Abstract
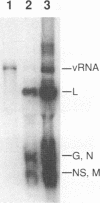
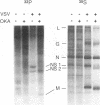
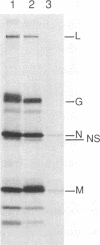
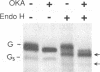
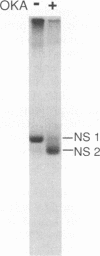
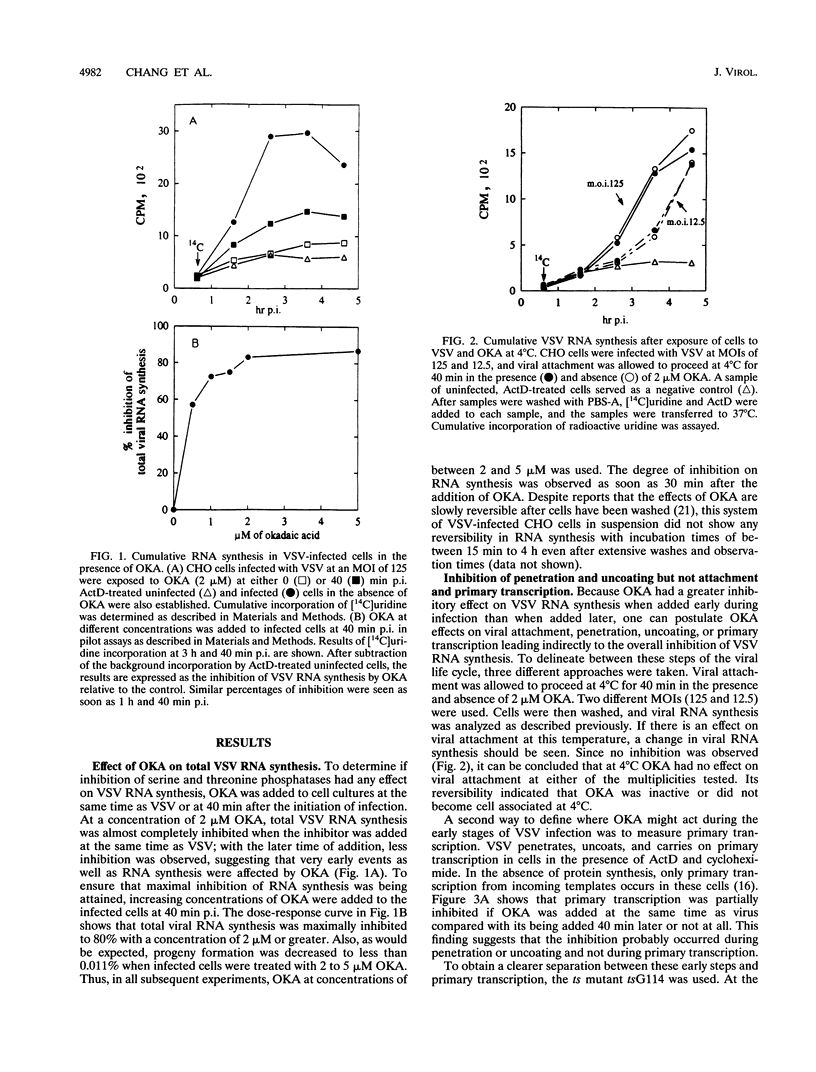
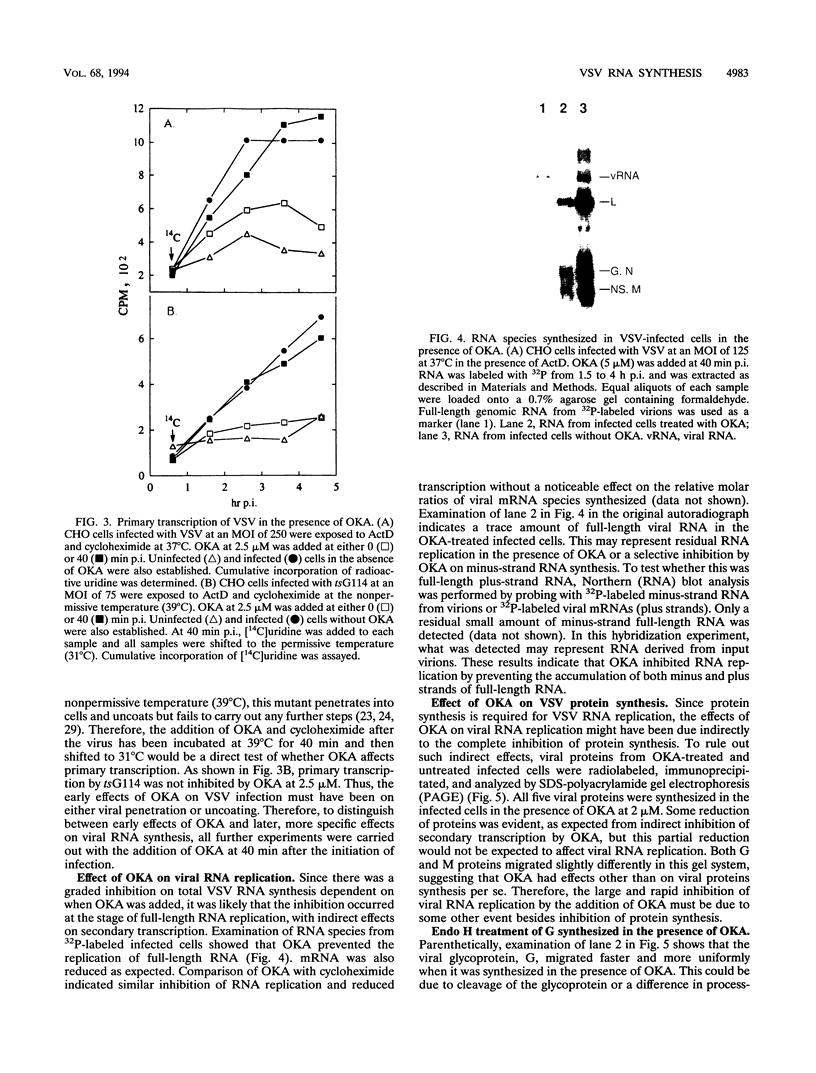
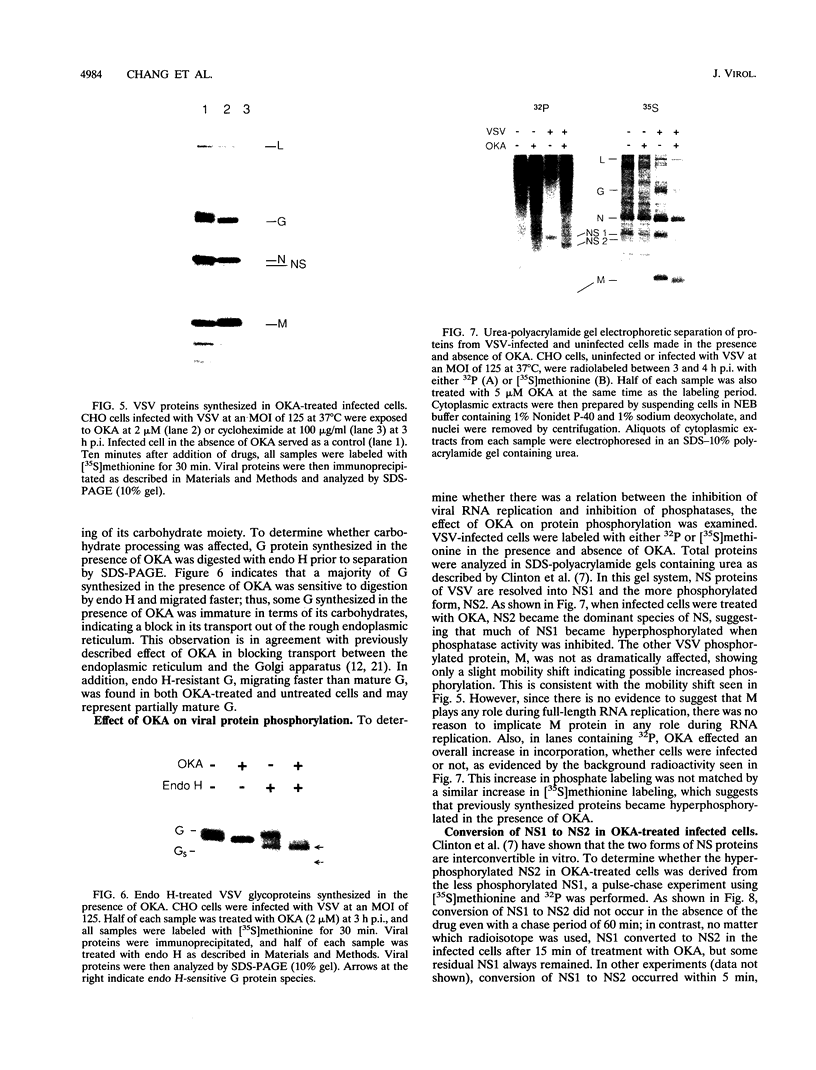
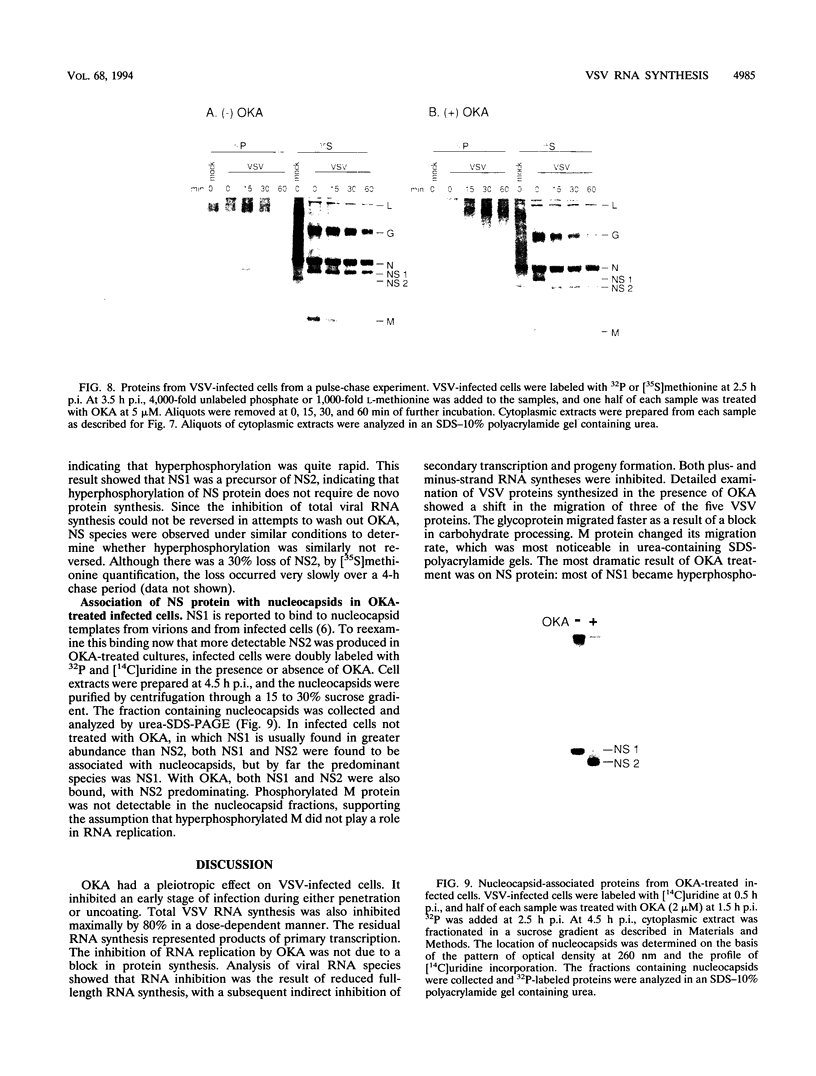
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) RNA synthesis requires the template nucleocapsid, the polymerase (L) protein, and the cofactor phosphorylated (P/NS) protein. To determine whether the degree of phosphorylation regulated VSV RNA synthesis, infected Chinese hamster ovary cells were treated with okadaic acid (OKA), a serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitor. OKA reduced viral penetration and uncoating but had little or no effect on primary transcription or viral protein synthesis. However, approximately 80% of total viral RNA synthesis was inhibited when 2 microM or more OKA was added to infected cells after viral uncoating had taken place. Analysis of proteins and RNA species in infected cells labeled with 32P showed that OKA led to hyperphosphorylation of two viral phosphoproteins, the P/NS protein and matrix protein (M), resulting in inhibition of full-length RNA synthesis and subsequent secondary transcription. Pulse-chase experiments demonstrated that the hyperphosphorylated P/NS species was converted rapidly from the less phosphorylated form. Hyperphosphorylated P/NS as well as the less phosphorylated form, but not M, were found to be associated with nucleocapsids isolated from cytoplasmic extracts. These results suggest that phosphorylation played an important role in the regulation between viral transcription and viral RNA replication as well as the turning off of RNA replication. Thus, phosphatase inhibitors promise to be a valuable tool for dissecting the regulatory mechanisms involving phosphorylated viral proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee A. K., Barik S. Gene expression of vesicular stomatitis virus genome RNA. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90495-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barge A., Gaudin Y., Coulon P., Ruigrok R. W. Vesicular stomatitis virus M protein may be inside the ribonucleocapsid coil. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7246–7253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7246-7253.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini L., Woodside M., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Takai A., Grinstein S. Okadaic acid, a phosphatase inhibitor, induces activation and phosphorylation of the Na+/H+ antiport. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15406–15413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. R., Wagner R. R. Role of the membrane (M) protein in endogenous inhibition of in vitro transcription by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.134-142.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Burge B. W., Huang A. S. Effects of phosphorylation and pH on the association of NS protein with vesicular stomatitis virus cores. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):340–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.340-346.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Burge B. W., Huang A. S. Phosphoproteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: identity and interconversion of phosphorylated forms. Virology. 1979 Nov;99(1):84–94. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Guerina N. G., Guo H. Y., Huang A. S. Host-dependent phosphorylation and kinase activity associated with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3313–3319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Huang A. S. Distribution of phosphoserine, phosphothreonine and phosphotyrosine in proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):510–514. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90459-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Little S. P., Hagen F. S., Huang A. S. The matrix (M) protein of vesicular stomatitis virus regulates transcription. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1455–1462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., McGowan C. H., Balch W. E. Evidence for the regulation of exocytic transport by protein phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1343–1355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Yu Y. Both NS and L proteins are required for in vitro RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1348–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1348-1356.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. 3. Multiple complementary messenger RNA molecules. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):946–957. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Manders E. K. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. IV. Transcription by standard virus in the presence of defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):909–916. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.909-916.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsford L., Emerson S. U. Transcriptional activities of different phosphorylated species of NS protein purified from vesicular stomatitis virions and cytoplasm of infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1097–1105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1097-1105.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesnaw J. A., Dickson L. R., Curry R. H. Proposed replicative role of the NS polypeptide of vesicular stomatitis virus: structural analysis of an electrophoretic variant. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.8-15.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucocq J., Warren G., Pryde J. Okadaic acid induces Golgi apparatus fragmentation and arrest of intracellular transport. J Cell Sci. 1991 Dec;100(Pt 4):753–759. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.4.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orringer E. P., Brockenbrough J. S., Whitney J. A., Glosson P. S., Parker J. C. Okadaic acid inhibits activation of K-Cl cotransport in red blood cells containing hemoglobins S and C. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 1):C591–C593. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.4.C591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repik P., Flamand A., Bishop D. H. Synthesis of RNA by mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana serotype) and the ability of wild-type VSV New Jersey to complement the VSV Indiana ts G I-114 transcription defect. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):157–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.157-169.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J. F. The involvement of calcium in transport of secretory proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):197–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90798-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Fafournoux P., Pouysségur J. Alpha-thrombin, epidermal growth factor, and okadaic acid activate the Na+/H+ exchanger, NHE-1, by phosphorylating a set of common sites. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19166–19171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Species of ribonucleic acid found in Chinese hamster ovary cells infected with plaque-forming and defective particles. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.154-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilágyi J. F., Pringle C. R. Effect of temperature-sensitive mutations on the virion-associated RNA transcriptase of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger J. T., Reichmann M. E. RNA synthesis in temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):570–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.570-578.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodman P. G., Mundy D. I., Cohen P., Warren G. Cell-free fusion of endocytic vesicles is regulated by phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):331–338. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]