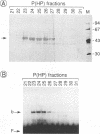
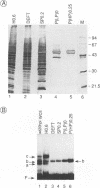
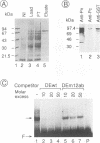
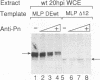
Abstract
During the course of lytic infection, the adenovirus major late promoter (MLP) is induced to high levels after replication of viral DNA has started. We had previously shown that sequence elements located downstream of the MLP start site were implicated in this late-specific transcriptional activation (DE1, between +85 and +98; DE2, between +100 and +120). Two positive transcription factors involved in this activation have been detected. DEF-A, which specifically binds to DE1 and also to the 3' portion of DE2 (DE2a), and DEF-B, which interacts with the 5' part of DE2 (DE2b). When present together, these two proteins cooperatively assemble onto the DE2 element. We now report the purification of DEF-B and show that it is identical to the product of the adenovirus IVa2 gene product. This conclusion is based on microsequence analysis of DEF-B as well as on the inhibitory effect of antibodies against IVa2 on the DNA-binding activity of DEF-B and also on DE-dependent in vitro transcription. In addition, we show that bacterially synthesized IVa2 protein binds to the DE sequences with the same specificity as DEF-B. Finally, in transfected cells, a recombinant IVa2 protein stimulates MLP activity in a DE-dependent fashion. The physiological implications of these findings are discussed.
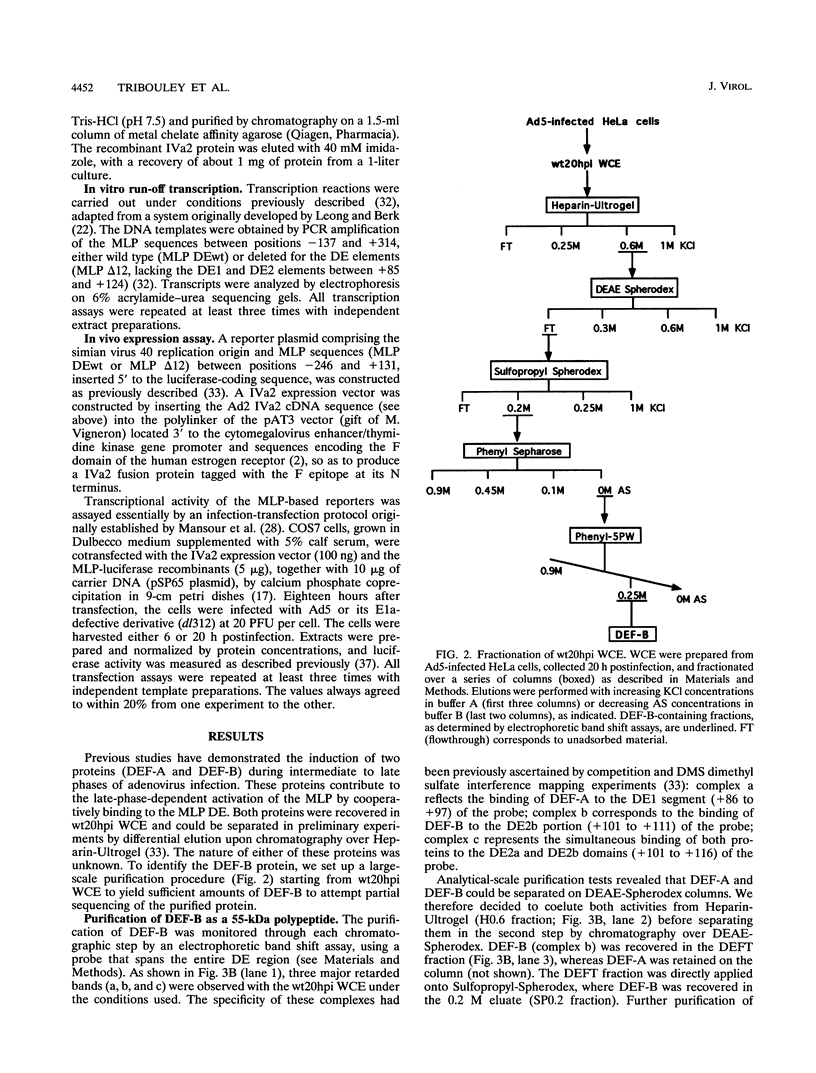
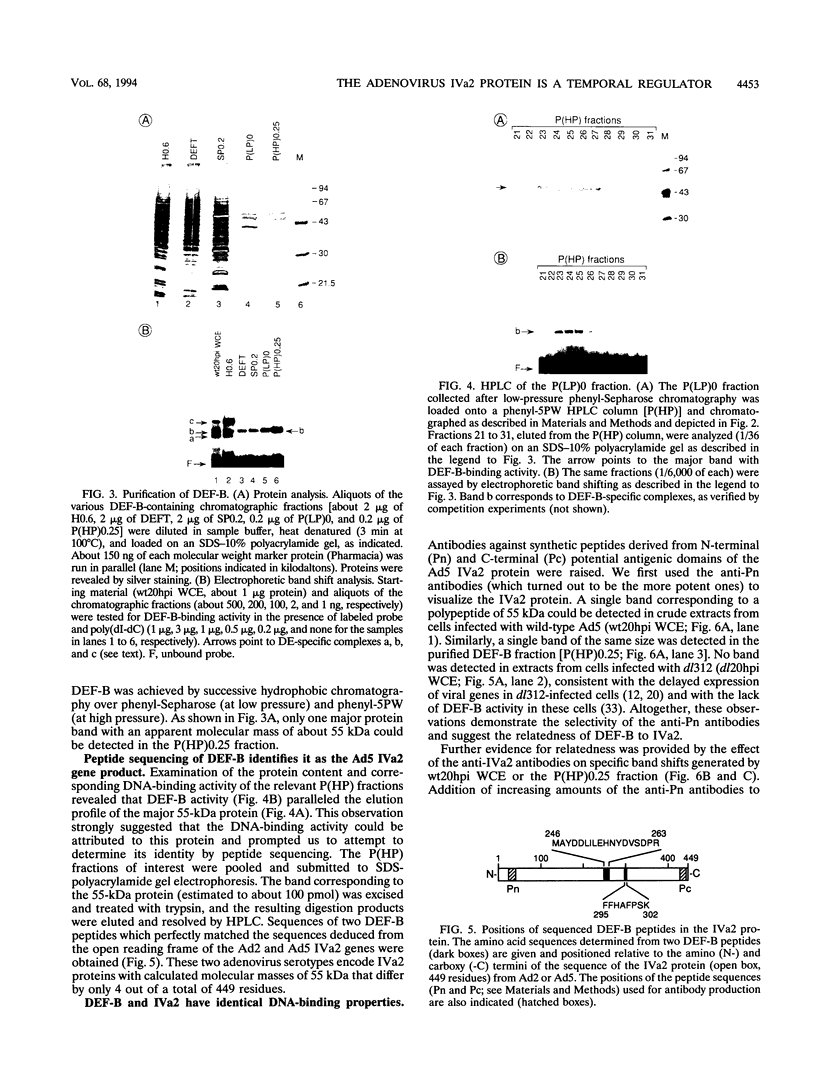
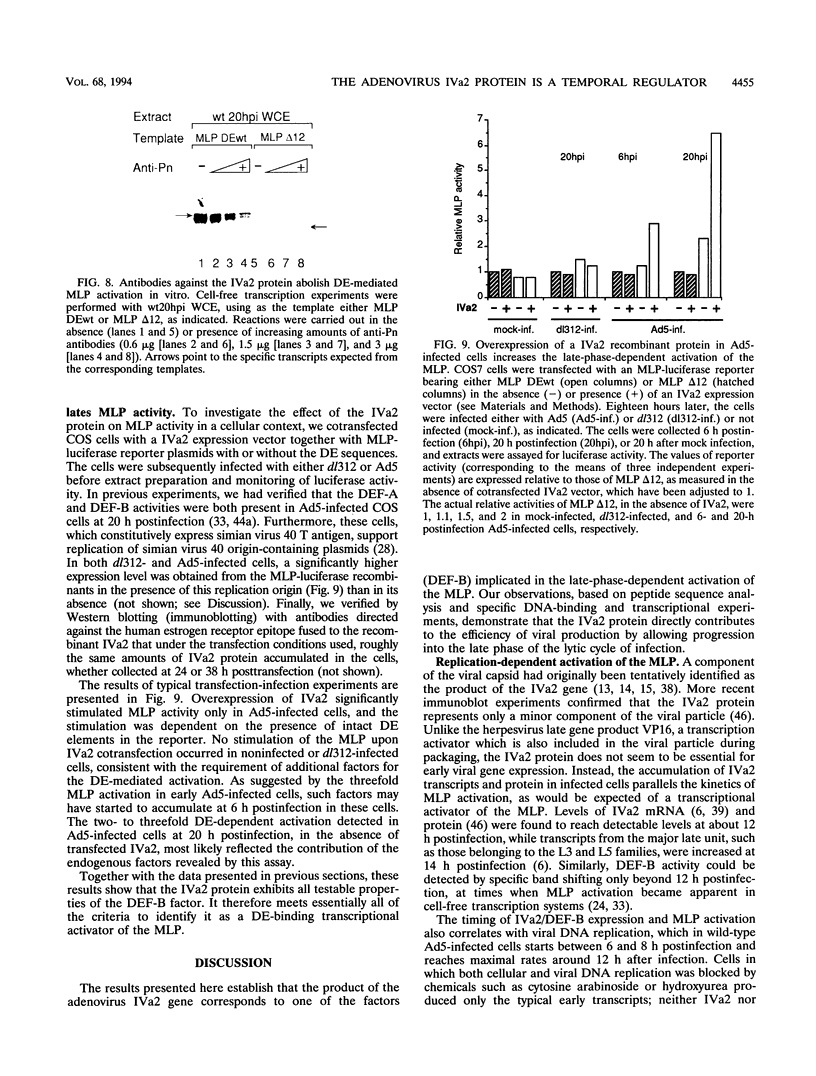
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adami G., Babiss L. E. Evidence that USF can interact with only a single general transcription complex at one time. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S., Lutz Y., Bellocq J. P., Chenard-Neu M. P., Rouyer N., Metzger D. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies recognising defined regions of the human oestrogen receptor. Hybridoma. 1993 Aug;12(4):391–405. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1993.12.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Caplen F. V., Katze M. G., Krug R. M. Efficient transcription, not translation, is dependent on adenovirus tripartite leader sequences at late times of infection. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1606–1616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1606-1616.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J. Adenovirus promoters and E1A transactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:45–79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binger M. H., Flint S. J. Accumulation of early and intermediate mRNA species during subgroup C adenovirus productive infections. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):387–403. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocco J. L., Reimund B., Chatton B., Kedinger C. Rb may act as a transcriptional co-activator in undifferentiated F9 cells. Oncogene. 