Abstract
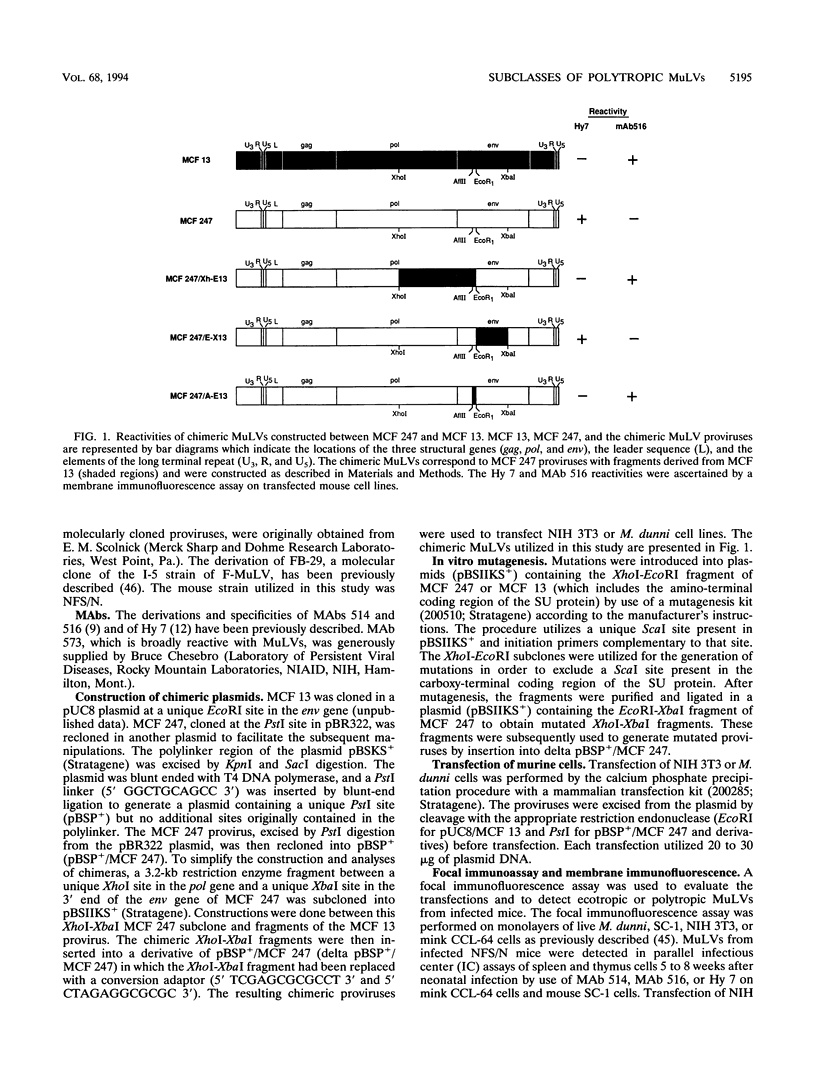
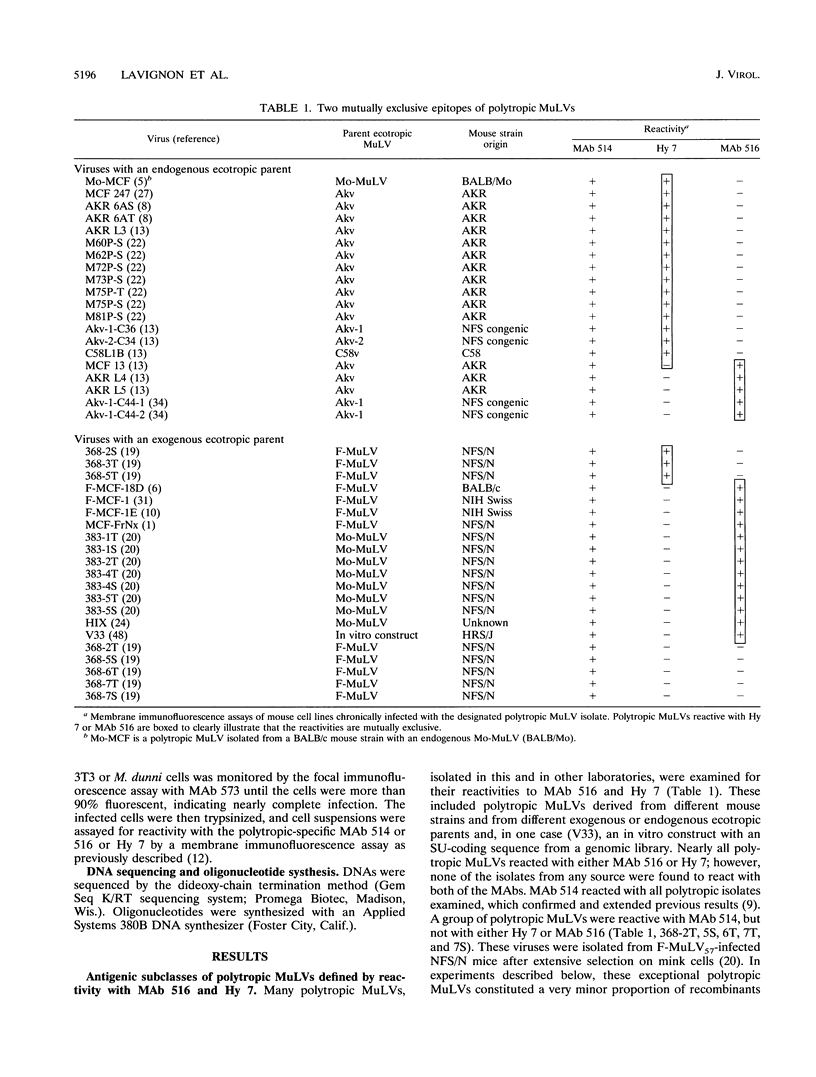
Polytropic murine leukemia viruses (MuLVs) arise in mice by recombination of ecotropic MuLVs with endogenous retroviral envelope genes and have been implicated in the induction of hematopoietic proliferative diseases. Inbred mouse strains contain many endogenous sequences which are homologous to the polytropic env genes; however, the extent to which particular sequences participate in the generation of the recombinants is unknown. Previous studies have established antigenic heterogeneity among the env genes of polytropic MuLVs, which may reflect recombination with distinct endogenous genes. In the present study, we have examined many polytropic MuLVs and found that nearly all isolates fall into two mutually exclusive antigenic subclasses on the basis of the ability of their SU proteins to react with one of two monoclonal antibodies, termed Hy 7 and MAb 516. Epitope-mapping studies revealed that reactivity to the two antibodies is dependent on the identity of a single amino acid residue encoded in a variable region of the receptor-binding domain of the env gene. This indicated that the two antigenic subclasses of MuLVs arose by recombination with distinct sets of endogenous genes. Evaluation of polytropic MuLVs in mice revealed distinctly different ratios of the two subclasses after inoculation of different ecotropic MuLVs, suggesting that individual ecotropic MuLVs preferentially recombine with distinct sets of endogenous polytropic env genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Sakai K., Kitamura N., Nakanishi S., Niwa O., Matsuyama M., Ishimoto A. Characterization of the env gene and long terminal repeat of molecularly cloned Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus DNA. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):813–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.813-821.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battini J. L., Heard J. M., Danos O. Receptor choice determinants in the envelope glycoproteins of amphotropic, xenotropic, and polytropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1468–1475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1468-1475.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Mileham K., Haas M., Nesbitt M. N., Harper M. E., Simon M. I. Chromosomal mapping of the mink cell focus-inducing and xenotropic env gene family in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6298–6302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., Van Griensven L. J., Vogt M., Verma I. M. Genome organization of retroviruses. VI. Heteroduplex analysis of ecotropic and xenotropic sequences of moloney mink cell focus-inducing viral RNA obtained from either a cloned isolate or a thymoma cell line. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):968–978. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.968-978.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., van Straaten F., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M., Vogt M. Analysis of the env gene of a molecularly cloned and biologically active Moloney mink cell focus-forming proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):19–31. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.19-31.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. S., Wehrly K., Portis J. L., Chesebro B. Host genes conferring resistance to a central nervous system disease induced by a polytropic recombinant Friend murine retrovirus. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):493–498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.493-498.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Britt W., Evans L., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Cloyd M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with murine leukemia viruses: use in analysis of strains of friend MCF and Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):134–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Evans L. Leukemia induction by a new strain of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: synergistic effect of Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):63–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.63-70.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y. H., Verma I. M., Shih T. Y., Scolnick E. M., Davidson N. Heteroduplex analysis of the sequence relations between the RNAs of mink cell focus-inducing and murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.352-360.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Chesebro B., Portis J. L., Weir M. MCF-specific murine monoclonal antibodies made against AKR-247 MCF virus recognize a unique determinant associated with the gp70-p-15(E) complex. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1112–1117. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1112-1117.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue D. J., Rothenberg E., Hopkins N., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Heteroduplex analysis of the nonhomology region between Moloney MuLV and the dual host range derivative HIX virus. