Abstract
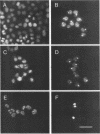
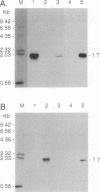
Cationic liposomes are known to facilitate efficient transfection of animal cells with DNA and even some viruses. As reported here, we have been able to use such a commercially available formulation (Lipofectamine) and introduce human hepatitis delta virus (HDV) into lines of cultured cells and demonstrate replication of the HDV genome both by immunofluorescence and by Northern (RNA) analysis. As much as 10% of the human hepatoma cell line Huh7 was transfected with HDV. Also transfected were the baby hamster kidney cell line BHK-21 and the Morris rat hepatoma line 7777. Two initial applications of HDV transfection have been made. (i) The ribonucleoprotein structure of HDV was isolated from disrupted virions and demonstrated as being sufficient to transfect Huh7 cells. In contrast, naked HDV RNA was not sufficient. (ii) From a study of cells transfected with HDV particles, it was found that, even after as long as 7 weeks and the associated replication of the transfected cells, the HDV RNA genome was still replicating. Apparently, HDV, in the absence of helper virus and in the absence of virus assembly, can maintain persistent replication and expression of the HDV genome. Transfection was also achieved with woodchuck hepatitis virus introduced into Huh7 cells. In summary, this transfection procedure should be of use for the study of these and maybe other recalcitrant animal viruses.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bchini R., Capel F., Dauguet C., Dubanchet S., Petit M. A. In vitro infection of human hepatoma (HepG2) cells with hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3025–3032. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3025-3032.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichko V., Schödel F., Nassal M., Gren E., Berzinsh I., Borisova G., Miska S., Peterson D. L., Gren E., Pushko P. Epitopes recognized by antibodies to denatured core protein of hepatitis B virus. Mol Immunol. 1993 Feb;30(3):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90051-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. J., Kalpana G., Goldberg J., Mason W., Werner B., Gerin J., Taylor J. Structure and replication of the genome of the hepatitis delta virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8774–8778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller D. V., Baltimore D. Liposome encapsulation of retrovirus allows efficient superinfection of resistant cell lines. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):269–272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.269-272.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu T. B., Taylor J. The RNAs of hepatitis delta virus are copied by RNA polymerase II in nuclear homogenates. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):6965–6972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.6965-6972.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sastre A., Palese P. Genetic manipulation of negative-strand RNA virus genomes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1993;47:765–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.47.100193.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J. S., Taylor J. M., White J. M. In vitro-synthesized hepatitis delta virus RNA initiates genome replication in cultured cells. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3104–3107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3104-3107.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innes C. L., Smith P. B., Langenbach R., Tindall K. R., Boone L. R. Cationic liposomes (Lipofectin) mediate retroviral infection in the absence of specific receptors. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):957–961. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.957-961.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. Y., Chao M., Taylor J. Initiation of replication of the human hepatitis delta virus genome from cloned DNA: role of delta antigen. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1945–1950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1945-1950.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. Y., Goldberg J., Coates L., Mason W., Gerin J., Taylor J. Molecular cloning of hepatitis delta virus RNA from an infected woodchuck liver: sequence, structure, and applications. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1855–1861. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1855-1861.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Taylor J. M. Experimental systems for the study of hepadnavirus and hepatitis delta virus infections. Hepatology. 1989 Apr;9(4):635–645. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Taketa K., Miyano K., Yamane T., Sato J. Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res. 1982 Sep;42(9):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negro F., Baldi M., Bonino F., Rocca G., Demartini A., Passarino G., Maran E., Lavarini C., Rizzetto M., Verme G. Chronic HDV (hepatitis delta virus) hepatitis. Intrahepatic expression of delta antigen, histologic activity and outcome of liver disease. J Hepatol. 1988 Feb;6(1):8–14. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(88)80457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Martin O. C., Kang H. C., Haugland R. P. A novel fluorescent ceramide analogue for studying membrane traffic in animal cells: accumulation at the Golgi apparatus results in altered spectral properties of the sphingolipid precursor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1267–1279. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramalho F., Brunetto M. R., Rocca G., Piccari G. G., Batista A., Chiaberge E., Lavarini C., Dal Monte R. P., Carneiro de Moura M., Bonino F. Serum markers of hepatitis B virus replication, liver histology and intrahepatic expression of hepatitis B core antigen. J Hepatol. 1988 Aug;7(1):14–20. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(88)80502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rima R. K., Martin S. J. Persistent infection of tissue culture cells by RNA viruses. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1976 Jun 1;162(2):89–119. doi: 10.1007/BF02121320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu W. S., Netter H. J., Bayer M., Taylor J. Ribonucleoprotein complexes of hepatitis delta virus. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3281–3287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3281-3287.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J., Mason W., Summers J., Goldberg J., Aldrich C., Coates L., Gerin J., Gowans E. Replication of human hepatitis delta virus in primary cultures of woodchuck hepatocytes. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2891–2895. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2891-2895.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Fujiyama A., Matsubara K. Stable expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in an integrated state in a human hepatoma cell line transfected with the cloned viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):444–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler G. V., Snyder R. L., Summers J. Experimental infection of the woodchuck (Marmota monax monax) with woodchuck hepatitis virus. Lab Invest. 1986 Jul;55(1):51–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]