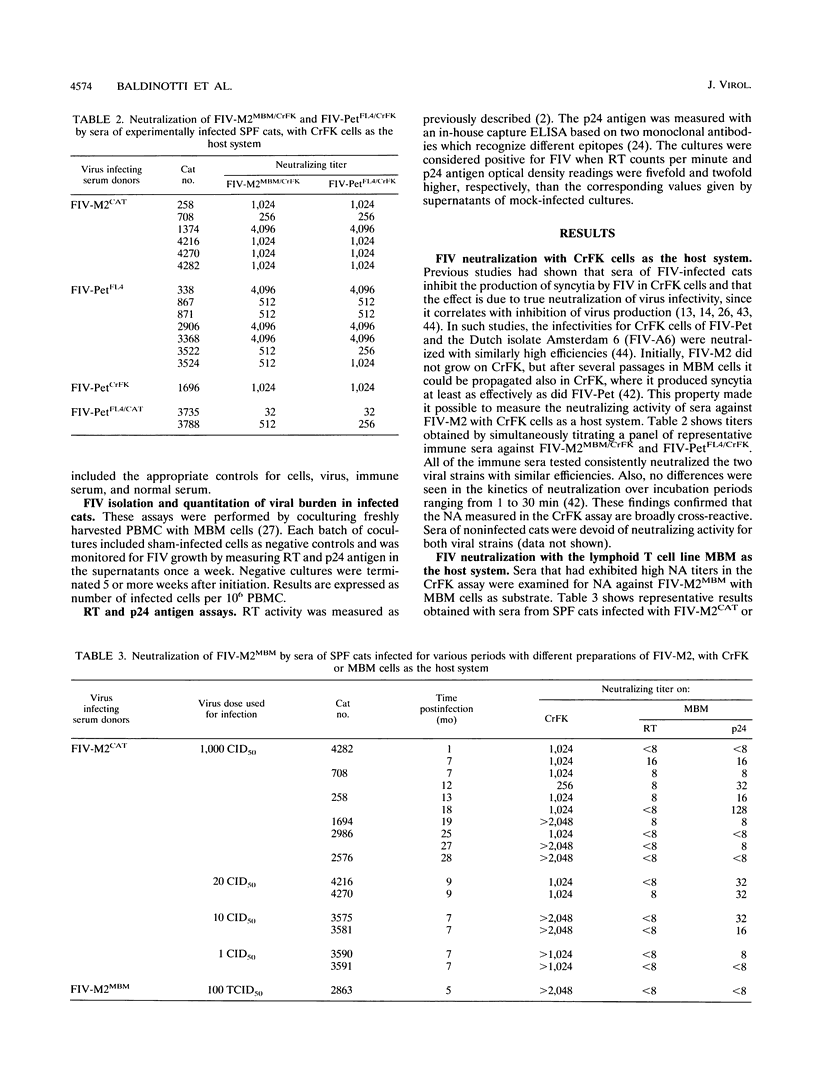
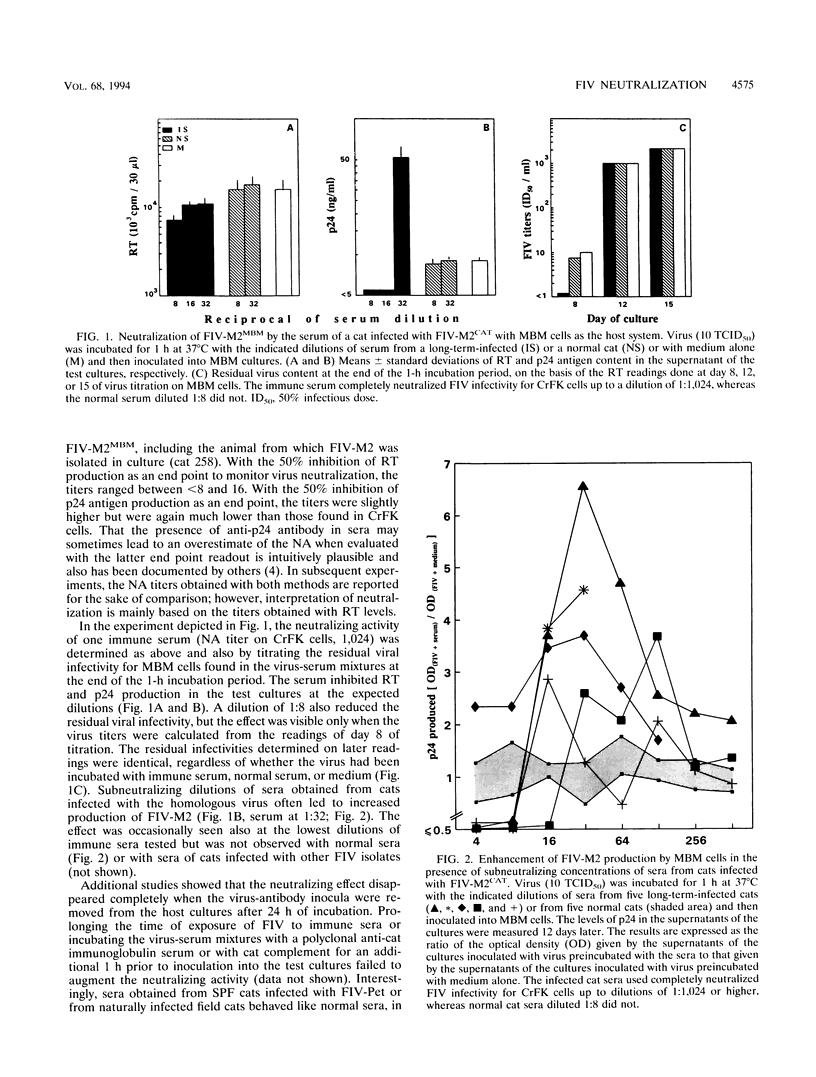
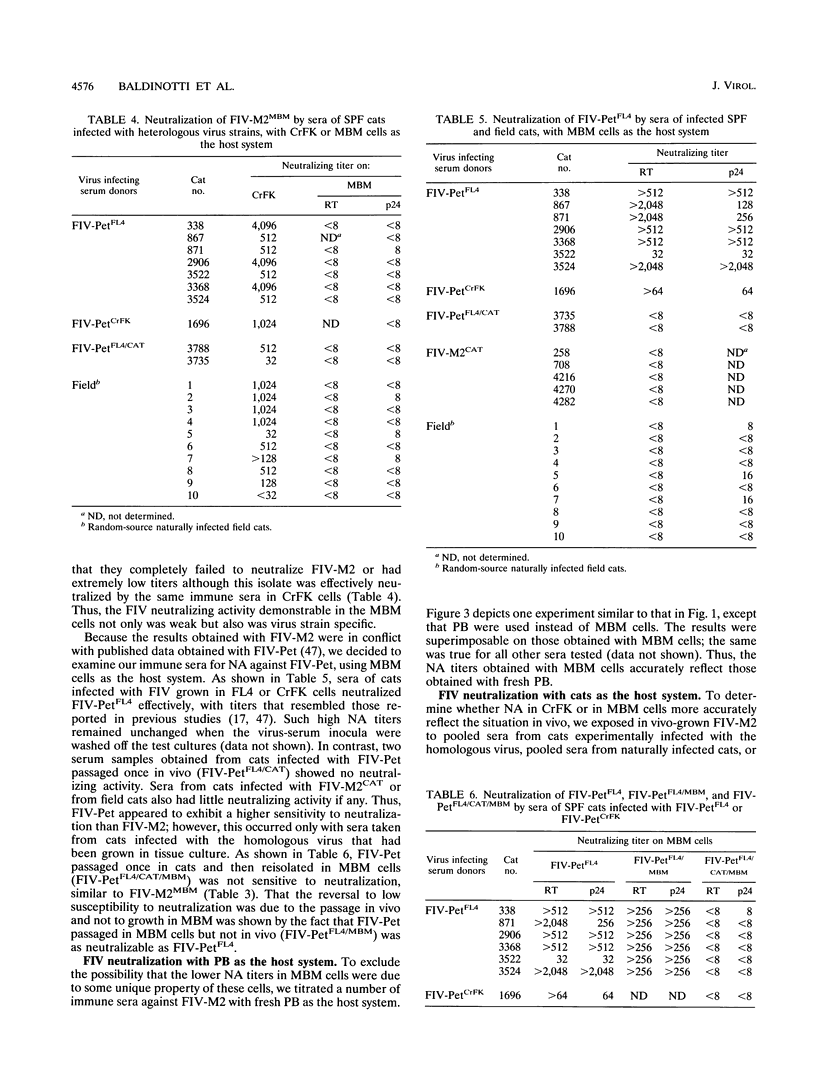
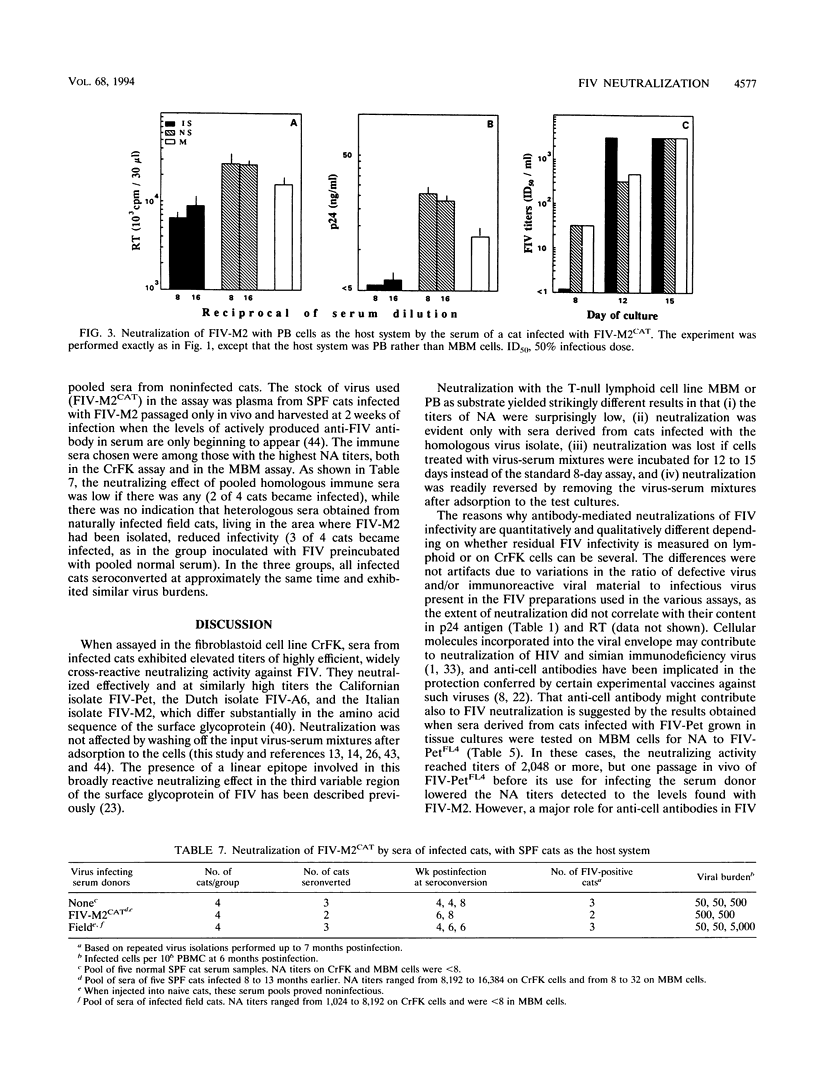
Abstract
Sera from feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV)-infected cats exhibited extremely low levels of neutralizing antibodies against virus passaged a few times in vitro (low passage), when residual infectivity was assayed in the CD3+ CD4- CD8- MBM lymphoid cell line or mitogen-activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. By sharp contrast, elevated titers of highly efficient neutralizing activity against FIV were measured, by use of high-passage virus, in assays on either the fibroblastoid CrFK or MBM cell line. However, high-passage virus behaved the same as low-passage virus after one in vivo passage in a specific-pathogen-free cat and reisolation. Subneutralizing concentrations of infected cat sera enhanced the production of low-passage virus by MBM cells, an effect not seen with high-passage virus in CrFK cells. These qualitative and quantitative discrepancies could not be attributed to differences in the amount of immunoreactive viral material, to the amount of infectious virus present in the viral stocks, or to the presence of anti-cell antibodies. The observed effects were most likely due to the different passage history of the viral preparations used. The observation that neutralizing antibodies detected with high-passage virus were broadly cross-reactive in assays with CrFK cells but isolate specific in MBM cells suggests also that the cell substrate can influence the result of FIV neutralization assays. This possibility could not be tested directly because FIV adapted to grow in CrFK cells had little infectivity for lymphoid cells and vice versa. In vitro exposure to infected cat sera had little or no effect on the ability of in vivo-passaged FIV to infect cats. These data reveal no obvious relationship between titers against high-passage virus and ability to block infectivity of FIV in cats and suggest caution in the use of such assays to measure vaccine efficacy. In conclusion, by contrast with what has been previously reported for the use of CrFK cells and high-passage virus, both natural and experimental infections of cats with FIV generate poor neutralizing antibody responses with regard to in vivo protection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur L. O., Bess J. W., Jr, Sowder R. C., 2nd, Benveniste R. E., Mann D. L., Chermann J. C., Henderson L. E. Cellular proteins bound to immunodeficiency viruses: implications for pathogenesis and vaccines. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1935–1938. doi: 10.1126/science.1470916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandecchi P., Matteucci D., Baldinotti F., Guidi G., Abramo F., Tozzini F., Bendinelli M. Prevalence of feline immunodeficiency virus and other retroviral infections in sick cats in Italy. