Abstract
An anti-gp120 monoclonal antibody (MAb), C108G (gamma 1, kappa), was isolated from a chimpanzee that had been infected with strain IIIB of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1IIIB) and subsequently immunized with the recombinant glycoprotein rgp160MN. This MAb is specific for the IIIB strain of HIV-1 and related clones and exhibits very potent neutralization of these viruses; e.g., 100% neutralization of approximately 8 x 10(3) infectious units of HXB2 was achieved with 125 ng of C108G per ml. Commensurate with this potent neutralizing activity, the apparent affinity of C108G for rgp160LAI was very high, i.e., approximately 3 x 10(10) liters/mol. The C108G epitope was not destroyed by reduction of gp120 disulfide bonds but was profoundly disrupted by removal of N-linked sugars from gp120. Despite the importance of a glycan(s) in forming the C108G epitope, specific binding of C108G to synthetic peptides overlapping in amino acids 162 to 169 of the V2 region was detected, albeit with an affinity approximately 2,000-fold lower than that of C108G's binding to glycosylated envelope protein. This epitope mapping correlated with results of competition assays using MAbs of known epitope specificities. To our knowledge, this is the first description of an anti-V2 MAb raised in response to HIV-1 infection. Its potent neutralizing activity and epitope specificity indicate that the V2 domain of gp120 may be an effective target of the protective immune response and, therefore, potentially an important component of HIV vaccines.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbas C. F., 3rd, Björling E., Chiodi F., Dunlop N., Cababa D., Jones T. M., Zebedee S. L., Persson M. A., Nara P. L., Norrby E. Recombinant human Fab fragments neutralize human type 1 immunodeficiency virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9339–9343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benichou S., Legrand R., Nakagawa N., Faure T., Traincard F., Vogt G., Dormont D., Tiollais P., Kieny M. P., Madaule P. Identification of a neutralizing domain in the external envelope glycoprotein of simian immunodeficiency virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Jun;8(6):1165–1170. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Perryman S. Macrophage-tropic human immunodeficiency virus isolates from different patients exhibit unusual V3 envelope sequence homogeneity in comparison with T-cell-tropic isolates: definition of critical amino acids involved in cell tropism. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6547–6554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6547-6554.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich P. H., Moustafa Z. A., Harfeldt K. E., Isaacson C., Ostberg L. Potential of primate monoclonal antibodies to substitute for human antibodies: nucleotide sequence of chimpanzee Fab fragments. Hum Antibodies Hybridomas. 1990;1(1):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich P. H., Moustafa Z. A., Justice J. C., Harfeldt K. E., Gadi I. K., Sciorra L. J., Uhl F. P., Isaacson C., Ostberg L. Human and primate monoclonal antibodies for in vivo therapy. Clin Chem. 1988 Sep;34(9):1681–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Risser R. Identification of conserved residues in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 principal neutralizing determinant that are involved in fusion. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Oct;7(10):807–811. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann U., Bause E., Legler G., Ploegh H. Novel mannosidase inhibitor blocking conversion of high mannose to complex oligosaccharides. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):755–758. doi: 10.1038/307755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. S., Sun C. R., Gordon W. L., Liou R. S., Chang T. W., Sun W. N., Daar E. S., Ho D. D. Identification and characterization of a neutralization site within the second variable region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):848–856. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.848-856.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M., Kieny M. P., Pinter A., Barre-Sinoussi F., Nara P., Kolbe H., Kusumi K., Chaput A., Reinhart T., Muchmore E. Immunization of chimpanzees confers protection against challenge with human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):542–546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorny M. K., Xu J. Y., Karwowska S., Buchbinder A., Zolla-Pazner S. Repertoire of neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies specific for the V3 domain of HIV-1 gp120. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):635–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaila R. J., Fuller B. A., Rennert P. D., Nelson M. B., Hammarskjöld M. L., Potts B., Murray M., Putney S. D., Gray G. Mutations in the principal neutralization determinant of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affect syncytium formation, virus infectivity, growth kinetics, and neutralization. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1875–1883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1875-1883.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groenink M., Fouchier R. A., Broersen S., Baker C. H., Koot M., van't Wout A. B., Huisman H. G., Miedema F., Tersmette M., Schuitemaker H. Relation of phenotype evolution of HIV-1 to envelope V2 configuration. Science. 1993 Jun 4;260(5113):1513–1516. doi: 10.1126/science.8502996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. E., Nielsen C., Arendrup M., Olofsson S., Mathiesen L., Nielsen J. O., Clausen H. Broadly neutralizing antibodies targeted to mucin-type carbohydrate epitopes of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6461–6467. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6461-6467.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Fung M. S., Cao Y. Z., Li X. L., Sun C., Chang T. W., Sun N. C. Another discontinuous epitope on glycoprotein gp120 that is important in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization is identified by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8949–8952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. S., Boyle T. J., Lyerly H. K., Cullen B. R. Identification of the envelope V3 loop as the primary determinant of cell tropism in HIV-1. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):71–74. doi: 10.1126/science.1905842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanoff L. A., Looney D. J., McDanal C., Morris J. F., Wong-Staal F., Langlois A. J., Petteway S. R., Jr, Matthews T. J. Alteration of HIV-1 infectivity and neutralization by a single amino acid replacement in the V3 loop domain. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Jul;7(7):595–603. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayman S. C., Wu Z., Revesz K., Chen H., Kopelman R., Pinter A. Presentation of native epitopes in the V1/V2 and V3 regions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 by fusion glycoproteins containing isolated gp120 domains. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):400–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.400-410.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent K. A., Rud E., Corcoran T., Powell C., Thiriart C., Collignon C., Stott E. J. Identification of two neutralizing and 8 non-neutralizing epitopes on simian immunodeficiency virus envelope using monoclonal antibodies. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Jun;8(6):1147–1151. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Rivière Y., Dott K., Schmitt D., Girard M., Montagnier L., Lecocq J. Improved antigenicity of the HIV env protein by cleavage site removal. Protein Eng. 1988 Sep;2(3):219–225. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koito A., Harrowe G., Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C. Functional role of the V1/V2 region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 in infection of primary macrophages and soluble CD4 neutralization. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2253–2259. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2253-2259.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita S., Robert-Guroff M., Rusche J., Koito A., Hattori T., Hoshino H., Javaherian K., Takatsuki K., Putney S. Characterization of a human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing monoclonal antibody and mapping of the neutralizing epitope. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2107–2114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2107-2114.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeating J. A., Moore J. P., Ferguson M., Marsden H. S., Graham S., Almond J. W., Evans D. J., Weiss R. A. Monoclonal antibodies to the C4 region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120: use in topological analysis of a CD4 binding site. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Apr;8(4):451–459. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeating J. A., Shotton C., Cordell J., Graham S., Balfe P., Sullivan N., Charles M., Page M., Bolmstedt A., Olofsson S. Characterization of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to linear and conformation-dependent epitopes within the first and second variable domains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4932–4944. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4932-4944.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Nara P. L. The role of the V3 loop of gp120 in HIV infection. AIDS. 1991;5 (Suppl 2):S21–S33. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199101001-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Sattentau Q. J., Yoshiyama H., Thali M., Charles M., Sullivan N., Poon S. W., Fung M. S., Traincard F., Pinkus M. Probing the structure of the V2 domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 surface glycoprotein gp120 with a panel of eight monoclonal antibodies: human immune response to the V1 and V2 domains. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6136–6151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6136-6151.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Thali M., Jameson B. A., Vignaux F., Lewis G. K., Poon S. W., Charles M., Fung M. S., Sun B., Durda P. J. Immunochemical analysis of the gp120 surface glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: probing the structure of the C4 and V4 domains and the interaction of the C4 domain with the V3 loop. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4785–4796. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4785-4796.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page K. A., Stearns S. M., Littman D. R. Analysis of mutations in the V3 domain of gp160 that affect fusion and infectivity. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):524–533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.524-533.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
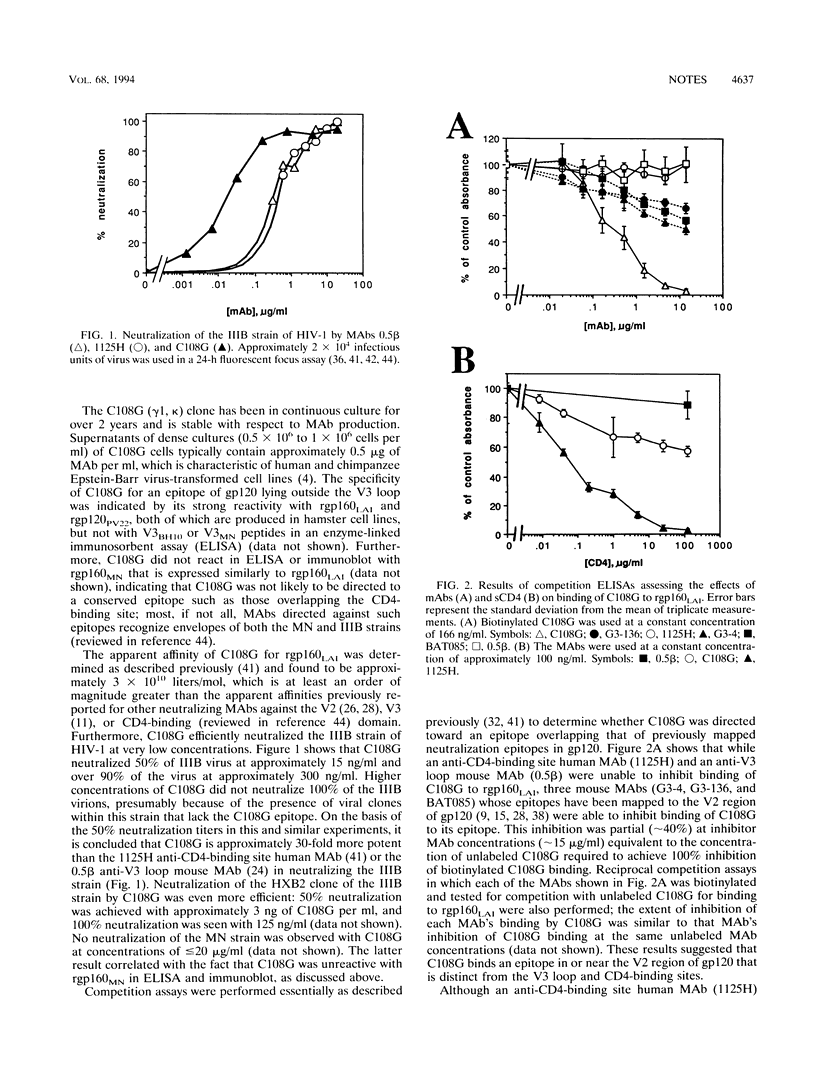
