Abstract
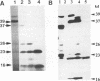
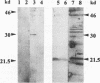
The gene encoding the phosphoprotein of the pneumovirus pneumonia virus of mice (PVM) has been cloned and sequenced. The gene is 903 nucleotides in length and contains a long open reading frame (ORF) capable of encoding a polypeptide of 295 amino acid residues. A smaller, second, overlapping ORF encoding a polypeptide 137 amino acids in length was also present. The large ORF directed the synthesis of a 39-kDa polypeptide and four additional polypeptides with masses of 37 kDa, 26 kDa, 23 kDa, and 16 kDa in vitro. The smaller polypeptides were generated by internal initiation on in-frame AUG initiation codons to generate carboxy co-terminal products. Western immunoblot analysis indicated that at least two of these proteins and several other related polypeptides are present in infected cells, and the possible origins of these are discussed. Western blot analysis using antiserum raised against a synthetic peptide and specific for the predicted second ORF product identified a polypeptide of 23 kDa in PVM-infected cells. The pattern of PVM P gene expression is unlike that of the closely related respiratory syncytial virus and is reminiscent of that of paramyxoviruses such as Sendai virus. This is the first example of a pneumovirus encoding multiple polypeptide products from a single mRNA in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barr J., Chambers P., Pringle C. R., Easton A. J. Sequence of the major nucleocapsid protein gene of pneumonia virus of mice: sequence comparisons suggest structural homology between nucleocapsid proteins of pneumoviruses, paramyxoviruses, rhabdoviruses and filoviruses. J Gen Virol. 1991 Mar;72(Pt 3):677–685. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-3-677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Rozenblatt S., Arnheiter H., Richardson C. D. Measles virus P gene codes for two proteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):908–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.908-919.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers P., Barr J., Pringle C. R., Easton A. J. Molecular cloning of pneumonia virus of mice. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1869–1872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1869-1872.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers P., Matthews D. A., Pringle C. R., Easton A. J. The nucleotide sequences of intergenic regions between nine genes of pneumonia virus of mice establish the physical order of these genes in the viral genome. Virus Res. 1991 Mar;18(2-3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(91)90023-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers P., Pringle C. R., Easton A. J. Genes 1 and 2 of pneumonia virus of mice encode proteins which have little homology with the 1C and 1B proteins of human respiratory syncytial virus. J Gen Virol. 1991 Oct;72(Pt 10):2545–2549. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-10-2545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers P., Pringle C. R., Easton A. J. Sequence analysis of the gene encoding the fusion glycoprotein of pneumonia virus of mice suggests possible conserved secondary structure elements in paramyxovirus fusion glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jul;73(Pt 7):1717–1724. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-7-1717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. The envelope-associated 22K protein of human respiratory syncytial virus: nucleotide sequence of the mRNA and a related polytranscript. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):65–71. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.65-71.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galinski M. S., Mink M. A., Lambert D. M., Wechsler S. L., Pons M. W. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the human parainfluenza 3 virus mRNA encoding the P and C proteins. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):46–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Collins P. L. Sequence comparison of the phosphoprotein mRNAs of antigenic subgroups A and B of human respiratory syncytial virus identifies a highly divergent domain in the predicted protein. J Gen Virol. 1990 Feb;71(Pt 2):481–485. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-2-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Bando H., Tsurudome M., Kawano M., Nishio M., Ito Y. Sequence analysis of the phosphoprotein (P) genes of human parainfluenza type 4A and 4B viruses and RNA editing at transcript of the P genes: the number of G residues added is imprecise. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90413-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R. Nucleotide sequence of the respiratory syncytial virus phosphoprotein gene. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1607–1612. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling R., Easton A. J., Pringle C. R. Sequence analysis of the 22K, SH and G genes of turkey rhinotracheitis virus and their intergenic regions reveals a gene order different from that of other pneumoviruses. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jul;73(Pt 7):1709–1715. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-7-1709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling R., Pringle C. R. Polypeptides of pneumonia virus of mice. I. Immunological cross-reactions and post-translational modifications. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jun;70(Pt 6):1427–1440. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-6-1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López J. A., Villanueva N., Melero J. A., Portela A. Nucleotide sequence of the fusion and phosphoprotein genes of human respiratory syncytial (RS) virus Long strain: evidence of subtype genetic heterogeneity. Virus Res. 1988 May;10(2-3):249–261. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallipeddi S. K., Samal S. K. Sequence comparison between the phosphoprotein mRNAs of human and bovine respiratory syncytial viruses identifies a divergent domain in the predicted protein. J Gen Virol. 1992 Sep;73(Pt 9):2441–2444. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-9-2441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka Y., Curran J., Pelet T., Kolakofsky D., Ray R., Compans R. W. The P gene of human parainfluenza virus type 1 encodes P and C proteins but not a cysteine-rich V protein. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3406–3410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3406-3410.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnes L., McQuain C., Morrison T. The P protein and the nonstructural 38K and 29K proteins of Newcastle disease virus are derived from the same open reading frame. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):256–264. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90643-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R., Eglin R. P. Murine pneumonia virus: seroepidemiological evidence of widespread human infection. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):975–982. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Elango N., Venkatesan S. Sequence analysis of the respiratory syncytial virus phosphoprotein gene. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):991–994. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.991-994.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Hidaka Y., Kanda T., Shibuta H., Nomoto A., Iwasaki K. Sequence of 3,687 nucleotides from the 3' end of Sendai virus genome RNA and the predicted amino acid sequences of viral NP, P and C proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7317–7330. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Collins P. L. Sequence analysis of the P and C protein genes of human parainfluenza virus type 3: patterns of amino acid sequence homology among paramyxovirus proteins. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2705–2719. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]