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Mar;31(3-4):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(92)90020-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. W., Gregory T. J., Riddle L., Nakamura G. R., Champe M. A., Porter J. P., Wurm F. M., Hershberg R. D., Cobb E. K., Eichberg J. W. Protection of chimpanzees from infection by HIV-1 after vaccination with recombinant glycoprotein gp120 but not gp160. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):622–625. doi: 10.1038/345622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. P., Desrosiers R. C. A caution on the use of SIV/HIV gag antigen detection systems in neutralization assays. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Jun;8(6):1189–1192. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Can Soviet science be rescued? Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):339–340. doi: 10.1038/354339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson J. R., McGraw T. P., Keddie E., Yee J. L., Rosenthal A., Langlois A. J., Dickover R., Donovan R., Luciw P. A., Jennings M. B. Vaccine protection of rhesus macaques against simian immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Nov;6(11):1239–1246. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K. Development of a sensitive quantitative focal assay for human immunodeficiency virus infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3779–3788. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3779-3788.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. Jitters jeopardize AIDS vaccine trials. Science. 1993 Nov 12;262(5136):980–981. doi: 10.1126/science.8235635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranage M. P., Ashworth L. A., Greenaway P. J., Murphey-Corb M., Desrosiers R. C. AIDS vaccine developments. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):685–686. doi: 10.1038/355685a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Letvin N. L., Sehgal P. K., Hunsmann G., Schmidt D. K., King N. W., Desrosiers R. C. Long-term persistent infection of macaque monkeys with the simian immunodeficiency virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Dec;68(Pt 12):3183–3189. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-12-3183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Wyand M. S., Kodama T., Ringler D. J., Arthur L. O., Sehgal P. K., Letvin N. L., King N. W., Daniel M. D. Vaccine protection against simian immunodeficiency virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6353–6357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. Neutralization of animal viruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1993;183:1–149. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77849-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Nara P. L., Schleif W. A., Lewis J. A., Davide J. P., Lee D. R., Kessler J., Conley S., Matsushita S., Putney S. D. Antibody-mediated in vitro neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 abolishes infectivity for chimpanzees. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3674–3678. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3674-3678.