Abstract
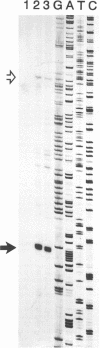
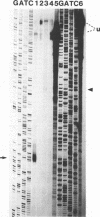
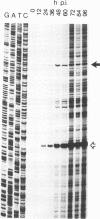
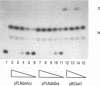
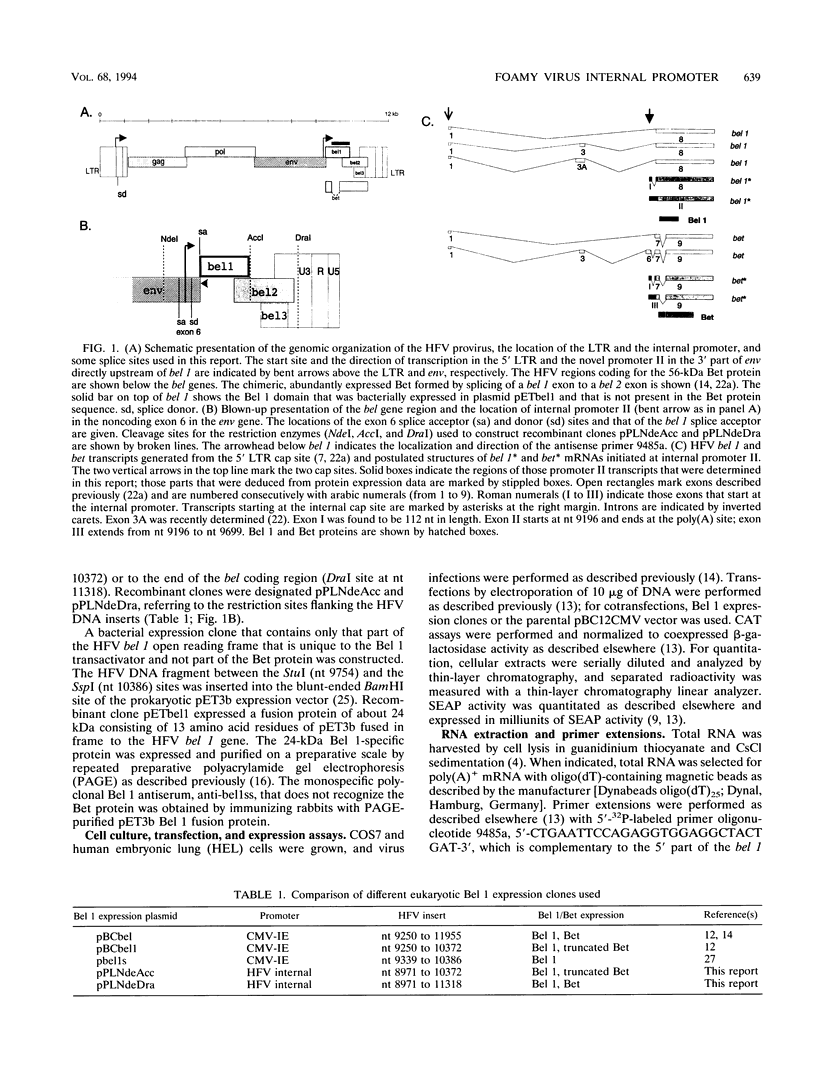
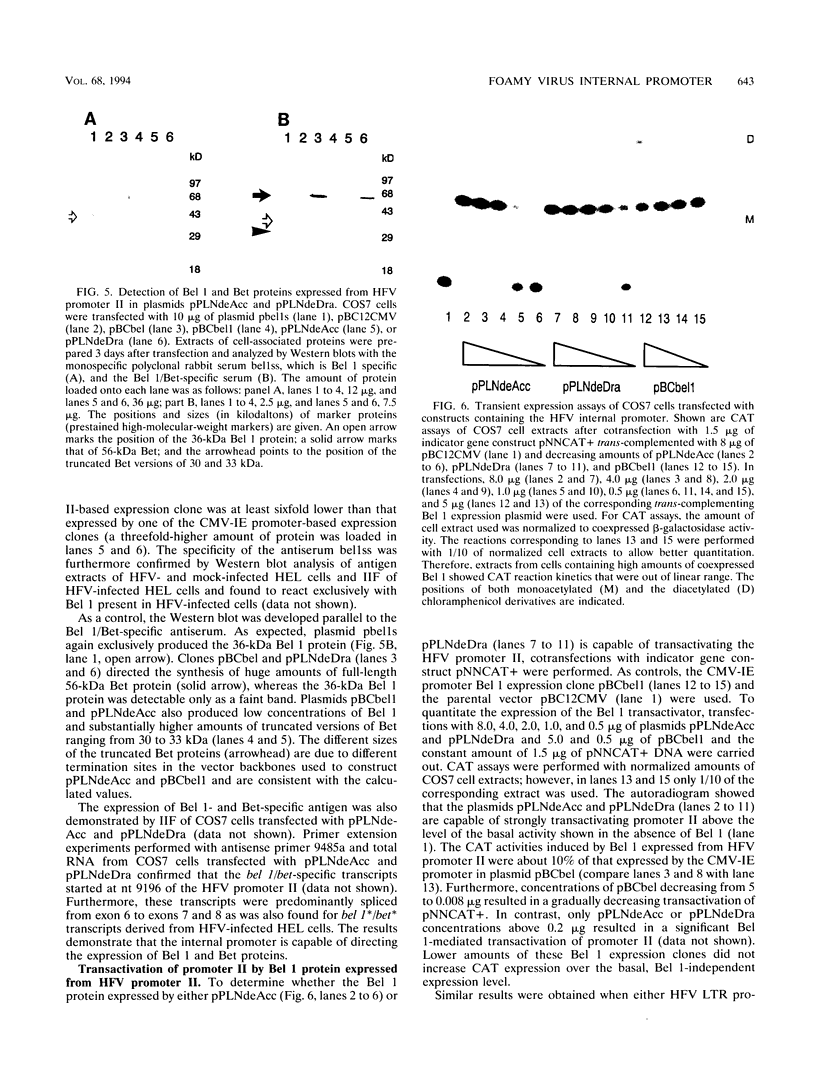
The human foamy virus or spumaretrovirus (HFV) is a complex retrovirus that has the capacity to code not only for the three retroviral genes gag, pol, and env but, in addition, for at least three bel genes. The HFV provirus contains two different and functionally active promoters: the classical retroviral promoter in the 5' long terminal repeat and a recently identified second promoter in the env gene upstream of the bel genes. Both promoter/enhancers are strongly dependent on the HFV transcriptional transactivator protein Bel 1. Here we report that the internal promoter directs the synthesis of viral transcripts that code for functionally active Bel 1 and for Bet proteins that appeared early after HFV infection. The viral mRNAs of the internal promoter have a 112-nucleotide-long leader exon and were spliced predominantly at the first splice donor site in the 5' untranslated region. The data were obtained by transient expression assays, transactivation experiments, and RNA analyses of transcripts derived from HFV-infected cells. The results provide strong evidence for the crucial role the internal promoter plays during HFV infection in generating bel-specific transcripts.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achong B. G., Mansell P. W., Epstein M. A., Clifford P. An unusual virus in cultures from a human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Feb;46(2):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguzzi A., Wagner E. F., Netzer K. O., Bothe K., Anhauser I., Rethwilm A. Human foamy virus proteins accumulate in neurons and induce multinucleated giant cells in the brain of transgenic mice. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):1061–1071. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothe K., Aguzzi A., Lassmann H., Rethwilm A., Horak I. Progressive encephalopathy and myopathy in transgenic mice expressing human foamy virus genes. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):555–557. doi: 10.1126/science.1650034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Human immunodeficiency virus as a prototypic complex retrovirus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1053–1056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1053-1056.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Rethwilm A., Maurer B., Darai G. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the env gene and its flanking regions of the human spumaretrovirus reveals two novel genes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2077–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A., Partin K. M., Löchelt M., Bannert H., Flügel R. M., Cullen B. R. Characterization of the transcriptional trans activator of human foamy retrovirus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2589–2594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2589-2594.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagaye S., Vexiau P., Morozov V., Guénebaut-Claudet V., Tobaly-Tapiero J., Canivet M., Cathelineau G., Périès J., Emanoil-Ravier R. Human spumaretrovirus-related sequences in the DNA of leukocytes from patients with Graves disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10070–10074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. J., Lee A. H., Sung Y. C. Multiple positive and negative cis-acting elements that mediate transactivation by bel1 in the long terminal repeat of human foamy virus. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2317–2326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2317-2326.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löchelt M., Aboud M., Flügel R. M. Increase in the basal transcriptional activity of the human foamy virus internal promoter by the homologous long terminal repeat promoter in cis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 11;21(18):4226–4230. