription are recent observations that the N-terminal acidic domain of p53 binds directly to the TATA box-binding protein subunit of the general transcription factor, TF IID. It is now demonstrated that wild-type p53 (wt-p53) inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) long terminal repeat (LTR)-directed chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity in a cotransfection assay system. Importantly, this effect of wt-p53 on the HIV-1 LTR was also demonstrated by in vitro transcription assays. In addition, the Sp1 sites and the TATA box of the HIV-1 LTR are demonstrated to be the primary sites involved with p53-induced effects on this viral promoter. The upstream elements of the HIV-1 LTR, including the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) binding sites, decrease the p53-induced inhibitory effects on viral transcription. In the presence of the HIV-1 TAR sequence and Tat protein, the HIV-1 LTR also becomes less sensitive to wt-p53-induced inhibition. By using a retroviral vector delivery system, mutant forms of p53 genes were expressed in two HIV-1 latently infected cell lines, ACH-2 and U1. In the ACH-2 cell line, which is now demonstrated to contain an endogenous mutant form of p53 (amino acid 248, Arg to Gln), additional mutant p53 proteins did not alter HIV-1 replication. In U1 cells, which completely lack endogenous p53, overexpression of mutant p53 led to an increase in HIV-1 replication. Thus, these data indicate a possible functional role for wt-p53 and mutant p53 proteins in the control of HIV-1 replication patterns and proviral latency.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama N., Nagase T., Sawazaki T., Mizuguchi G., Nakagoshi H., Fujisawa J. I., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Overlap of the p53-responsive element and cAMP-responsive element in the enhancer of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5403–5407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak Y., Juven T., Haffner R., Oren M. mdm2 expression is induced by wild type p53 activity. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):461–468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielinska A., Krasnow S., Nabel G. J. NF-kappa B-mediated activation of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer: site of transcriptional initiation is independent of the TATA box. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4097–4100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4097-4100.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borellini F., Glazer R. I. Induction of Sp1-p53 DNA-binding heterocomplexes during granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor-dependent proliferation in human erythroleukemia cell line TF-1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7923–7928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y. Z., Friedman-Kien A. E., Huang Y. X., Li X. L., Mirabile M., Moudgil T., Zucker-Franklin D., Ho D. D. CD4-independent, productive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of hepatoma cell lines in vitro. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2553–2559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2553-2559.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B. K., Saksela K., Andino R., Baltimore D. Distinct modes of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 proviral latency revealed by superinfection of nonproductively infected cell lines with recombinant luciferase-encoding viruses. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):654–660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.654-660.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Farmer G., Zhu H., Prywes R., Prives C. Cooperative DNA binding of p53 with TFIID (TBP): a possible mechanism for transcriptional activation. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1837–1849. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin K. V., Ueda K., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Modulation of activity of the promoter of the human MDR1 gene by Ras and p53. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):459–462. doi: 10.1126/science.1346476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy B., Green M. R. Eukaryotic activators function during multiple steps of preinitiation complex assembly. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):531–536. doi: 10.1038/366531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. General initiation factors for RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:161–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Jackson C. T., Subler M. A., Martin D. W. Modulation of cellular and viral promoters by mutant human p53 proteins found in tumor cells. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6164–6170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6164-6170.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan L., Oakes J. W., Ferraro A., Bagasra O., Pomerantz R. J. Tat and rev differentially affect restricted replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in various cells. Virology. 1994 Mar;199(2):474–478. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embretson J., Zupancic M., Beneke J., Till M., Wolinsky S., Ribas J. L., Burke A., Haase A. T. Analysis of human immunodeficiency virus-infected tissues by amplification and in situ hybridization reveals latent and permissive infections at single-cell resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):357–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feitelson M. A., Zhu M., Duan L. X., London W. T. Hepatitis B x antigen and p53 are associated in vitro and in liver tissues from patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1109–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. Cellular transcription factors involved in the regulation of HIV-1 gene expression. AIDS. 1992 Apr;6(4):347–363. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199204000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Mechta F., Yaniv M., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can down-modulate the activity of various promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9979–9983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy O., Hall A., Oren M. Stabilization of the p53 transformation-related protein in mouse fibrosarcoma cell lines: effects of protein sequence and intracellular environment. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3385–3392. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrich D., Garcia J., Wu F., Mitsuyasu R., Gonazalez J., Gaynor R. Role of SP1-binding domains in in vivo transcriptional regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2585–2591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2585-2591.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Finlay C. A., Quartin R. S., Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B., Levine A. J. Mutant p53 DNA clones from human colon carcinomas cooperate with ras in transforming primary rat cells: a comparison of the "hot spot" mutant phenotypes. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Dec;1(12):571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Hirsch M. S. Infection of monocyte/macrophages by human T lymphotropic virus type III. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1712–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI112491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Luciw P. A., Tjian R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3008338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klehr D., Schlake T., Maass K., Bode J. Scaffold-attached regions (SAR elements) mediate transcriptional effects due to butyrate. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 31;31(12):3222–3229. doi: 10.1021/bi00127a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Botchan M. R. The acidic transcriptional activation domains of VP16 and p53 bind the cellular replication protein A and stimulate in vitro BPV-1 DNA replication. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1207–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90649-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao S. M., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain contributes to the response to multiple acidic activators in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2431–2440. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Lane D. P. Differential induction of transcriptionally active p53 following UV or ionizing radiation: defects in chromosome instability syndromes? Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):765–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90496-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. H., Vartikar J., Pipas J. M., Laimins L. A. Specific repression of TATA-mediated but not initiator-mediated transcription by wild-type p53. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):281–283. doi: 10.1038/363281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D. p53 and the Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1993 Apr;66(2):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(93)90233-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Street A. J. Nuclear protein phosphorylation and growth control. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 1;287(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1042/bj2870001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley C. A., Fisher C. J., Bártek J., Vojtesek B., Lane D., Barnes D. M. Analysis of p53 expression in human tumours: an antibody raised against human p53 expressed in Escherichia coli. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):183–189. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Michalovitz D., Ben-Zeev A., Oren M. Specific interaction between the p53 cellular tumour antigen and major heat shock proteins. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):182–184. doi: 10.1038/320182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Feinberg M. B., Trono D., Baltimore D. Lipopolysaccharide is a potent monocyte/macrophage-specific stimulator of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):253–261. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Trono D., Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D. Cells nonproductively infected with HIV-1 exhibit an aberrant pattern of viral RNA expression: a molecular model for latency. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1271–1276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puisieux A., Galvin K., Troalen F., Bressac B., Marcais C., Galun E., Ponchel F., Yakicier C., Ji J., Ozturk M. Retinoblastoma and p53 tumor suppressor genes in human hepatoma cell lines. FASEB J. 1993 Nov;7(14):1407–1413. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.14.8224613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Schmidt J. R., Yoas K., Hao M. M., Lozano G. Analysis of p53 mutants for transcriptional activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6067–6074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Rowan A., Smith M. E., Kerr I. B., Bodmer W. F., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 mutations in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7555–7559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg Z. F., Fauci A. S. Immunopathogenesis of HIV infection. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2382–2390. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.1676689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. K., Buckler-White A. J., Rabson A. B., Englund G., Martin M. A. Contribution of NF-kappa B and Sp1 binding motifs to the replicative capacity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: distinct patterns of viral growth are determined by T-cell types. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4350–4358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4350-4358.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santhanam U., Ray A., Sehgal P. B. Repression of the interleukin 6 gene promoter by p53 and the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7605–7609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subler M. A., Martin D. W., Deb S. Activation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat by transforming mutants of human p53. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):103–110. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.103-110.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subler M. A., Martin D. W., Deb S. Inhibition of viral and cellular promoters by human wild-type p53. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4757–4762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4757-4762.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekely L., Selivanova G., Magnusson K. P., Klein G., Wiman K. G. EBNA-5, an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen, binds to the retinoblastoma and p53 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5455–5459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. P., Pomerantz R., Bagasra O., Chowdhury M., Rappaport J., Khalili K., Amini S. TAR-independent transactivation by Tat in cells derived from the CNS: a novel mechanism of HIV-1 gene regulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3395–3403. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truant R., Xiao H., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct interaction between the transcriptional activation domain of human p53 and the TATA box-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2284–2287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Wu J. Y., Robinson W. S. Transcriptional activation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat by hepatitis B virus X-protein requires de novo protein synthesis. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):406–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90501-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaishnav Y. N., Wong-Staal F. The biochemistry of AIDS. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:577–630. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. Interactions of human papillomavirus transforming proteins with the products of tumor suppressor genes. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):872–879. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8393818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. H., Friedman P. N., Prives C. The murine p53 protein blocks replication of SV40 DNA in vitro by inhibiting the initiation functions of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90913-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Hauschka S., Tapscott S. J. The MCK enhancer contains a p53 responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4570–4571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will H., Cattaneo R., Darai G., Deinhardt F., Schellekens H., Schaller H. Infectious hepatitis B virus from cloned DNA of known nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):891–895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow B. J., Pomerantz R. J., Bagasra O., Trono D. HIV-1 latency due to the site of proviral integration. Virology. 1993 Oct;196(2):849–854. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Bargonetti J., Walker K., Prives C., Levine A. J. Wild-type p53 mediates positive regulation of gene expression through a specific DNA sequence element. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1143–1152. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Levine A. J. A comparison of the biological activities of wild-type and mutant p53. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):855–865. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8344485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimran A., Glass C., Thorpe V. S., Beutler E. Analysis of 'color PCR' by automatic DNA sequencer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7538–7538. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]