Abstract
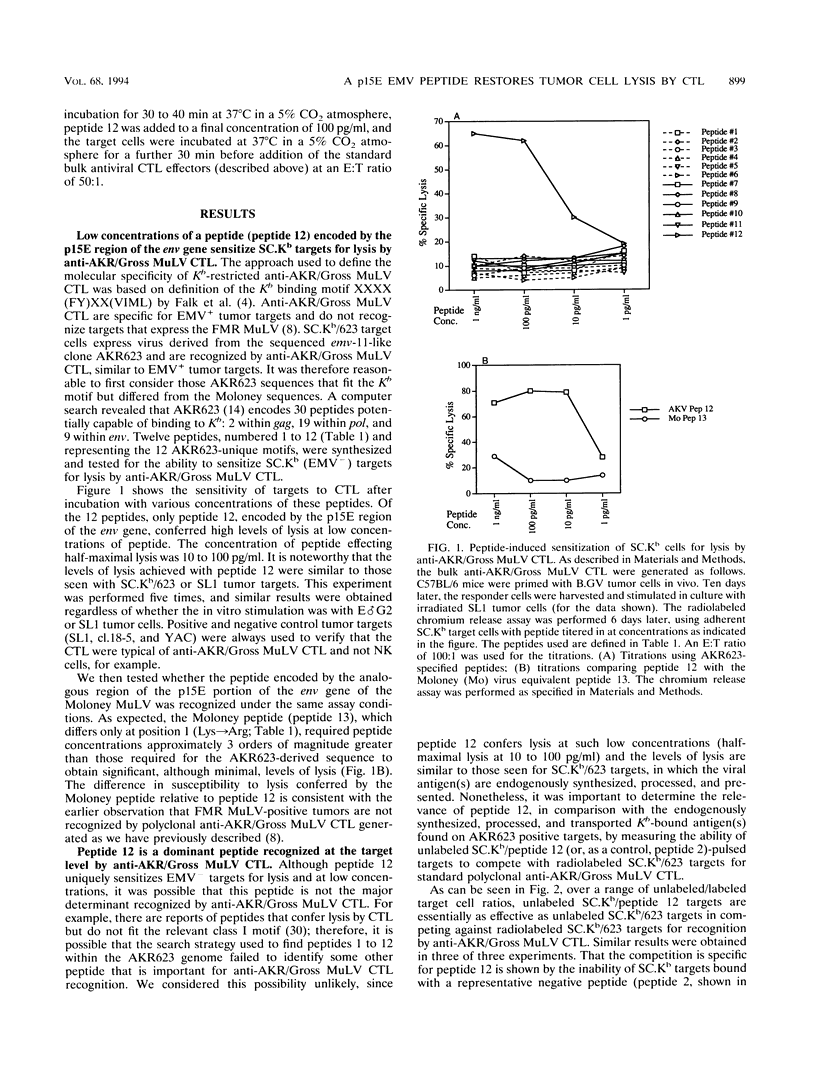
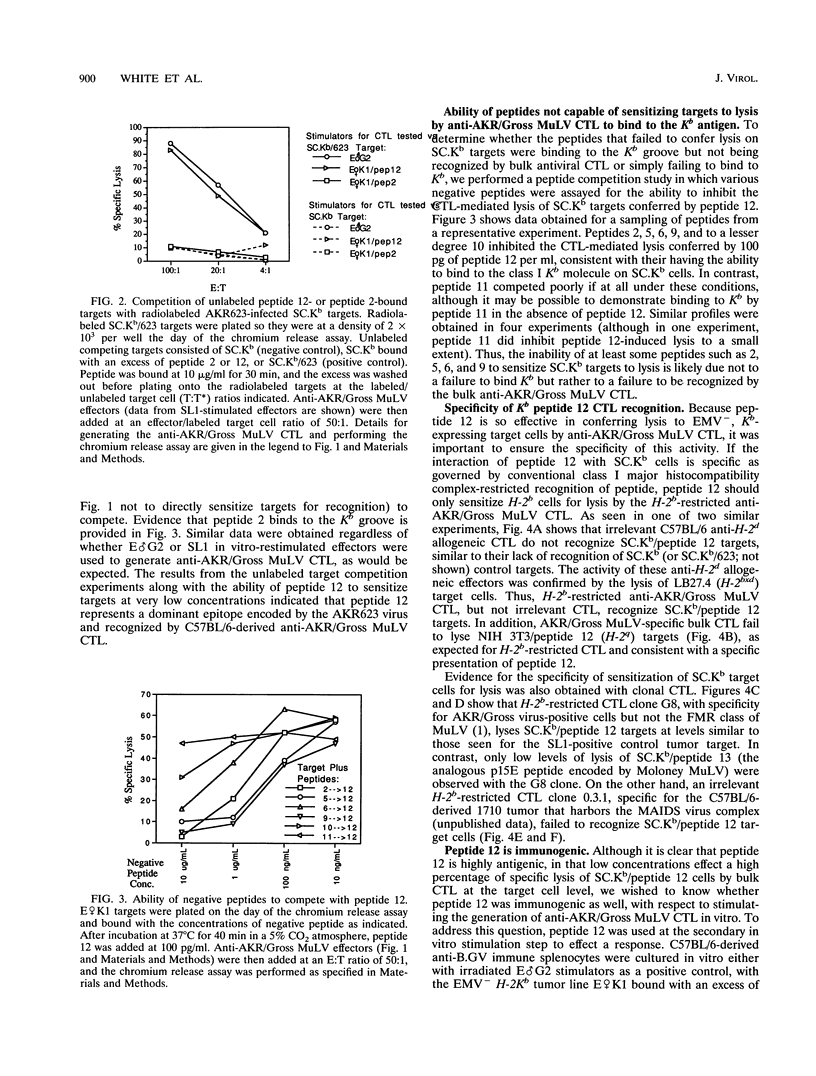
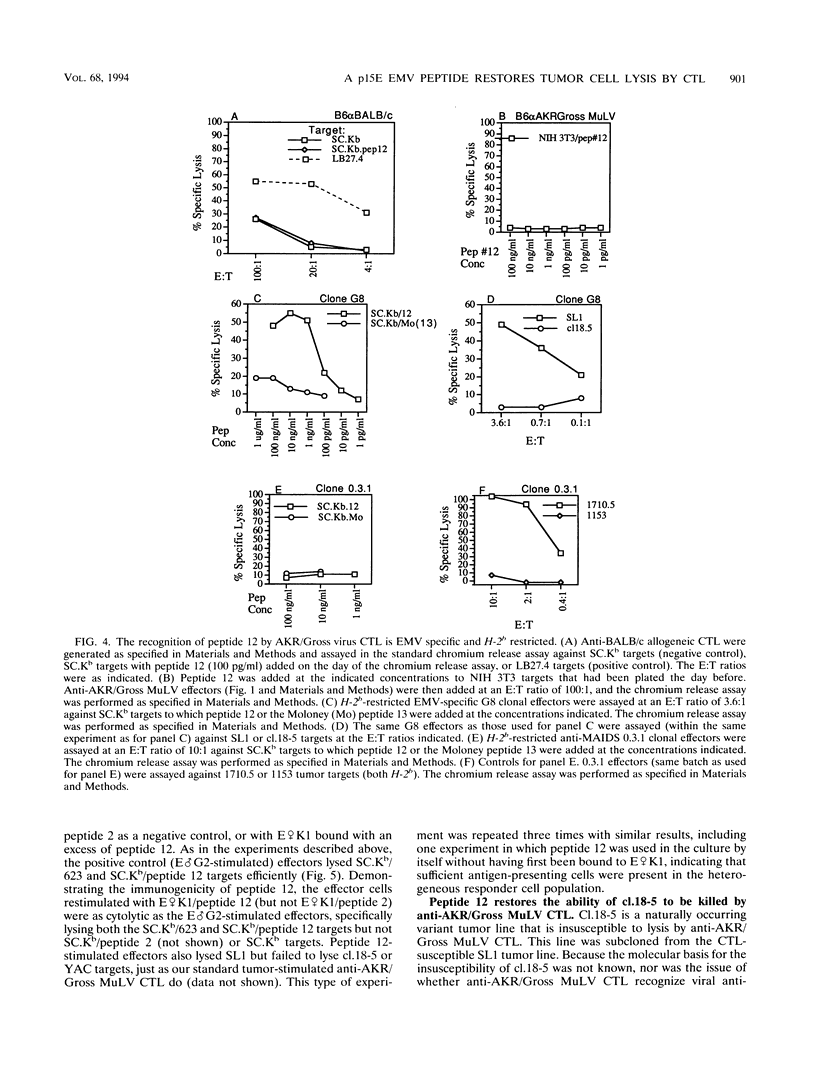
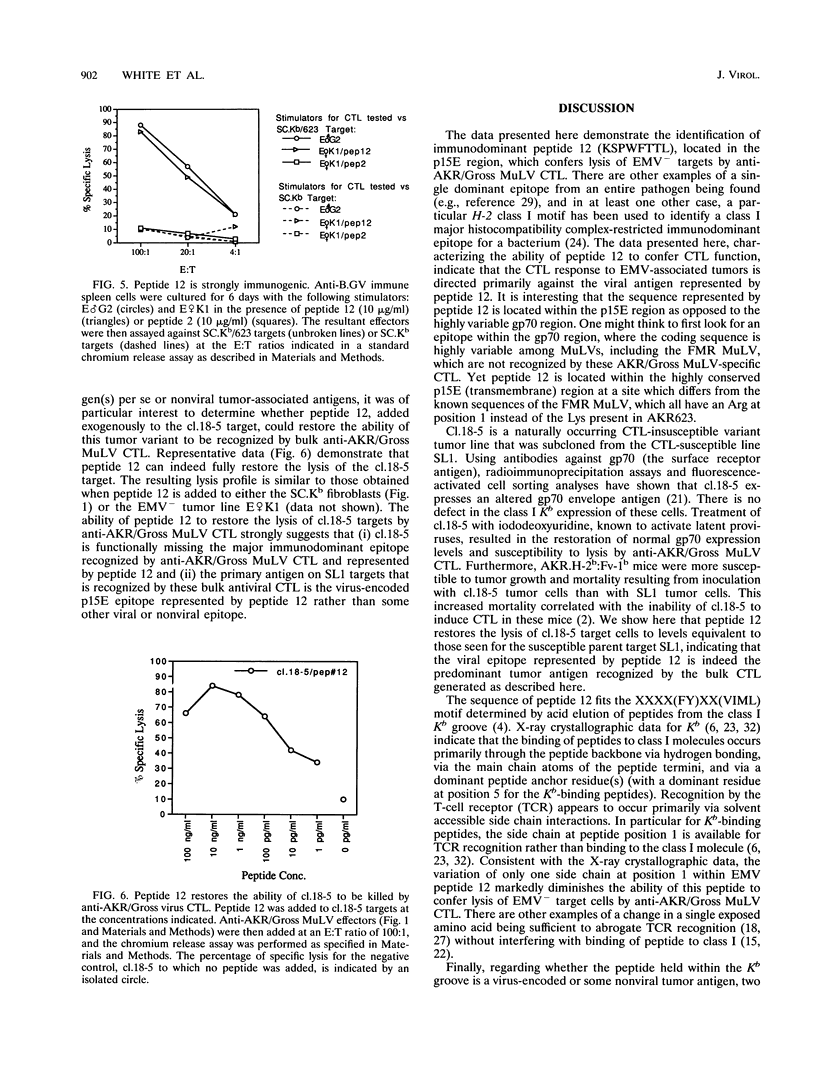
H-2b tumor cells expressing the endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus (EMV) induce an anti-AKR/Gross murine leukemia virus (MuLV) cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) response in the C57BL/6 mouse strain. The EMV clone AKR623 has been used to infect SC.Kb fibroblast cells, resulting in SC.Kb/623 targets that are lysed by bulk anti-AKR/Gross MuLV CTL with a profile that is similar to that for the EMV+ AKR.H-2b SL1 tumor target. Anti-AKR/Gross MuLV CTL are restricted by the class I Kb antigen and do not cross-react with Friend-Moloney-Rauscher virus-positive targets. The AKR623 genome was searched by computer for coding sequences that fit the motif XXXX(FY)XX(VIML) for peptides that bind Kb. Of 30 octameric peptides identified, 12 that were unique to AKR623 and different from published Friend-Moloney-Rauscher sequences were synthesized and bound to EMV-negative SC.Kb cells, which were then assayed as targets against anti-AKR/Gross MuLV CTL. One peptide, peptide 12 (KSPWFTTL) from the p15E transmembrane protein, sensitized SC.Kb target cells to lysis by anti-AKR/Gross MuLV CTL with a profile similar to those seen for AKR.H-2b SL1 tumor targets and SC.Kb/623 fibroblast targets. Low concentrations of peptide were sufficient, the half-maximal lysis occurring at 10 to 100 pg/ml. SC.Kb/peptide 12 targets were recognized by the H-2b-restricted bulk CTL in a conventional class I Kb-restricted fashion. Unlabeled SC.Kb/peptide 12-pulsed targets were effective in competing with radiolabeled SC.Kb/623 targets for lysis by anti-AKR/Gross MuLV CTL. This finding is consistent with the notion that peptide 12 represents the dominant endogenously processed epitope recognized by these antiviral CTL. In addition, peptide 12 is immunogenic in that it could stimulate the in vitro generation of an anti-AKR/Gross MuLV CTL response from tumor-primed C57BL/6 responder spleen cells. Finally, the physiological relevance of peptide 12 was suggested by its ability to fully restore the recognition and lysis of AKR.H-2b SL1 clone 18-5 tumor cells, a naturally occurring variant tumor clone that is insusceptible to lysis by anti-AKR/Gross MuLV CTL. These data indicate that a virus-encoded antigen, represented by peptide 12, and not a nonviral tumor antigen, is the immunodominant epitope responsible for the recognition of EMV+ tumor cells by C57BL/6-derived anti-AKR/Gross MuLV CTL.