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):959–970. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90350-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Biochemical evidence that MCF murine leukemia viruses are envelope (env) gene recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4676–4680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H. Characterization of polytropic MuLVs from three-week-old AKR/J mice. Virology. 1986 Aug;153(1):122–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Cloyd M. W. Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses specifically recombine with different endogenous retroviral sequences to generate mink cell focus-forming viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Cloyd M. W. Generation of mink cell focus-forming viruses by Friend murine leukemia virus: recombination with specific endogenous proviral sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):772–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.772-781.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Duesberg P. H. Isolation of a transformation-defective deletion mutant of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):735–743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.735-743.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Malik F. G. Class II polytropic murine leukemia viruses (MuLVs) of AKR/J mice: possible role in the generation of class I oncogenic polytropic MuLVs. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1882–1892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1882-1892.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Morrey J. D. Tissue-specific replication of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses in infected mice. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1350–1357. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1350-1357.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L., Nunn M., Duesberg P. H., Troxler D., Scolnick E. RNAs of defective and nondefective components of Friend anemia and polycythemia virus strains identified and compared. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):823–835. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Nomura S., Bolognesi D. P. A novel murine oncornavirus with dual eco- and xenotropic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5150–5155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Hiai H., Elder J. H., Schwartz R. S., Khiroya R. H., Thomas C. Y., Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. Expression of leukemogenic recombinant viruses associated with a recessive gene in HRS/J mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):249–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson I. C., Lieber M. M., Todaro G. J. Mink cell line Mv 1 Lu (CCL 64). Focus formation and the generation of "nonproducer" transformed cell lines with murine and feline sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):282–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Wozney J., Hopkins N. Nucleotide sequence of the gp70 gene of murine retrovirus MCF 247. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):413–420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.413-420.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Holland C. A., Lung M. L., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Hopkins N. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of MCF 247 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.291-298.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Zimmermann W., Oliff A., Friedrich R. Molecular analysis of the envelope gene and long terminal repeat of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: implications for the functions of these sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):828–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.828-840.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. A Mus dunni cell line that lacks sequences closely related to endogenous murine leukemia viruses and can be infected by ectropic, amphotropic, xenotropic, and mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):695–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.695-698.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. H. Large RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides encoding p15E and the U3 region of the long terminal repeat distinguish two biological classes of mink cell focus-forming type C viruses of inbred mice. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.275-290.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda M., Hoffman P. M., Ruscetti S. K. Viral determinants that control the neuropathogenicity of PVC-211 murine leukemia virus in vivo determine brain capillary endothelial cell tropism of the virus in vitro. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4580–4587. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4580-4587.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Stockert E., Obata Y., Old L. J. Leukemogenic properties of AKR dualtropic (MCF) viruses: amplification of murine leukemia virus-related antigens on thymocytes and acceleration of leukemia development in AKR mice. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):548–563. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90301-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. R., Khan A. S., Hoggan M. D., Hartley J. W., Martin M. A., Repaske R. Specific hybridization probes demonstrate fewer xenotropic than mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus env-related sequences in DNAs from inbred laboratory mice. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):359–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.359-366.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A. I., Hager G. L., Chang E. H., Scolnick E. M., Chan H. W., Lowy D. R. Transfection of molecularly cloned Friend murine leukemia virus DNA yields a highly leukemogenic helper-independent type C virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):475–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.475-486.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott D., Rein A. Basis for receptor specificity of nonecotropic murine leukemia virus surface glycoprotein gp70SU. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4632–4638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4632-4638.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. Characterization and mapping of RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides derived from the genomes of Akv and MCF murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):495–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Lenz J., Ruprecht R., Cloyd M. W. Tissue selectivity of murine leukemia virus infection is determined by long terminal repeat sequences. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):862–866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.862-866.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W. Status of the association of mink cell focus-forming viruses with leukemogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1265–1268. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S., Davis L., Feild J., Oliff A. Friend murine leukemia virus-induced leukemia is associated with the formation of mink cell focus-inducing viruses and is blocked in mice expressing endogenous mink cell focus-inducing xenotropic viral envelope genes. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):907–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Zijlstra M., Melief C., Berns A. Involvement of c-myc in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas in mice: frequency and mechanisms of activation. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3215–3222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Weeks M. O., Troxler D. H., Coffin J. M., Scolnick E. M. Mapping host range-specific oligonucleotides within genomes of the ecotropic and mink cell focus-inducing strains of Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):71–83. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.71-83.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Lodmell D., Chesebro B. Use of a focal immunofluorescence assay on live cells for quantitation of retroviruses: distinction of host range classes in virus mixtures and biological cloning of dual-tropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):110–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Sola B., Evans L., Nishio J., Hayes S. F., Nathanson K., Garon C. F., Chesebro B. Hemolytic anemia and erythroleukemia, two distinct pathogenic effects of Friend MuLV: mapping of the effects to different regions of the viral genome. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. Polymorphism of murine endogenous proviruses revealed by using virus class-specific oligonucleotide probes. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):168–175. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.168-175.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. The four classes of endogenous murine leukemia virus: structural relationships and potential for recombination. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2659–2669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2659-2669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. Y., Boykin B. J., Famulari N. G., Coppola M. A. Association of recombinant murine leukemia viruses of the class II genotype with spontaneous lymphomas in CWD mice. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):314–323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.314-323.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt M., Haggblom C., Swift S., Haas M. Envelope gene and long terminal repeat determine the different biological properties of Rauscher, Friend, and Moloney mink cell focus-inducing viruses. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.184-192.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Putten H., Quint W., van Raaij J., Maandag E. R., Verma I. M., Berns A. M-MuLV-induced leukemogenesis: integration and structure of recombinant proviruses in tumors. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]