Abstract
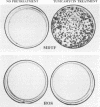
The ecotropic murine leukemia virus (E-MuLV) receptor expressed on Mus dunni tail fibroblast (MDTF) cells is a receptor for all E-MuLVs with the notable of Moloney murine leukemia virus (Mo-MuLV). Substitution of isoleucine for valine at position 214 in the third extracellular region (the putative E-MuLV binding site) of the MDTF receptor molecule allows this molecule to function as a Mo-MuLV receptor (M.V. Eiden, K. Farrell, J. Warsowe, L. A. Mahan, and C. A. Wilson, J. Virol. 67:4056-4061, 1993). We have now determined that treating MDTF cells with tunicamycin, an inhibitor of N-linked glycosylation, also renders them susceptible to Mo-MuLV infection. Two potential N-linked glycosylation sites are present in the third extracellular regions of both the NIH 3T3 and MDTF ecotropic receptors. The glycosylation site at position 229 of the MDTF receptor cDNA was eliminated by substituting a threonine codon for the asparagine codon. Mo-MuLV-resistant human HOS cells, expressing this form of the receptor, are susceptible to Mo-MuLV infection. Thus, our studies suggest that without a glycan moiety at position 229, the valine residue at 214 is no longer restrictive for Mo-MuLV infection. BHK-21 and CHO K1 hamster cells also express glycosylation-inactivated forms of the ecotropic receptor. Sequence analysis of these receptors together with our analysis of MDTF receptor function suggests that a single asparagine-linked glycosylation site is responsible for glycosylation inactivation of these receptors.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton L. M., Kim J. W., Tseng L., Cunningham J. M. Envelope-binding domain in the cationic amino acid transporter determines the host range of ecotropic murine retroviruses. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2091–2096. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2091-2096.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albritton L. M., Tseng L., Scadden D., Cunningham J. M. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Mulligan R. C. Safe and efficient generation of recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden M. V., Farrell K., Warsowe J., Mahan L. C., Wilson C. A. Characterization of a naturally occurring ecotropic receptor that does not facilitate entry of all ecotropic murine retroviruses. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4056–4061. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4056-4061.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. W., Closs E. I., Albritton L. M., Cunningham J. M. Transport of cationic amino acids by the mouse ecotropic retrovirus receptor. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):725–728. doi: 10.1038/352725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. A Mus dunni cell line that lacks sequences closely related to endogenous murine leukemia viruses and can be infected by ectropic, amphotropic, xenotropic, and mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):695–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.695-698.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierendorf R. C., Pfeffer D. Direct sequencing of denatured plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:556–562. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Garcia J. V., von Suhr N., Lynch C. M., Wilson C., Eiden M. V. Construction and properties of retrovirus packaging cells based on gibbon ape leukemia virus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2220–2224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2220-2224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Turner D., Cepko C. Lineage analysis in the vertebrate nervous system by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P. Membrane mutants of animal cells: rapid identification of those with a primary defect in glycosylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):923–929. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Kavanaugh M. P., North R. A., Kabat D. Cell-surface receptor for ecotropic murine retroviruses is a basic amino-acid transporter. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):729–731. doi: 10.1038/352729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. A., Eiden M. V. Viral and cellular factors governing hamster cell infection by murine and gibbon ape leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5975–5982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5975-5982.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Yoshimoto E., Meruelo D. Identification of amino acid residues critical for infection with ecotropic murine leukemia retrovirus. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1310–1314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1310-1314.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Yoshimoto E., Meruelo D. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel human gene homologous to the murine ecotropic retroviral receptor. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):10–17. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90748-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]