Abstract
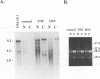
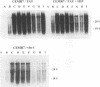
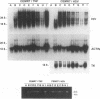
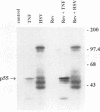
Tat-independent transcription of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) plays an important role in virus life cycle before biologically significant levels of Tat protein have been accumulated. Using a latently infected T-cell line containing an integrated Tat-defective HIV-1 provirus, we examined whether factors known to up-regulate the HIV-1 expression in vitro can replace the requirement for a functional Tat protein and induce the expression of the Tat-defective HIV-1 provirus. Both tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) infection stimulated transcription of the Tat-defective HIV-1 provirus to comparable levels, but in HSV-1-infected cells, the cytoplasmic HIV-1 transcripts were not efficiently translated in the absence of Tat protein and were excluded from the large polysomes. However, HSV-1 infection did not affect the distribution of cellular gamma-actin RNA or 28S RNA in the polysomal fractions. The translational block of HIV-1 RNA was not mediated by the virion-associated host cell shutoff protein (vhs); dissociation of HIV-1 transcripts from the polysomes and inefficient translation was also observed in cells infected with the vhs-defective mutant of HSV-1 (vhs-1). Overexpression of Rev protein did not rescue the synthesis of HIV-1 proteins in these cells; however, the observed inhibition of HIV-1 RNA translation was efficiently overcome in the presence of Tat protein or TNF-alpha. These findings suggest that, in contrast to TNF-alpha, HSV-1 infection is not able to induce a full cycle of HIV-1 replication and that cytokines and Tat have a critical role in the activation of HIV-1 provirus by HSV-1.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht M. A., DeLuca N. A., Byrn R. A., Schaffer P. A., Hammer S. M. The herpes simplex virus immediate-early protein, ICP4, is required to potentiate replication of human immunodeficiency virus in CD4+ lymphocytes. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1861–1868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1861-1868.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S. J., Chen I. S. Rev is necessary for translation but not cytoplasmic accumulation of HIV-1 vif, vpr, and env/vpu 2 RNAs. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):808–819. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S. J., Heaphy S., Haines J. K. In vivo binding of wild-type and mutant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev proteins: implications for function. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5569–5575. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5569-5575.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bednarik D. P., Mosca J. D., Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) replication by HIV-trans-activated alpha 2-interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4958–4962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benko D. M., Robinson R., Solomin L., Mellini M., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Binding of trans-dominant mutant Rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to the cis-acting Rev-responsive element does not affect the fate of viral mRNA. New Biol. 1990 Dec;2(12):1111–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braddock M., Chambers A., Wilson W., Esnouf M. P., Adams S. E., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. HIV-1 TAT "activates" presynthesized RNA in the nucleus. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90841-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braddock M., Thorburn A. M., Chambers A., Elliott G. D., Anderson G. J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. A nuclear translational block imposed by the HIV-1 U3 region is relieved by the Tat-TAR interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1123–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90389-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. W., Jones K. S., Beidas S., Dillon P. J., Skalka A. M., Rosen C. A. Identification and characterization of intragenic sequences which repress human immunodeficiency virus structural gene expression. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5305–5313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5305-5313.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Agostino D. M., Felber B. K., Harrison J. E., Pavlakis G. N. The Rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promotes polysomal association and translation of gag/pol and vpu/env mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1375–1386. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. The trans-activator gene of the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III is required for replication. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh E. J., Maury W. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Rabson A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embretson J., Zupancic M., Ribas J. L., Burke A., Racz P., Tenner-Racz K., Haase A. T. Massive covert infection of helper T lymphocytes and macrophages by HIV during the incubation period of AIDS. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):359–362. doi: 10.1038/362359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Vazeux R., Peden K. The rev gene product of the human immunodeficiency virus affects envelope-specific RNA localization. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1155–1165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D., Frankel A. D. The role of Tat in the human immunodeficiency virus life cycle indicates a primary effect on transcriptional elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Jarrett R. F., Aldovini A., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. HTLV-III expression and production involve complex regulation at the levels of splicing and translation of viral RNA. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):807–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Cladaras C., Copeland T., Pavlakis G. N. rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects the stability and transport of the viral mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1495–1499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Feinberg M. B., Josephs S. F., Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Reyes G., Gonda M. A., Aldovini A., Debouk C., Gallo R. C. The trans-activator gene of HTLV-III is essential for virus replication. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):367–371. doi: 10.1038/320367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Gray M. K. Variable inhibition of cell-free translation by HIV-1 transcript leader sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4291–4297. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimble J. M., Duh E., Ostrove J. M., Gendelman H. E., Max E. E., Rabson A. B. Activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by herpes simplex virus type 1 is associated with induction of a nuclear factor that binds to the NF-kappa B/core enhancer sequence. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4104–4112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4104-4112.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin G. E., Leung K., Folks T. M., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Activation of HIV gene expression during monocyte differentiation by induction of NF-kappa B. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):70–73. doi: 10.1038/339070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Felber B. K., Cladaras C., Athanassopoulos A., Tse A., Pavlakis G. N. The rev (trs/art) protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects viral mRNA and protein expression via a cis-acting sequence in the env region. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1265–1274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1265-1274.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarskjöld M. L., Heimer J., Hammarskjöld B., Sangwan I., Albert L., Rekosh D. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus env expression by the rev gene product. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1959–1966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1959-1966.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrich D., Garcia J., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. TAR independent activation of the human immunodeficiency virus in phorbol ester stimulated T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4417–4423. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Ransone L. J., Bengal E., Hunter T., Verma I. M. c-rel activates but v-rel suppresses transcription from kappa B sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël N., Hazan U., Alcami J., Munier A., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Bachelerie F., Israël A., Virelizier J. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates transcription of HIV-1 in human T lymphocytes, independently and synergistically with mitogens. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3956–3960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Sumimoto H., Pognonec P., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Roeder R. G. HIV-1 Tat acts as a processivity factor in vitro in conjunction with cellular elongation factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):655–666. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., DeCorato D., Krug R. M. Cellular mRNA translation is blocked at both initiation and elongation after infection by influenza virus or adenovirus. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1027–1039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1027-1039.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalik T. F., Wing B., Haskill J. S., Azizkhan J. C., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Huang E. S. Multiple mechanisms are implicated in the regulation of NF-kappa B activity during human cytomegalovirus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1107–1111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong A. D., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus virion host shutoff function. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4834–4839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4834-4839.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. HIV-1 Tat protein increases transcriptional initiation and stabilizes elongation. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldarelli F., Martin M. A., Strebel K. Identification of posttranscriptionally active inhibitory sequences in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA: novel level of gene regulation. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5732–5743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5732-5743.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Sharp P. A. HIV-1 Tat protein promotes formation of more-processive elongation complexes. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4189–4196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino M. W., Feld L. J., Jaffe E. A., Pfeffer L. M., Han H. M., Donner D. B. Phosphorylation of the proto-oncogene product eukaryotic initiation factor 4E is a common cellular response to tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2685–2688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Bednarik D. P., Raj N. B., Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Hayward G. S., Pitha P. M. Activation of human immunodeficiency virus by herpesvirus infection: identification of a region within the long terminal repeat that responds to a trans-acting factor encoded by herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7408–7412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Bednarik D. P., Raj N. B., Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Pitha P. M. Herpes simplex virus type-1 can reactivate transcription of latent human immunodeficiency virus. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):67–70. doi: 10.1038/325067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchardt C., Seeler J. S., Nirula A., Shurland D. L., Gaynor R. B. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus enhancer function by PRDII-BF1 and c-rel gene products. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):244–250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.244-250.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrove J. M., Leonard J., Weck K. E., Rabson A. B., Gendelman H. E. Activation of the human immunodeficiency virus by herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3726–3732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3726-3732.