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevereiro M., Roneker C., Laufs A., Tavares L., de Noronha F. Characterization of two monoclonal antibodies against feline immunodeficiency virus gag gene products and their application in an assay to evaluate neutralizing antibody activity. J Gen Virol. 1991 Mar;72(Pt 3):617–622. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-3-617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevereiro M., Roneker C., de Noronha F. Enhanced neutralization of feline immunodeficiency virus by complement viral lysis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Apr;36(3):191–206. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(93)90019-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M., Kieny M. P., Pinter A., Barre-Sinoussi F., Nara P., Kolbe H., Kusumi K., Chaput A., Reinhart T., Muchmore E. Immunization of chimpanzees confers protection against challenge with human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):542–546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Sarngadharan M. G., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T., Rota T. R., Kennedy R. C., Chanh T. C., Sato V. L. Human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing antibodies recognize several conserved domains on the envelope glycoproteins. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2024–2028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2024-2028.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohdatsu T., Pu R., Torres B. A., Trujillo S., Gardner M. B., Yamamoto J. K. Passive antibody protection of cats against feline immunodeficiency virus infection. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2344–2348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2344-2348.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homsy J., Meyer M., Levy J. A. Serum enhancement of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection correlates with disease in HIV-infected individuals. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1437–1440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1437-1440.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosie M. J., Osborne R., Reid G., Neil J. C., Jarrett O. Enhancement after feline immunodeficiency virus vaccination. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Dec;35(1-2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(93)90149-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosie M. J., Willett B. J., Dunsford T. H., Jarrett O., Neil J. C. A monoclonal antibody which blocks infection with feline immunodeficiency virus identifies a possible non-CD4 receptor. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1667–1671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1667-1671.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler H., Kodama T., Ringler D., Marthas M., Pedersen N., Lackner A., Regier D., Sehgal P., Daniel M., King N. Induction of AIDS in rhesus monkeys by molecularly cloned simian immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1109–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.2160735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Grand R., Vaslin B., Vogt G., Roques P., Humbert M., Dormont D. AIDS vaccine developments. