Abstract
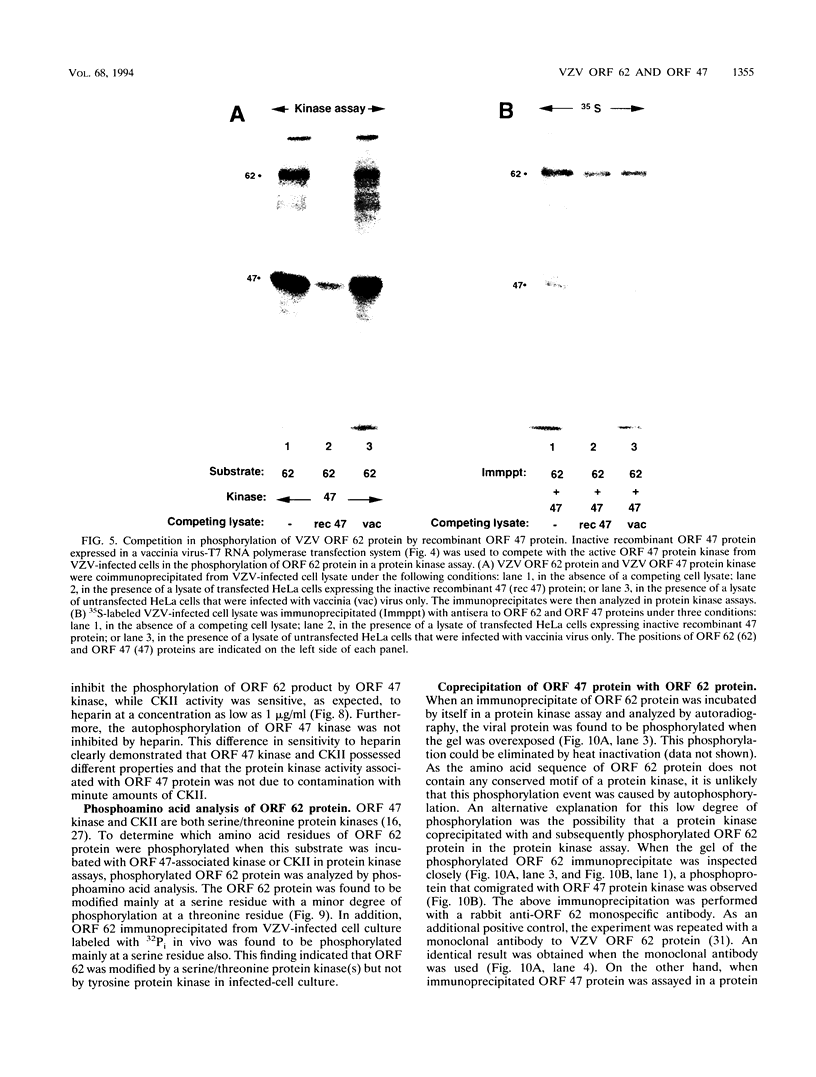
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) encodes within its unique long region a gene product with protein kinase motifs. In a previous study, we demonstrated that immunoprecipitated VZV open reading frame (ORF) 47 protein was associated with a functional protein kinase activity, on the basis of its ability to both autophosphorylate and phosphorylate artificial substrates. To further define potential substrates of ORF 47-associated protein kinase, we analyzed individual viral phosphoproteins to determine whether any were modified by the viral protein kinase. These candidates included gene products of VZV ORFs 4, 61, 62, and 63, which are homologs of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) immediate-early proteins. Each of the above VZV proteins was coimmunoprecipitated with ORF 47 kinase, and the immune complex was incubated in a protein kinase assay. Under these conditions, only the VZV immediate-early ORF 62 protein was phosphorylated by ORF 47-associated protein kinase. The specificity of this phosphorylation event was analyzed by a competition assay in which a recombinant ORF 47 protein lacking enzymatic activity was able to reduce the amount of phosphorylation of ORF 62 protein by VZV ORF 47-associated kinase. To provide an additional evaluation of specificity, the experiment was repeated with [32P]GTP instead of [32P]ATP, because the VZV ORF 47 kinase has the distinctive property of using GTP as a phosphate donor. Again the ORF 62 substrate was phosphorylated. In summary, the VZV ORF 47-associated protein kinase (the HSV-1 UL13 homolog) catalyzed the in vitro phosphorylation of the VZV ORF 62 protein, the homolog of the HSV-1 ICP4 regulatory protein.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cabirac G. F., Mahalingam R., Wellish M., Gilden D. H. Trans-activation of viral tk promoters by proteins encoded by varicella zoster virus open reading frames 61 and 62. Virus Res. 1990 Jan;15(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Lawrence G. L., Barrell B. G. Alpha-, beta- and gammaherpesviruses encode a putative phosphotransferase. J Gen Virol. 1989 May;70(Pt 5):1151–1160. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-5-1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham C., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McGeoch D. J., Meredith D. M., Moss H. W., Orr A. C. The UL13 virion protein of herpes simplex virus type 1 is phosphorylated by a novel virus-induced protein kinase. J Gen Virol. 1992 Feb;73(Pt 2):303–311. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-2-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felser J. M., Kinchington P. R., Inchauspe G., Straus S. E., Ostrove J. M. Cell lines containing varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 62 and expressing the "IE" 175 protein complement ICP4 mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2076–2082. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2076-2082.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., Lee J. H., Scheppler J. A., Herrmann C., Harlow E., Deuschle U., Beach D., Franza B. R., Jr Cell cycle regulation of histone H1 kinase activity associated with the adenoviral protein E1A. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1271–1275. doi: 10.1126/science.1653969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., Whyte P., Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Beach D., Draetta G. A 60 kd cdc2-associated polypeptide complexes with the E1A proteins in adenovirus-infected cells. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):981–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90949-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Edwards D. P., Friedrichs W. E., Weigle K. A., McGuire W. L. Monoclonal antibodies against three major glycoproteins of varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):381–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.381-388.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Jackson W., Traugh J. A. Phosphorylation of varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein gpI by mammalian casein kinase II and casein kinase I. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3912–3918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3912-3918.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Perrotta D. M., Brunell P. A., Smith G. C. Cell-free varicella-zoster virus in cultured human melanoma cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 Apr;43(1):15–27. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C. The synthesis of glycoproteins in human melanoma cells infected with varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90478-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Traugh J. A. Casein kinase II. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:317–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Nagpal S., Ostrove J. M. Mapping of two varicella-zoster virus-encoded genes that activate the expression of viral early and late genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):700–709. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Ostrove J. M. Differential regulation by varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and herpes simplex virus type-1 trans-activating genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):710–714. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katan M., Stevely W. S., Leader D. P. Partial purification and characterization of a new phosphoprotein kinase from cells infected with pseudorabies virus. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):57–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinchington P. R., Hougland J. K., Arvin A. M., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. The varicella-zoster virus immediate-early protein IE62 is a major component of virus particles. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):359–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.359-366.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Katan M. Viral aspects of protein phosphorylation. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1441–1464. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Purves F. C. The herpesvirus protein kinase: a new departure in protein phosphorylation? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Jul;13(7):244–246. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W. J., Traugh J. A. Renaturation of casein kinase II from recombinant subunits produced in Escherichia coli: purification and characterization of the reconstituted holoenzyme. Protein Expr Purif. 1993 Jun;4(3):256–264. doi: 10.1006/prep.1993.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littler E., Stuart A. D., Chee M. S. Human cytomegalovirus UL97 open reading frame encodes a protein that phosphorylates the antiviral nucleoside analogue ganciclovir. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):160–162. doi: 10.1038/358160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Davison A. J. Alphaherpesviruses possess a gene homologous to the protein kinase gene family of eukaryotes and retroviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1765–1777. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Elroy-Stein O., Mizukami T., Alexander W. A., Fuerst T. R. Product review. New mammalian expression vectors. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):91–92. doi: 10.1038/348091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. I., Grose C. Serine protein kinase associated with varicella-zoster virus ORF 47. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90161-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Ogle W. O., Roizman B. Processing of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein alpha 22 mediated by the UL13 protein kinase determines the accumulation of a subset of alpha and gamma mRNAs and proteins in infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6701–6705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Roizman B. The UL13 gene of herpes simplex virus 1 encodes the functions for posttranslational processing associated with phosphorylation of the regulatory protein alpha 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7310–7314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Spector D., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 protein kinase encoded by the US3 gene mediates posttranslational modification of the phosphoprotein encoded by the UL34 gene. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5757–5764. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5757-5764.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. E., Moninger T., Grose C. Entry and egress of varicella virus blocked by same anti-gH monoclonal antibody. Virology. 1993 Oct;196(2):840–844. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Smith T. F. Identification of new protein kinase-related genes in three herpesviruses, herpes simplex virus, varicella-zoster virus, and Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):450–455. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.450-455.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson D., Colman K. L., Davison A. J. Characterization of the putative protein kinases specified by varicella-zoster virus genes 47 and 66. J Gen Virol. 1994 Feb;75(Pt 2):317–326. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-2-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson D., Colman K. L., Davison A. J. Characterization of the varicella-zoster virus gene 61 protein. J Gen Virol. 1992 Mar;73(Pt 3):521–530. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-3-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan V., Talarico C. L., Stanat S. C., Davis M., Coen D. M., Biron K. K. A protein kinase homologue controls phosphorylation of ganciclovir in human cytomegalovirus-infected cells. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):162–164. doi: 10.1038/358162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A. Casein kinase I and II--multipotential serine protein kinases: structure, function, and regulation. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:123–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. W., Kohn A., Sklyanskaya E., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. I. Phosphate cycles on and off some viral polypeptides and can alter their affinity for DNA. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):167–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.167-182.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. L., Wilcox K. W. The conserved DNA-binding domains encoded by the herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4, pseudorabies virus IE180, and varicella-zoster virus ORF62 genes recognize similar sites in the corresponding promoters. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1149–1159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1149-1159.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao F., Courtney R. J. A major transcriptional regulatory protein (ICP4) of herpes simplex virus type 1 is associated with purified virions. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3338–3344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3338-3344.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Lyall R., Jariwala N., Zilberstein A., Haimovich J. Antigen- and ionophore-induced signal transduction in rat basophilic leukemia cells involves protein tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22564–22568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang G., Stevens R., Leader D. P. The protein kinase encoded in the short unique region of pseudorabies virus: description of the gene and identification of its product in virions and in infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1990 Aug;71(Pt 8):1757–1765. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-8-1757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wind N., Domen J., Berns A. Herpesviruses encode an unusual protein-serine/threonine kinase which is nonessential for growth in cultured cells. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5200–5209. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5200-5209.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]