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Demarest J. F., Butini L., Montroni M., Fox C. H., Orenstein J. M., Kotler D. P., Fauci A. S. HIV infection is active and progressive in lymphoid tissue during the clinically latent stage of disease. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):355–358. doi: 10.1038/362355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin N. T., Cohen E. A., Darveau A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sonenberg N. Mutational analysis of the 5' non-coding region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: effects of secondary structure on translation. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2831–2837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Bressler P., Kinter A., Duh E., Timmer W. C., Rabson A., Justement J. S., Stanley S., Fauci A. S. Interleukin 6 induces human immunodeficiency virus expression in infected monocytic cells alone and in synergy with tumor necrosis factor alpha by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):151–158. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popik W., Pitha P. M. Inhibition by interferon of herpes simplex virus type 1-activated transcription of tat-defective provirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9573–9577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
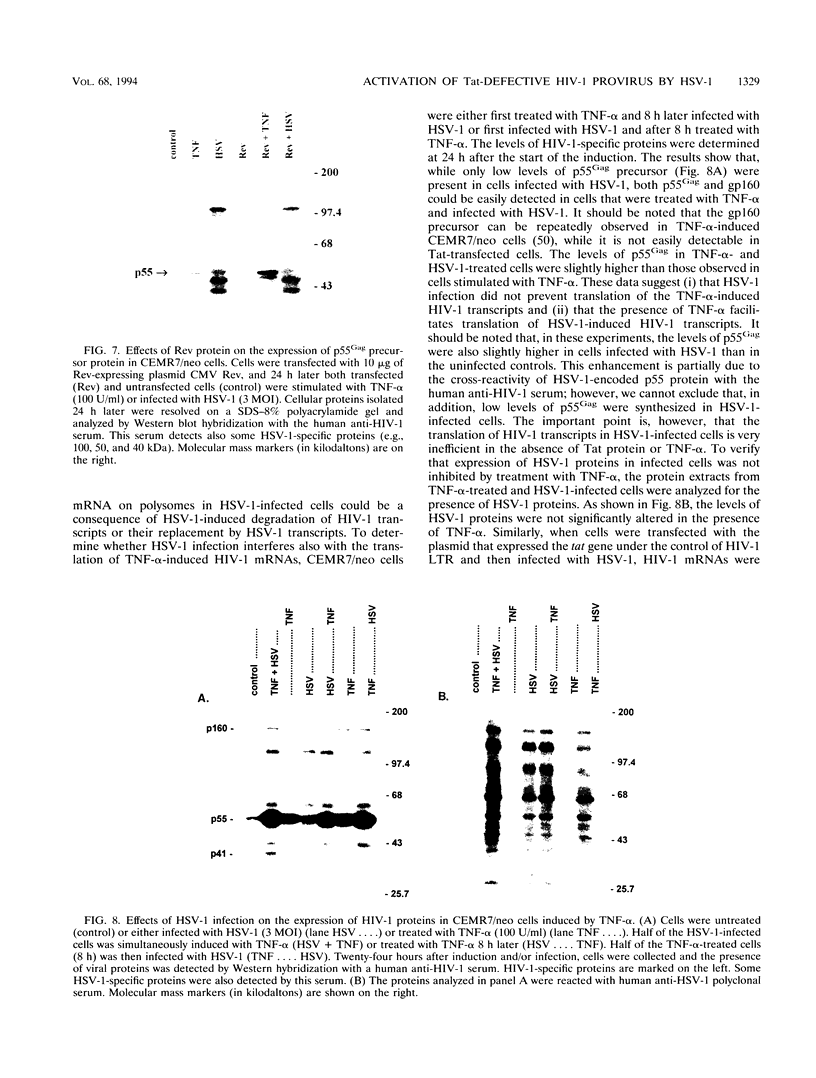
- Popik W., Pitha P. M. Role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in activation and replication of the tat-defective human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):1094–1099. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.1094-1099.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popik W., Pitha P. M. Transcriptional activation of the tat-defective human immunodeficiency virus type-1 provirus: effect of interferon. Virology. 1992 Aug;189(2):435–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90567-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston B. D., Poiesz B. J., Loeb L. A. Fidelity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1168–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.2460924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. C., Piot P., McCormick J. B., Feinsod F. M., Taelman H., Kapita B., Stevens W., Fauci A. S. Serologic and immunologic studies in patients with AIDS in North America and Africa. The potential role of infectious agents as cofactors in human immunodeficiency virus infection. JAMA. 1987 May 15;257(19):2617–2621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Analysis of interferon mRNA in human fibroblast cells induced to produce interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7426–7430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Mendoza G. E. A herpesvirus regulatory protein appears to act post-transcriptionally by affecting mRNA processing. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):848–863. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Distinct RNA sequences in the gag region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 decrease RNA stability and inhibit expression in the absence of Rev protein. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):150–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.150-159.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Bain E. S., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Structure, sequence, and position of the stem-loop in tar determine transcriptional elongation by tat through the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):547–558. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SenGupta D. N., Berkhout B., Gatignol A., Zhou A. M., Silverman R. H. Direct evidence for translational regulation by leader RNA and Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7492–7496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi Y., Pitha P. M. Alpha interferon inhibits early stages of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication cycle. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1321–1328. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1321-1328.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Cho M. I., Hammarskjöld M. L., Rekosh D. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Pr55gag and Pr160gag-pol expressed from a simian virus 40 late replacement vector are efficiently processed and assembled into viruslike particles. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2743–2750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2743-2750.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Dayton A., Terwilliger E., Haseltine W. A second post-transcriptional trans-activator gene required for HTLV-III replication. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):412–417. doi: 10.1038/321412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Rosen C., Wong-Staal F., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Arya S., Gallo R. C., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional regulation of human T-cell leukemia virus type III long terminal repeat. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):171–173. doi: 10.1126/science.2981427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson C. M., Hart P. A., Ross J. Analysis of herpes simplex virus-induced mRNA destabilizing activity using an in vitro mRNA decay system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4459–4465. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thach R. E. Cap recap: the involvement of eIF-4F in regulating gene expression. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90461-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlach J., Pitha P. M. Differential contribution of herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products and cellular factors to the activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 provirus. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4427–4431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4427-4431.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlach J., Pitha P. M. Herpes simplex virus type 1-mediated induction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 provirus correlates with binding of nuclear proteins to the NF-kappa B enhancer and leader sequence. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3616–3623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3616-3623.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]