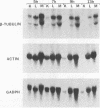
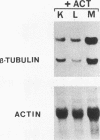
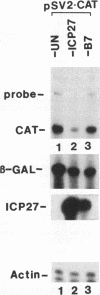
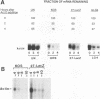
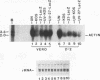
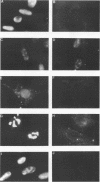
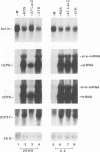
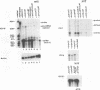
Abstract
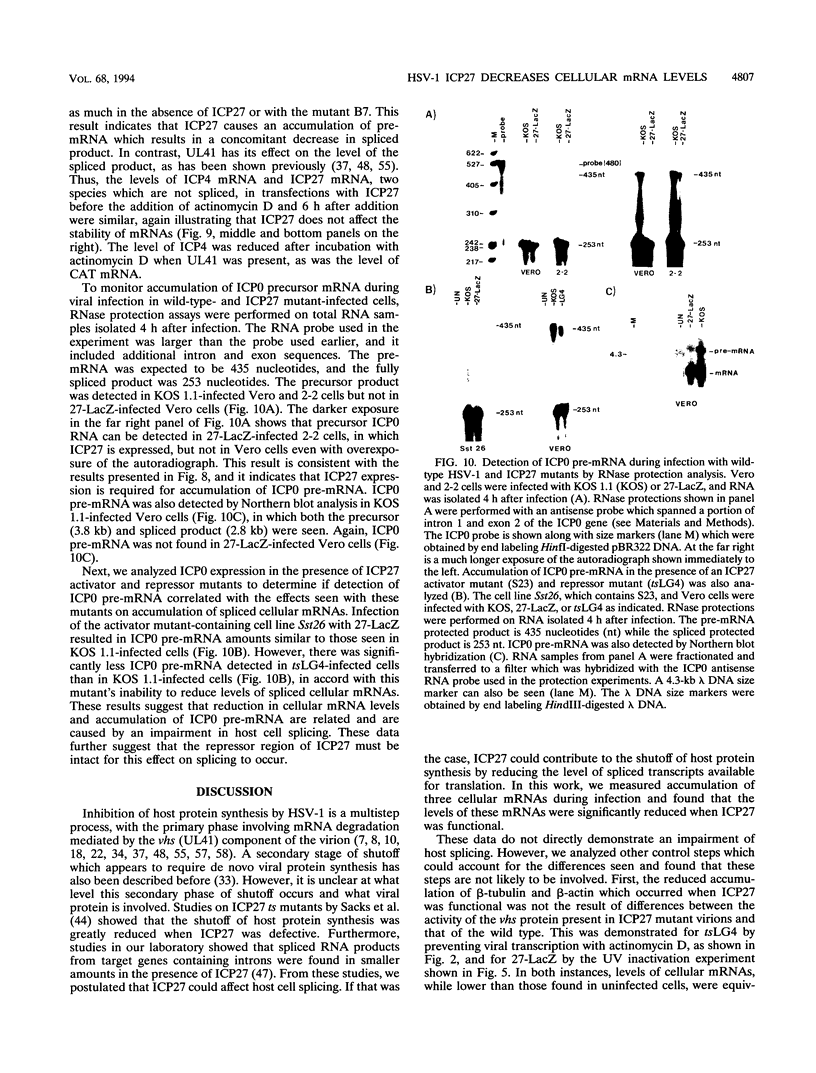
We have previously shown that the herpes simplex virus immediate-early regulatory protein ICP27 acts posttranscriptionally to affect mRNA processing (R. M. Sandri-Goldin and G. E. Mendoza, Genes Dev. 6:848-863, 1992). Specifically, in the presence of ICP27, spliced target mRNAs were decreased 5- to 10-fold in transfections with target genes containing a 5' or 3' intron. Here, we have investigated the effect of ICP27 during herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) infection on accumulation of spliced cellular mRNAs. ICP27 viral mutants have been shown to be defective in host shutoff (W. R. Sacks, C. C. Greene, D. P. Aschman, and P. A. Schaffer, J. Virol. 55:796-805, 1985). Therefore, we examined whether ICP27 could contribute to this complex process by decreasing cellular mRNA levels through its effects on host cell splicing. It was found that in infections with viral mutants defective in ICP27, the accumulated levels of three spliced host mRNAs were higher than those seen with wild-type HSV-1. The differences occurred posttranscriptionally as shown by nuclear runoff transcription assays. The stabilities of the spliced products during infection with wild-type or ICP27 mutant viruses were similar, and unspliced precursor mRNA for a viral spliced gene was detected in infections with wild-type HSV-1 but not in infections in which ICP27 was not expressed. These results suggest that the reduction in cellular mRNA levels and the accumulation of pre-mRNA are related and may be caused by an impairment in host cell splicing. These data further show that ICP27 is required for these effects to occur.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Block T., Jordan R. Herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha gene containing plasmids can inhibit expression regulated from an alpha promoter in CV-1 but not HeLa cells. Virus Res. 1988 Nov;11(4):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman C. J., Harris J. D., Hardwicke M. A., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Collins M. K., Latchman D. S. Promoter-independent activation of heterologous virus gene expression by the herpes simplex virus immediate-early protein ICP27. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):573–578. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90023-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Promoter sequence and cell type can dramatically affect the efficiency of transcriptional activation induced by herpes simplex virus type 1 and its immediate-early gene products Vmw175 and Vmw110. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Clark J. Early and delayed shut-off of host protein synthesis in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jul;61(Pt 50):121–125. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Everett R. D. Inactivation of the shutoff gene (UL41) of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Gen Virol. 1990 Dec;71(Pt 12):2961–2967. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-12-2961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., McMenamin M. M. Early virion-associated suppression of cellular protein synthesis by herpes simplex virus is accompanied by inactivation of mRNA. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jul;65(Pt 7):1225–1228. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-7-1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Walker M. J. Suppression of the synthesis of cellular macromolecules by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Oct;41(1):37–51. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao M., Knipe D. M. Potential role for herpes simplex virus ICP8 DNA replication protein in stimulation of late gene expression. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2666–2675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2666-2675.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Cloning of herpes simplex virus type 1 sequences representing the whole genome. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.50-58.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez I. L., Gorski J. L., Campen T. J., Dorney D. J., Erickson J. M., Sylvester J. E., Schmickel R. D. Variation among human 28S ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7666–7670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwicke M. A., Vaughan P. J., Sekulovich R. E., O'Conner R., Sandri-Goldin R. M. The regions important for the activator and repressor functions of herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27 map to the C-terminal half of the molecule. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4590–4602. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4590-4602.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Sinden R. R., Sadler J. R. Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 induce shutoff of host protein synthesis by different mechanisms in Friend erythroleukemia cells. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):241–250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.241-250.