1993 Nov;8(11):2977–2986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H., Vinnakota R., Flint S. J. Intragenic activating and repressing elements control transcription from the adenovirus IVa2 initiator. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):676–685. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concino M. F., Lee R. F., Merryweather J. P., Weinmann R. The adenovirus major late promoter TATA box and initiation site are both necessary for transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7423–7433. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossland L. D., Raskas H. J. Identification of adenovirus genes that require template replication for expression. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):737–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.737-748.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Halluin J. C., Martin G. R., Torpier G., Boulanger P. A. Adenovirus type 2 assembly analyzed by reversible cross-linking of labile intermediates. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):357–363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.357-363.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaux B., Albrecht G., Kedinger C. Identical genomic footprints of the adenovirus EIIa promoter are detected before and after EIa induction. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4560–4563. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvardsson B., Everitt E., Jörnvall H., Prage L., Philipson L. Intermediates in adenovirus assembly. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):533–547. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.533-547.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H. S., Pereira H. G., Valentine R. C., Wilcox W. C. A proposed terminology for the adenovirus antigens and virion morphological subunits. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):782–783. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Durr P., Boeuf H., Kédinger C. Replication-induced stimulation of the major late promoter of adenovirus is correlated to the binding of a factor to sequences in the first intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3771–3786. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Durr P., Mondésert G., Kédinger C. Replication-dependent activation of the adenovirus major late promoter is mediated by the increased binding of a transcription factor to sequences in the first intron. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5124–5132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5124-5132.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K., Berk A. J. Adenovirus early region 1A protein increases the number of template molecules transcribed in cell-free extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5844–5848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K., Brunet L., Berk A. J. Factors responsible for the higher transcriptional activity of extracts of adenovirus-infected cells fractionate with the TATA box transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1765–1774. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K., Lee W., Berk A. J. High-level transcription from the adenovirus major late promoter requires downstream binding sites for late-phase-specific factors. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):51–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.51-60.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Esche H., Smart J. E., Stillman B. W., Harter M. L., Mathews M. B. Organization and expression of the left third of the genome of adenovirus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):493–508. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. C., Huang W. L., Flint S. J. The downstream regulatory sequence of the adenovirus type 2 major late promoter is functionally redundant. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5685–5690. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5685-5690.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Shenk T. In vivo identification of sequence elements required for normal function of the adenovirus major late transcriptional control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6327–6335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Grodzicker T., Tjian R. Downstream sequences affect transcription initiation from the adenovirus major late promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2684–2694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason B. B., Davis A. R., Bhat B. M., Chengalvala M., Lubeck M. D., Zandle G., Kostek B., Cholodofsky S., Dheer S., Molnar-Kimber K. Adenovirus vaccine vectors expressing hepatitis B surface antigen: importance of regulatory elements in the adenovirus major late intron. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):452–461. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90509-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Kempf A., Egly J. M. The mammalian upstream element factor recognizes two sites in the adenovirus type 2 IVa2-major late promoter intergenic region and stimulates both promoters. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3199–3206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3199-3206.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Miyamoto N. G., Zheng X. M., Egly J. M. Purification of a factor specific for the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2577–2584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondesert G., Tribouley C., Kedinger C. Identification of a novel downstream binding protein implicated in late-phase-specific activation of the adenovirus major late promotor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3881–3889. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondésert G., Kédinger C. Cooperation between upstream and downstream elements of the adenovirus major late promoter for maximal late phase-specific transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3221–3228. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan V., Madden M. J., Salzman N. P. Identification of a transcription factor which interacts with the distal domain of the adenovirus IVa2 promoter. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):646–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.646-652.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan V., Madden M. J., Salzman N. P. Positive and negative control sequences within the distal domain of the adenovirus IVa2 promoter overlap with the major late promoter. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.10-15.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Wilson M. C. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):113–118. doi: 10.1038/290113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K. Luciferase reporter gene vectors for analysis of promoters and enhancers. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reach M., Babiss L. E., Young C. S. The upstream factor-binding site is not essential for activation of transcription from the adenovirus major late promoter. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5851–5860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5851-5860.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reach M., Xu L. X., Young C. S. Transcription from the adenovirus major late promoter uses redundant activating elements. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3439–3446. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld J., Capdevielle J., Guillemot J. C., Ferrara P. In-gel digestion of proteins for internal sequence analysis after one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1992 May 15;203(1):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90061-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Manley J., Fire A., Gefter M. Regulation of adenovirus mRNA synthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. R., Ziff E. B. Transcripts from the adenovirus-2 major late promoter yield a single early family of 3' coterminal mRNAs and five late families. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. R., Ziff E. B. Transcripts from the adenovirus-2 major late promoter yield a single early family of 3' coterminal mRNAs and five late families. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Control of messenger RNA concentration by differential cytoplasmic half-life. Adenovirus messenger RNAs from transcription units 1A and 1B. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):231–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter N., D'Halluin J. C. Regulation of the biosynthesis of subgroup C adenovirus protein IVa2. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5250–5259. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5250-5259.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zock C., Doerfler W. A mitigator sequence in the downstream region of the major late promoter of adenovirus type 12 DNA. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1615–1623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]