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):684–684. doi: 10.1038/355684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi S., Garzelli C., La Rosa C., Zaccaro L., Specter S., Malvaldi G., Tozzini F., Esposito F., Bendinelli M. Identification of a linear neutralization site within the third variable region of the feline immunodeficiency virus envelope. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4742–4749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4742-4749.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi S., Poli A., Massi C., Abramo F., Zaccaro L., Bazzichi A., Malvaldi G., Bendinelli M., Garzelli C. Detection of feline immunodeficiency virus p24 antigen and p24-specific antibodies by monoclonal antibody-based assays. J Virol Methods. 1994 Mar;46(3):287–301. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(94)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüke W., Voss G., Stahl-Hennig C., Coulibaly C., Putkonen P., Petry H., Hunsmann G. Protection of cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis) against infection with the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 strain ben (HIV-2ben) by immunization with the virion-derived envelope glycoprotein gp130. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 May;9(5):387–394. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteucci D., Baldinotti F., Mazzetti P., Pistello M., Bandecchi P., Ghilarducci R., Poli A., Tozzini F., Bendinelli M. Detection of feline immunodeficiency virus in saliva and plasma by cultivation and polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Mar;31(3):494–501. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.3.494-501.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphey-Corb M., Martin L. N., Davison-Fairburn B., Montelaro R. C., Miller M., West M., Ohkawa S., Baskin G. B., Zhang J. Y., Putney S. D. A formalin-inactivated whole SIV vaccine confers protection in macaques. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1293–1297. doi: 10.1126/science.2555923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Garrity R. R., Goudsmit J. Neutralization of HIV-1: a paradox of humoral proportions. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2437–2455. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.1712328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orentas R. J., Hildreth J. E. Association of host cell surface adhesion receptors and other membrane proteins with HIV and SIV. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Nov;9(11):1157–1165. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancino G., Chappey C., Saurin W., Sonigo P. B epitopes and selection pressures in feline immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoproteins. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):664–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.664-672.