- Pinter A., Honnen W. J., Racho M. E., Tilley S. A. A potent, neutralizing human monoclonal antibody against a unique epitope overlapping the CD4-binding site of HIV-1 gp120 that is broadly conserved across North American and African virus isolates. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Oct;9(10):985–996. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Honnen W. J., Tilley S. A., Bona C., Zaghouani H., Gorny M. K., Zolla-Pazner S. Oligomeric structure of gp41, the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2674–2679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2674-2679.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakoyama Y., Hong K. J., Byun S. M., Hisajima H., Ueda S., Yaoita Y., Hayashida H., Miyata T., Honjo T. Nucleotide sequences of immunoglobulin epsilon genes of chimpanzee and orangutan: DNA molecular clock and hominoid evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1080–1084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shang F., Huang H., Revesz K., Chen H. C., Herz R., Pinter A. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the human immunodeficiency virus matrix protein, p17gag: identification of epitopes exposed at the surfaces of infected cells. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4798–4804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4798-4804.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C. Small amino acid changes in the V3 hypervariable region of gp120 can affect the T-cell-line and macrophage tropism of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9434–9438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
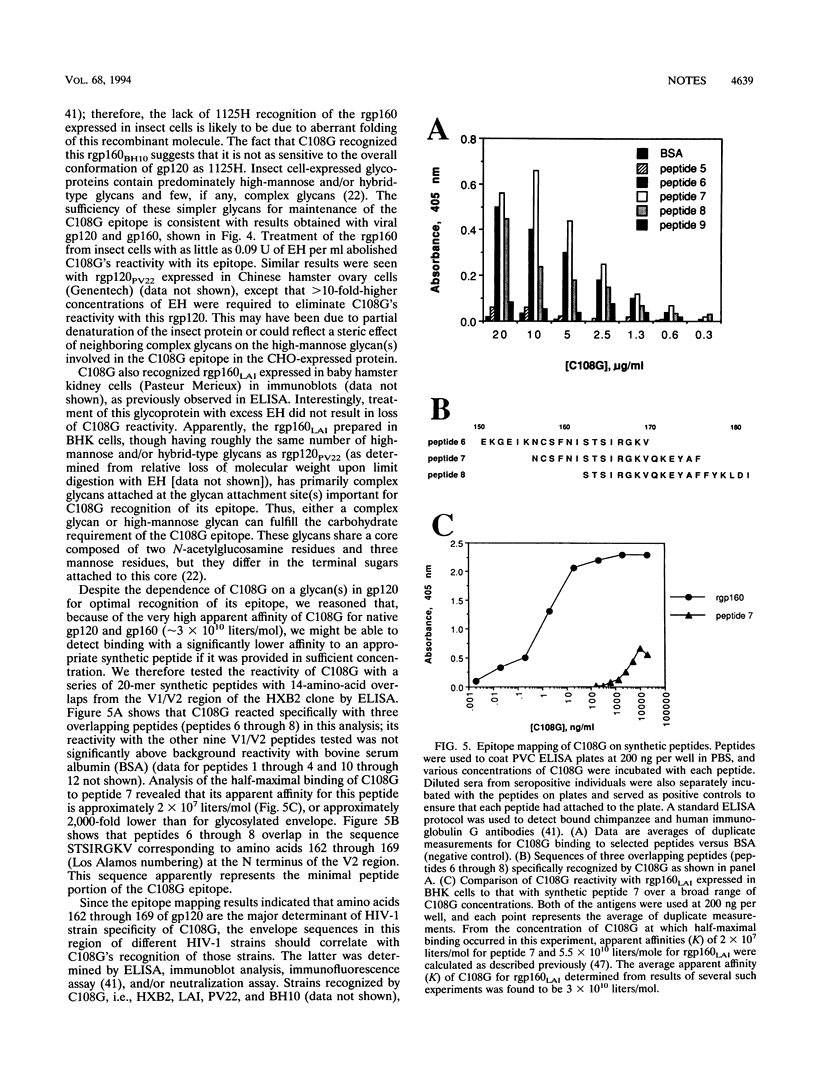
- Sullivan N., Thali M., Furman C., Ho D. D., Sodroski J. Effect of amino acid changes in the V1/V2 region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein on subunit association, syncytium formation, and recognition by a neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3674–3679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3674-3679.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptomyces griseus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thali M., Furman C., Ho D. D., Robinson J., Tilley S., Pinter A., Sodroski J. Discontinuous, conserved neutralization epitopes overlapping the CD4-binding region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5635–5641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5635-5641.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley S. A., Honnen W. J., Racho M. E., Chou T. C., Pinter A. Synergistic neutralization of HIV-1 by human monoclonal antibodies against the V3 loop and the CD4-binding site of gp120. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Apr;8(4):461–467. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley S. A., Honnen W. J., Racho M. E., Hilgartner M., Pinter A. A human monoclonal antibody against the CD4-binding site of HIV1 gp120 exhibits potent, broadly neutralizing activity. Res Virol. 1991 Jul-Aug;142(4):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(91)90010-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis B. M., Dykers T. I., Hewgill D., Ledbetter J., Tsu T. T., Hu S. L., Lewis J. B. Functional roles of the V3 hypervariable region of HIV-1 gp160 in the processing of gp160 and in the formation of syncytia in CD4+ cells. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda S., Matsuda F., Honjo T. Multiple recombinational events in primate immunoglobulin epsilon and alpha genes suggest closer relationship of humans to chimpanzees than to gorillas. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(1):77–83. doi: 10.1007/BF02099732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt P., Gendelman H. E., Ratner L. Identification of a determinant within the human immunodeficiency virus 1 surface envelope glycoprotein critical for productive infection of primary monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3097–3101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt P., Trowbridge D. B., Epstein L. G., Blumberg B. M., Li Y., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Price R. W., Ratner L. Macrophage tropism determinants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vivo. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2577–2582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2577-2582.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]