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma H., Phillips J. D., Green W. R. Clonal heterogeneity of anti-AKR/gross leukemia virus cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Evidence for two distinct antigen systems. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2464–2473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma H., Wegmann K. W., Green W. R. Correlations of in vivo growth of CTL-susceptible and -resistant variant tumor cell lines in CTL-responder AKR.H-2b:Fv-1b and -nonresponder AKR.H-2b mice. Cell Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;116(1):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O., Stevanović S., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):290–296. doi: 10.1038/351290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flyer D. C., Burakoff S. J., Faller D. V. The immune response to Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced tumors: induction of cytolytic T lymphocytes specific for both viral and tumor-associated antigens. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 15;137(12):3968–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremont D. H., Matsumura M., Stura E. A., Peterson P. A., Wilson I. A. Crystal structures of two viral peptides in complex with murine MHC class I H-2Kb. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):919–927. doi: 10.1126/science.1323877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomard E., Levy J. P., Plata F., Henin Y., Duprez V., Bismuth A., Reme T. Studies on the nature of the cell surface antigen reacting with cytolytic T lymphocytes in murine oncornavirus-induced tumors. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Apr;8(4):228–236. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. R. Genetic control of the induction of cytolytic T lymphocyte responses to AKR/Gross viral leukemias. I. H-2-encoded dominant gene control. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2658–2664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. R., Graziano R. F. Cytolytic T lymphocyte-defined retroviral antigens on normal cells: encoding by the Akv-1 proviral locus. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(2):106–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00377969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. R. H-2-restricted cytolytic T lymphocytes specific for a subclass of AKR endogenous leukemia virus-induced tumors: correlation of tumor cell susceptibility with expression of the gross cell surface antigen. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2584–2590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. R., Nowinski R. C., Henney C. S. Specificity of cytolytic T cells directed against AKR/Gross virus-induced syngeneic leukemias: antibodies directed against H-2K, but not against viral proteins, inhibit lysis. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):647–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. R., Nowinski R. C., Henney C. S. The generation and specificity of cytotoxic T cells raised against syngeneic tumor cells bearing AKR/Gross murine leukemia virus antigens. J Exp Med. 1979 Jul 1;150(1):51–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. R. The specificity of H-2-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes directed to AKR/Gross leukemia virus-induced tumors. I. Isolation of a selectively resistant variant tumor subclone. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Nov;13(11):863–870. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830131102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Nucleotide sequence of AKV murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):471–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.471-478.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky T. S., Gorga J. C., Busch R., Rothbard J., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Peptide binding to HLA-DR1: a peptide with most residues substituted to alanine retains MHC binding. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1797–1803. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08304.