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Horowitz B., Baker L., Shulman R. W., Ralph H., Valinsky J., Cundell A., Brotman B., Boehle W., Rey F. Failure of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) immune globulin to protect chimpanzees against experimental challenge with HIV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6944–6948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Reesink H., Pascual D., Horowitz B., Hewlett I., Murthy K. K., Cobb K. E., Eichberg J. W. Prevention of HIV infection by passive immunization with HIV immunoglobulin. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Dec;7(12):971–973. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkonen P., Thorstensson R., Ghavamzadeh L., Albert J., Hild K., Biberfeld G., Norrby E. Prevention of HIV-2 and SIVsm infection by passive immunization in cynomolgus monkeys. Nature. 1991 Aug 1;352(6334):436–438. doi: 10.1038/352436a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby M. A., Holmes E. C., Pistello M., Mackay A., Brown A. J., Neil J. C. Evolution of structural proteins of feline immunodeficiency virus: molecular epidemiology and evidence of selection for change. J Gen Virol. 1993 Mar;74(Pt 3):425–436. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-3-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebelink K. H., Rimmelzwaan G. F., Bosch M. L., Meloen R. H., Osterhaus A. D. A single amino acid substitution in hypervariable region 5 of the envelope protein of feline immunodeficiency virus allows escape from virus neutralization. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2202–2208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2202-2208.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozzini F., Matteucci D., Bandecchi P., Baldinotti F., Poli A., Pistello M., Siebelink K. H., Ceccherini-Nelli L., Bendinelli M. Simple in vitro methods for titrating feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) and FIV neutralizing antibodies. J Virol Methods. 1992 Jun;37(3):241–252. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(92)90026-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozzini F., Matteucci D., Bandecchi P., Baldinotti F., Siebelink K., Osterhaus A., Bendinelli M. Neutralizing antibodies in cats infected with feline immunodeficiency virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jun;31(6):1626–1629. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.6.1626-1629.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vujcic L., Katzenstein D., Martin M., Quinnan G. International collaborative study to compare assays for antibodies that neutralize human immunodeficiency virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Jul;6(7):847–853. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A. How does HIV cause AIDS? Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1273–1279. doi: 10.1126/science.8493571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto J. K., Okuda T., Ackley C. D., Louie H., Pembroke E., Zochlinski H., Munn R. J., Gardner M. B. Experimental vaccine protection against feline immunodeficiency virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Nov;7(11):911–922. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