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., Everett R. D. DNA replication is required for abundant expression of a plasmid-borne late US11 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3609–3625. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr Differentiation, not determination, regulates muscle gene activation: transfection of troponin I genes into multipotential and muscle lineages of 10T1/2 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2423–2432. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikorian C. R., Read G. S. In vitro mRNA degradation system to study the virion host shutoff function of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):112–122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.112-122.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong A. D., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus-infected cells contain a function(s) that destabilizes both host and viral mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1926–1930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong A. D., Kruper J. A., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus virion host shutoff function. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):912–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.912-921.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Lewis S. A., Wilde C. D., Cowan N. J. Evolutionary history of a multigene family: an expressed human beta-tubulin gene and three processed pseudogenes. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90429-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: the alpha 27 gene promoter-thymidine kinase chimera is positively regulated in converted L cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1015-1023.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. E., Barghusen S. C., Leser G. P., Spear P. G. Redistribution of nuclear ribonucleoprotein antigens during herpes simplex virus infection. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2069–2082. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy A. M., McMahan L., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 deletion mutants exhibit altered patterns of transcription and are DNA deficient. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):18–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.18-27.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Phelan A., Loney C., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Clements J. B. Herpes simplex virus IE63 acts at the posttranscriptional level to stimulate viral mRNA 3' processing. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):6939–6945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.6939-6945.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan L., Schaffer P. A. The repressing and enhancing functions of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP27 map to C-terminal regions and are required to modulate viral gene expression very early in infection. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3471–3485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3471-3485.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Pitha P. M., Hayward G. S. Herpes simplex virus infection selectively stimulates accumulation of beta interferon reporter gene mRNA by a posttranscriptional mechanism. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3811–3822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3811-3822.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Degradation of cellular mRNA during infection by herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2370–2374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Requirement of protein synthesis for the degradation of host mRNA in Friend erythroleukemia cells infected wtih herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):619–627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.619-627.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroskar A. A., Read G. S. A mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1 exhibits increased stability of immediate-early (alpha) mRNAs. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):604–606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.604-606.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Rixon F. J., Everett R. D., Frame M. C., McGeoch D. J. Characterization of the IE110 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2365–2380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan A., Carmo-Fonseca M., McLaughlan J., Lamond A. I., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early gene product, IE63, regulates small nuclear ribonucleoprotein distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9056–9060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus mutants defective in the virion-associated shutoff of host polypeptide synthesis and exhibiting abnormal synthesis of alpha (immediate early) viral polypeptides. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):498–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.498-512.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Karr B. M., Knight K. Isolation of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant with a deletion in the virion host shutoff gene and identification of multiple forms of the vhs (UL41) polypeptide. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7149–7160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7149-7160.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Knipe D. M. Gene-specific transactivation by herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3814–3823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3814-3823.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Knipe D. M. Genetic evidence for two distinct transactivation functions of the herpes simplex virus alpha protein ICP27. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1704–1715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1704-1715.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Lam V., Knipe D. M. The acidic amino-terminal region of herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27 is required for an essential lytic function. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1778–1787. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1778-1787.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Su L. S., Knipe D. M. Herpes simplex virus alpha protein ICP27 possesses separable positive and negative regulatory activities. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3399–3407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3399-3407.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Greene C. C., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.796-805.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Holland L. E., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Expression of herpes simplex virus beta and gamma genes integrated in mammalian cells and their induction by an alpha gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2028–2044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Method for induction of mutations in physically defined regions of the herpes simplex virus genome. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):41–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.41-49.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Mendoza G. E. A herpesvirus regulatory protein appears to act post-transcriptionally by affecting mRNA processing. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):848–863. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schek N., Bachenheimer S. L. Degradation of cellular mRNAs induced by a virion-associated factor during herpes simplex virus infection of Vero cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):601–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.601-610.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Falke D., Weise K., Bachmann M., Carmo-Fonseca M., Zaubitzer T., Müller W. E. Change of processing and nucleocytoplasmic transport of mRNA in HSV-1-infected cells. Virus Res. 1989 May;13(1):61–78. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekulovich R. E., Leary K., Sandri-Goldin R. M. The herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27 can act as a trans-repressor or a trans-activator in combination with ICP4 and ICP0. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4510–4522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4510-4522.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. L., Hardwicke M. A., Sandri-Goldin R. M. Evidence that the herpes simplex virus immediate early protein ICP27 acts post-transcriptionally during infection to regulate gene expression. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):74–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90062-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. L., Sandri-Goldin R. M. Evidence that transcriptional control is the major mechanism of regulation for the glycoprotein D gene in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1474–1477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1474-1477.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. L., Sekulovich R. E., Hardwicke M. A., Sandri-Goldin R. M. Mutations in the activation region of herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP27 can be trans dominant. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3656–3666. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3656-3666.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom T., Frenkel N. Effects of herpes simplex virus on mRNA stability. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2198–2207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2198-2207.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L., Knipe D. M. Herpes simplex virus alpha protein ICP27 can inhibit or augment viral gene transactivation. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):496–504. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90441-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sydiskis R. J., Roizman B. Polysomes and protein synthesis in cells infected with a DNA virus. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):76–78. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls establish the cascade of herpes simplex virus protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):819–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao F., Courtney R. J. Association of ICP0 but not ICP27 with purified virions of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2709–2716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2709-2716.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]