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang D., Flyer D. C. Immune response to Moloney murine leukemia virus nonviral, tumor-associated antigens fails to provide in vivo tumor protection. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):974–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang D., Flyer D. C. In vivo immune selection of a Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced tumor results in the loss of viral- but not tumor-associated antigens. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3502–3506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. L., Reay P. A., Ehrich E. W., Davis M. M. Molecular components of T-cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:835–873. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.004155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinken S. P., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Evolution of B cell lineage lymphomas in mice with a retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome, MAIDS. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1123–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rands E., Chattopadhyay S. K., Garon C. F., Hager G. L. Molecular cloning of infectious integrated murine leukemia virus DNA from infected mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):614–618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manjunath R., Graziano R. F., Green W. R. The specificity of H-2-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes directed to AKR/Gross leukemia virus-induced tumors. III. Coordinate alterations in viral gp70 antigen expression and restoration of CTL-susceptibility to insusceptible variant tumors. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2271–2279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. L., Verdini A. S., Weber P. C., Salemme F. R., Corradin G. Competitor analogs for defined T cell antigens: peptides incorporating a putative binding motif and polyproline or polyglycine spacers. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90716-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura M., Fremont D. H., Peterson P. A., Wilson I. A. Emerging principles for the recognition of peptide antigens by MHC class I molecules. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):927–934. doi: 10.1126/science.1323878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pamer E. G., Harty J. T., Bevan M. J. Precise prediction of a dominant class I MHC-restricted epitope of Listeria monocytogenes. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):852–855. doi: 10.1038/353852a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer A., Schmidt W. Resistance to cellular immune response in AKR leukemias. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jul;16(7):753–759. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata K., Imarai M., van Bleek G. M., Joyce S., Nathenson S. G. Vesicular stomatitis virus antigenic octapeptide N52-59 is anchored into the groove of the H-2Kb molecule by the side chains of three amino acids and the main-chain atoms of the amino terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3135–3139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Galleshaw J. A., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome of a murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Bleek G. M., Nathenson S. G. Isolation of an endogenously processed immunodominant viral peptide from the class I H-2Kb molecule. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):213–216. doi: 10.1038/348213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. D., Robbins M. D., Green W. R. Mechanism of escape of endogenous murine leukemia virus emv-14 from recognition by anti-AKR/Gross virus cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2608–2619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2608-2619.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Young A. C., Imarai M., Nathenson S. G., Sacchettini J. C. Crystal structure of the major histocompatibility complex class I H-2Kb molecule containing a single viral peptide: implications for peptide binding and T-cell receptor recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8403–8407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bleek G. M., Nathenson S. G. The structure of the antigen-binding groove of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules determines specific selection of self-peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11032–11036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


