Abstract
Simian and human foamy viruses (HFV and SFV), genetically related members of the spumavirus genus of retroviruses, have complex genome structures which encode the gag, pol, and env genes for virion proteins as well as additional open reading frames. One of these open reading frames is a viral transactivator, encoded by genes designated taf for SFV and bel-1 for HFV, which augments transcription directed by the long terminal repeat (LTR) through cis-acting targets in the U3 domain of the LTR. Recently, an internal transcriptional promoter has been identified in sequences within the 3' end of the HFV env gene (M. Lochelt, W. Muranyi, and R. M. Flugel, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 90:7317-7321, 1993). We have demonstrated by using transient expression assays in several tissue culture cell lines and by analyzing viral transcripts in infected cells that SFV-1 from a rhesus macaque and SFV-3 from an African green monkey also encode an internal promoter in the env gene. Transcription directed by the internal promoters of SFV-1 and SFV-3 is activated by the taf-1 and taf-3 gene products, respectively, in several cell types. The importance of a TATA box for the SFV-1 internal promoter was established by site-specific mutagenesis, and the 5' ends of transcripts initiating in the internal promoter have been determined. cis-acting sequences in the SFV-1 env gene required for the response to taf-1 are contained within a 121-bp element located 5' to the TATA box in the internal promoter. This taf-1-responsive element in the internal promoter functions in a position- and orientation-independent fashion in a heterologous promoter and thus has the properties of an enhancer which depends on taf-1 activity. Alignments reveal that the SFV-1 internal promoter and the SFV-1 LTR have little sequence relatedness. Cross-transactivation studies show that the transactivators of SFV-1 and HFV function on the internal promoter and LTR of the homologous virus but not on the heterologous virus. In summary, the genomes of simian and human foamy viruses direct viral transcription through both the promoter in the LTR and an internal promoter within the env gene, and each promoter contains unique enhancer-like elements regulated by the viral transactivator.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguzzi A., Bothe K., Wagner E. F., Rethwilm A., Horak I. Human foamy virus: an underestimated neuropathogen? Brain Pathol. 1992 Jan;2(1):61–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L. Enhancers: mechanisms of action and cell specificity. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:127–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. F., Pohajdak B., Talbot D. J., Shaw J., Paetkau V. Phorbol diester-inducible, cyclosporine-suppressible transcription from a novel promoter within the mouse mammary tumor virus env gene. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1373–1380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1373-1380.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlwein O., Rethwilm A. BEL-1 transactivator responsive sequences in the long terminal repeat of human foamy virus. Virology. 1993 Sep;196(1):256–268. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Kim P. S. Modular structure of transcription factors: implications for gene regulation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):717–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90378-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett E. D., He F., Bogerd H. P., Cullen B. R. Transcriptional trans activators of human and simian foamy viruses contain a small, highly conserved activation domain. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6824–6827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6824-6827.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. Roles of TFIID in transcriptional initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90027-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He F., Sun J. D., Garrett E. D., Cullen B. R. Functional organization of the Bel-1 trans activator of human foamy virus. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1896–1904. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1896-1904.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Gibbs C. J., Jr The foamy viruses. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Sep;39(3):169–185. doi: 10.1128/br.39.3.169-185.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A., Garrett E. D., Cullen B. R. The Bel-1 protein of human foamy virus activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gene expression via a novel DNA target site. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3946–3949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3946-3949.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A., Partin K. M., Löchelt M., Bannert H., Flügel R. M., Cullen B. R. Characterization of the transcriptional trans activator of human foamy retrovirus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2589–2594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2589-2594.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. J., Lee A. H., Sung Y. C. Multiple positive and negative cis-acting elements that mediate transactivation by bel1 in the long terminal repeat of human foamy virus. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2317–2326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2317-2326.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löchelt M., Aboud M., Flügel R. M. Increase in the basal transcriptional activity of the human foamy virus internal promoter by the homologous long terminal repeat promoter in cis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 11;21(18):4226–4230. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.18.4226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löchelt M., Flügel R. M., Aboud M. The human foamy virus internal promoter directs the expression of the functional Bel 1 transactivator and Bet protein early after infection. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):638–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.638-645.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löchelt M., Muranyi W., Flügel R. M. Human foamy virus genome possesses an internal, Bel-1-dependent and functional promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7317–7321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löchelt M., Zentgraf H., Flügel R. M. Construction of an infectious DNA clone of the full-length human spumaretrovirus genome and mutagenesis of the bel 1 gene. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90820-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Serfling E., ter Meulen V., Rethwilm A. Transcription factor AP-1 modulates the activity of the human foamy virus long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6353–6357. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6353-6357.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Luciw P. A. Replication and regulation of primate foamy viruses. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):475–482. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90417-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Pratt-Lowe E., Shaw K. E., Renshaw-Gegg L. W., Luciw P. A. cis-acting regulatory regions in the long terminal repeat of simian foamy virus type 1. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):251–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.251-257.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Renshaw-Gegg L. W., Stout M. W., Renne R., Herchenröeder O. Functional domains of the simian foamy virus type 1 transcriptional transactivator (Taf). J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4598–4604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4598-4604.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Shaw K. E., Pratt-Lowe E., Barry P. A., Luciw P. A. Identification of the simian foamy virus transcriptional transactivator gene (taf). J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2903–2909. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2903-2909.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Shaw K. E., Pratt-Lowe E., Barry P. A., Luciw P. A. Simian foamy virus type 1 is a retrovirus which encodes a transcriptional transactivator. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3598–3604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3598-3604.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
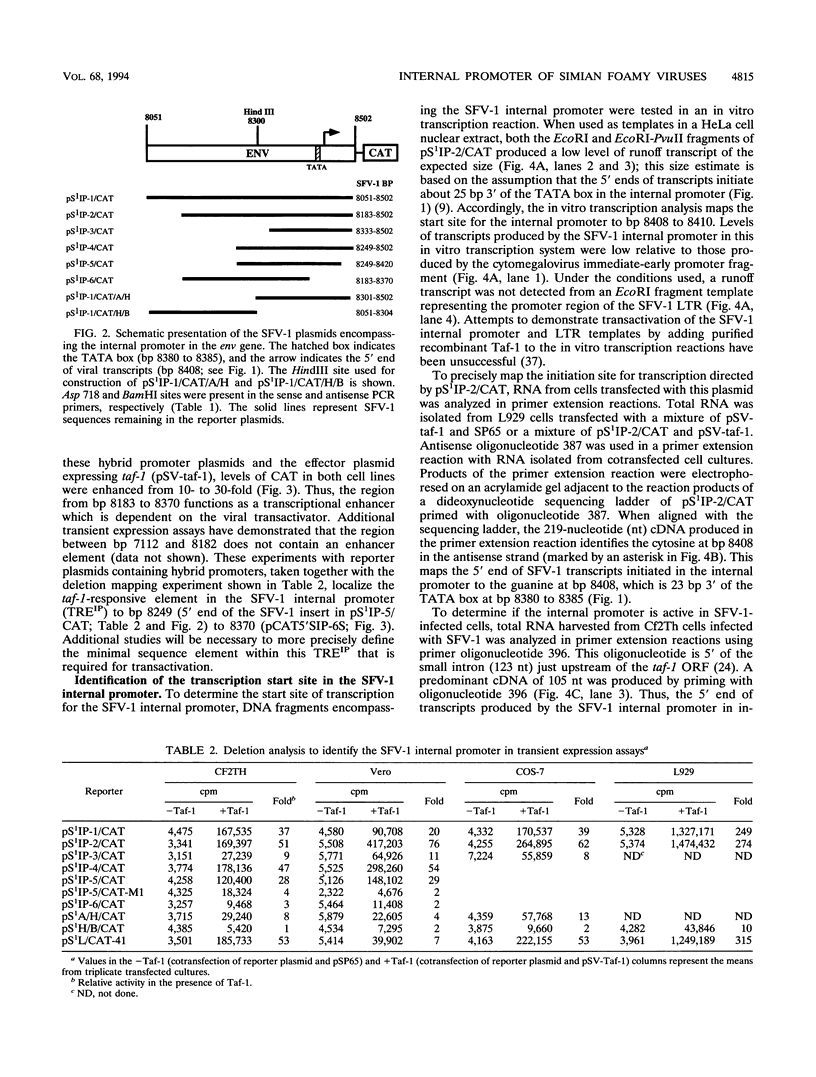
- Mergia A. Simian foamy virus type 1 contains a second promoter located at the 3' end of the env gene. Virology. 1994 Feb 15;199(1):219–222. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. L., Garner R., Paetkau V. An activation-dependent, T-lymphocyte-specific transcriptional activator in the mouse mammary tumor virus env gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3262–3272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muranyi W., Flügel R. M. Analysis of splicing patterns of human spumaretrovirus by polymerase chain reaction reveals complex RNA structures. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):727–735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.727-735.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K., Green P. P., 3rd, Fowlkes D. M. A rapid, sensitive, and inexpensive assay for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. DNA. 1987 Apr;6(2):173–178. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosaka T., Ariumi Y., Sakurai M., Takeuchi R., Hatanaka M. Novel internal promoter/enhancer of HTLV-I for Tax expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5124–5129. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renne R., Friedl E., Schweizer M., Fleps U., Turek R., Neumann-Haefelin D. Genomic organization and expression of simian foamy virus type 3 (SFV-3). Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):597–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90026-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renne R., Mergia A., Renshaw-Gegg L. W., Neumann-Haefelin D., Luciw P. A. Regulatory elements in the long terminal repeat (LTR) of simian foamy virus type 3 (SFV-3). Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):365–369. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Erlwein O., Baunach G., Maurer B., ter Meulen V. The transcriptional transactivator of human foamy virus maps to the bel 1 genomic region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):941–945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparger E. E., Shacklett B. L., Renshaw-Gegg L., Barry P. A., Pedersen N. C., Elder J. H., Luciw P. A. Regulation of gene expression directed by the long terminal repeat of the feline immunodeficiency virus. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh L. K., Theodorakis P. A., Chinnadurai G. Distinct cis-acting regions in U3 regulate trans-activation of the human spumaretrovirus long terminal repeat by the viral bel1 gene product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3661–3666. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh L. K., Yang C., Theodorakis P. A., Chinnadurai G. Functional dissection of the human spumaretrovirus transactivator identifies distinct classes of dominant-negative mutants. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):161–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.161-169.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A. Foamy retroviruses. A virus in search of a disease. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):497–498. doi: 10.1038/333497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]