Abstract
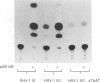
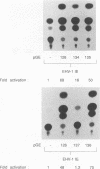
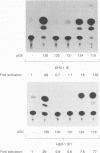
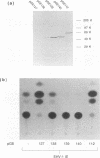
Gene 12 of equine herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1), the homolog of herpes simplex virus (HSV) VP16 (alpha TIF, Vmw65), was cloned into a eukaryotic expression vector by PCR and used in transactivation studies of both the EHV-1 and HSV-1 IE1 promoters. Results demonstrated that the product of gene 12 is a potent transactivator of immediate-early gene expression of both viruses, which requires sequences in the upstream HSV-1 promoter for activity. Mutational analysis of the gene 12 open reading frame indicated that removal of the C-terminal 7 amino acids, which contain a short region of homology with the extreme C terminus of VP16, inactivated the protein. Within this region, only a single methionine residue appeared to be essential for activity, implying that gene 12 may have a modular array of organization similar to that of VP16. However, fusion of the gene 12 C terminus to a truncated form of VP16, which contained the complex formation domain, did not restore activity to the HSV-1 protein. These data demonstrate that the EHV-1 immediate-early transactivator may not be functionally colinear with VP16, with transactivation requiring both the C terminus and another region(s) present within the N-terminal portion.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ace C. I., Dalrymple M. A., Ramsay F. H., Preston V. G., Preston C. M. Mutational analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 trans-inducing factor Vmw65. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2595–2605. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ace C. I., McKee T. A., Ryan J. M., Cameron J. M., Preston C. M. Construction and characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant unable to transinduce immediate-early gene expression. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2260–2269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2260-2269.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams S. E., Johnson I. D., Braddock M., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M., Edwards R. M. Synthesis of a gene for the HIV transactivator protein TAT by a novel single stranded approach involving in vivo gap repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4287–4298. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Faller D. V. A rapid micropreparation technique for extraction of DNA-binding proteins from limiting numbers of mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2499–2499. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousens D. J., Greaves R., Goding C. R., O'Hare P. The C-terminal 79 amino acids of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein, Vmw65, efficiently activate transcription in yeast and mammalian cells in chimeric DNA-binding proteins. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2337–2342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08361.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J. Critical structural elements of the VP16 transcriptional activation domain. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1846049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott G. D., Meredith D. M. The herpes simplex virus type 1 tegument protein VP22 is encoded by gene UL49. J Gen Virol. 1992 Mar;73(Pt 3):723–726. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-3-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elton D. M., Bonass W. A., Killington R. A., Meredith D. M., Halliburton I. W. Location of open reading frames coding for equine herpesvirus type-1 glycoproteins with homology to gE and gI of herpes simplex virus. Am J Vet Res. 1991 Aug;52(8):1252–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Triezenberg S. J., McKnight S. L. Expression of a truncated viral trans-activator selectively impedes lytic infection by its cognate virus. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):452–454. doi: 10.1038/335452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich J. A., Hoey T., Thut C. J., Admon A., Tjian R. Drosophila TAFII40 interacts with both a VP16 activation domain and the basal transcription factor TFIIB. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):519–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90386-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. L., Baumann R. P., Robertson A. T., Caughman G. B., O'Callaghan D. J., Staczek J. Regulation of equine herpesvirus type 1 gene expression: characterization of immediate early, early, and late transcription. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves R., O'Hare P. Separation of requirements for protein-DNA complex assembly from those for functional activity in the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein Vmw65. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1641–1650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1641-1650.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S., O'Hare P. Mapping of a major surface-exposed site in herpes simplex virus protein Vmw65 to a region of direct interaction in a transcription complex assembly. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):852–862. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.852-862.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Sturm R. A., Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A., Ingraham H. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1513–1516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J., Shales M., Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J., Greenblatt J. Reduced binding of TFIID to transcriptionally compromised mutants of VP16. Nature. 1991 Jun 13;351(6327):588–590. doi: 10.1038/351588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinchington P. R., Hougland J. K., Arvin A. M., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. The varicella-zoster virus immediate-early protein IE62 is a major component of virus particles. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):359–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.359-366.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., LeBowitz J. H., Sharp P. A. The octamer-binding proteins form multi-protein--DNA complexes with the HSV alpha TIF regulatory protein. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4229–4238. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Host cell proteins bind to the cis-acting site required for virion-mediated induction of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):71–75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Sharp P. A. Interactions of the Oct-1 POU subdomains with specific DNA sequences and with the HSV alpha-trans-activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2383–2396. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Thompson Y. G., Caughman G. B. Transcriptional control of the equine herpesvirus 1 immediate early gene. Virology. 1993 Dec;197(2):788–792. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Ha I., Maldonado E., Reinberg D., Green M. R. Binding of general transcription factor TFIIB to an acidic activating region. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):569–571. doi: 10.1038/353569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee T. A., Disney G. H., Everett R. D., Preston C. M. Control of expression of the varicella-zoster virus major immediate early gene. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):897–906. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight J. L., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Binding of the virion protein mediating alpha gene induction in herpes simplex virus 1-infected cells to its cis site requires cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7061–7065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriuchi H., Moriuchi M., Straus S. E., Cohen J. I. Varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 10 protein, the herpes simplex virus VP16 homolog, transactivates herpesvirus immediate-early gene promoters. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2739–2746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2739-2746.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R., Haigh A. Direct combinatorial interaction between a herpes simplex virus regulatory protein and a cellular octamer-binding factor mediates specific induction of virus immediate-early gene expression. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4231–4238. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03320.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Williams G. Structural studies of the acidic transactivation domain of the Vmw65 protein of herpes simplex virus using 1H NMR. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):4150–4156. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. E., McKnight J. L., Jenkins F. J., Roizman B. Nucleotide sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of a protein encoded in a small herpes simplex virus DNA fragment capable of trans-inducing alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5870–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purewal A. S., Allsopp R., Riggio M., Telford E. A., Azam S., Davison A. J., Edington N. Equid herpesviruses 1 and 4 encode functional homologs of the herpes simplex virus type 1 virion transactivator protein, VP16. Virology. 1994 Jan;198(1):385–389. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purewal A. S., Smallwood A. V., Kaushal A., Adegboye D., Edington N. Identification and control of the cis-acting elements of the immediate early gene of equid herpesvirus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1992 Mar;73(Pt 3):513–519. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regier J. L., Shen F., Triezenberg S. J. Pattern of aromatic and hydrophobic amino acids critical for one of two subdomains of the VP16 transcriptional activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):883–887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford E. A., Watson M. S., McBride K., Davison A. J. The DNA sequence of equine herpesvirus-1. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):304–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90706-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., Kingsbury R. C., McKnight S. L. Functional dissection of VP16, the trans-activator of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):718–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., LaMarco K. L., McKnight S. L. Evidence of DNA: protein interactions that mediate HSV-1 immediate early gene activation by VP16. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):730–742. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S., Greaves R., O'Hare P. Transcriptional activation by the acidic domain of Vmw65 requires the integrity of the domain and involves additional determinants distinct from those necessary for TFIIB binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5233–5244. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer S. P., Boyd B. A., Durham S. K., Resnick J. L., O'Boyle D. R., 2nd Deletion of the VP16 open reading frame of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):258–269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.258-269.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werstuck G., Capone J. P. Mutational analysis of the herpes simplex virus trans-inducing factor Vmw65. Gene. 1989 Feb 20;75(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao P., Capone J. P. A cellular factor binds to the herpes simplex virus type 1 transactivator Vmw65 and is required for Vmw65-dependent protein-DNA complex assembly with Oct-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4974–4977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]