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.18.4226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löchelt M., Muranyi W., Flügel R. M. Human foamy virus genome possesses an internal, Bel-1-dependent and functional promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7317–7321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löchelt M., Zentgraf H., Flügel R. M. Construction of an infectious DNA clone of the full-length human spumaretrovirus genome and mutagenesis of the bel 1 gene. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90820-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahnke C., Kashaiya P., Rössler J., Bannert H., Levin A., Blattner W. A., Dietrich M., Luande J., Löchelt M., Friedman-Kien A. E. Human spumavirus antibodies in sera from African patients. Arch Virol. 1992;123(3-4):243–253. doi: 10.1007/BF01317261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahnke C., Löchelt M., Bannert H., Flügel R. M. Specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of antibodies to the human spumavirus. J Virol Methods. 1990 Jul;29(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Bannert H., Darai G., Flügel R. M. Analysis of the primary structure of the long terminal repeat and the gag and pol genes of the human spumaretrovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1590–1597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1590-1597.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Luciw P. A. Replication and regulation of primate foamy viruses. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):475–482. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90417-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Shaw K. E., Pratt-Lowe E., Barry P. A., Luciw P. A. Identification of the simian foamy virus transcriptional transactivator gene (taf). J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2903–2909. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2903-2909.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Shaw K. E., Pratt-Lowe E., Barry P. A., Luciw P. A. Simian foamy virus type 1 is a retrovirus which encodes a transcriptional transactivator. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3598–3604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3598-3604.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller H. K., Ball G., Epstein M. A., Achong B. G., Lenoir G., Levin A. The prevalence of naturally occurring antibodies to human syncytial virus in East African populations. J Gen Virol. 1980 Apr;47(2):399–406. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-47-2-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muranyi W., Flügel R. M. Analysis of splicing patterns of human spumaretrovirus by polymerase chain reaction reveals complex RNA structures. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):727–735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.727-735.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Erlwein O., Baunach G., Maurer B., ter Meulen V. The transcriptional transactivator of human foamy virus maps to the bel 1 genomic region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):941–945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh L. K., Theodorakis P. A., Chinnadurai G. Distinct cis-acting regions in U3 regulate trans-activation of the human spumaretrovirus long terminal repeat by the viral bel1 gene product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3661–3666. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh L. K., Yang C., Theodorakis P. A., Chinnadurai G. Functional dissection of the human spumaretrovirus transactivator identifies distinct classes of dominant-negative mutants. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):161–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.161-169.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]